Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects: Novel Biomarkers and Other Measurements of Disease Activity
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Rho-associated protein kinases (ROCKs) regulate cytoskeletal reorganization and gene expression through protein phosphorylation, and are implicated in the pathogenesis of a wide range of disorders including SLE. ROCK activation is associated with TH17 differentiation and production of interleukin 17 (IL17) and IL21, two cytokines associated with SLE and RA. We aimed to 1) evaluate ROCK activity and cytokine profile in RA patients, and 2) correlate ROCK activity with use of disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), smoking status, erosions, disease duration, and disease activity.
Methods:
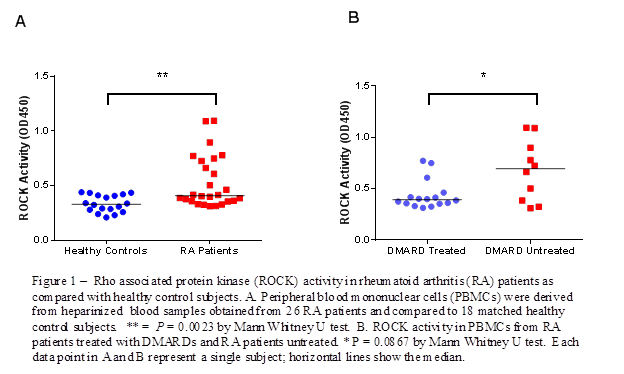
We performed a cross-sectional analysis of 26 RA patients meeting 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria compared to 18 age±5 years, gender, and race/ethnicity matched healthy controls. ROCK activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) lysates was determined by an ELISA. Plasma samples were analyzed by specific ELISAs for IL-17 and IL21. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 using appropriate non-parametric tests.
Results:
Clinical characteristics of RA patients are noted in Table 1. RA PBMCs expressed significantly higher levels of ROCK activity than did healthy control PBMCs (0.4085 vs. 0.3303; P = 0.0023). DMARD untreated RA patients had a trend towards higher ROCK activity compared to DMARD treated RA patients, (0.6935 vs. 0.3925; P = 0.0867), (Figure 1). Spearman’s correlation revealed no association of ROCK activity levels with disease duration (r= 0.277, P = 0.171) or disease activity as measured by Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) (r=0.162, P = 0.429). There was no significant difference in ROCK levels based on erosions (P = 0.440) or smoking status (P = 0.651). Patients with moderate or high disease activity (CDAI ≥10.1) had increased ROCK levels (OR=1.96, 95% CI 0.3866-9.938), but this was not statistically significant. No statistically significant differences in IL17 and IL21 levels between RA patients and healthy controls were detected.
Conclusion:
ROCK levels were higher in RA patients compared to healthy controls suggesting ROCK deregulation in RA pathogenesis. There was a trend towards higher ROCK activity in DMARD untreated RA patients suggesting that ROCK activity is sensitive to RA therapies. Further studies are needed to understand the role of ROCK activity in RA.
|
Table 1: Clinical Characteristics of RA Patients, n=26 |
|
|
Mean Age, ±SD, range |
57.5±13.8 (23-79) |
|
Female, n, (%) |
23 (88.5) |
|
Race, n, (%) |
|
|
White |
15 (57.7) |
|
Black |
3 (11.5) |
|
Mixed |
4 (15.4) |
|
Asian |
4 (15.3) |
|
Mean Disease Duration in months, ±SD, range |
56.0±55 (3-240) |
|
Erosive Disease, n, (%) [imaging available on 15 patients] |
4/15 (26.7) |
|
Autoantibody Status |
|
|
IgM RF or ACPA positive, n, (%) |
3 (11.5) |
|
IgM RF and ACPA negative, n, (%) |
3 (11.5) |
|
IgM-RF and ACPA positive, n, (%) |
20 (76.9) |
|
Mean ACPA titer (U),* ± SD, range |
195.1±67.9 (60-250) |
|
Mean IgM-RF titer (IU/mL)* ± SD, range |
143.8±166.8, (21.1-587) |
|
*[titers available on 20 patients] |
|
|
Disease Activity Parameters |
|
|
Mean ESR (mm/hr) ± SD, range |
22.5 ± 14.5 (5-44) |
|
Mean CRP (mg/dL) ±SD, range |
1.2 ± 0.5(1 – 3.2) |
|
CDAI, Mean ± SD, Range |
13.0 ± 7.3, (6-30) |
|
Current smokers, n, (%) |
4 (15.4) |
|
Current Medications, n, (%) |
|
|
NSAIDs alone |
8 (30.8) |
|
Hydroxychloroquine alone |
1 (3.8) |
|
Conventional DMARDs (Methotrexate ± Leflunomide) |
8 (30.8) |
|
Anti TNF agents (Etanercept, Adalimumab) |
8 (30.8) |
|
Prednisone |
1 (3.8) |
Disclosure:
R. Khianey,
None;
C. Rozo,
None;
S. Gupta,
None;
V. P. Bykerk,
None;
S. M. Goodman,
None;
A. B. Pernis,
Kadmon Pharmaceuticals,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rho-associated-protein-kinase-rock-activity-is-elevated-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-and-may-be-responsive-to-ra-therapies/