Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: RheumMadness is an online educational initiative developed to engage learners of all levels in social constructivist learning. Participants were recruited via social media, email, and word of mouth to complete a March Madness style bracket of 16 teams, representing learning concepts in rheumatology. Additional curricular elements included scouting reports reviewing each team, a podcast series, and social media-based discussion. One objective of RheumMadness is to engage medical students and residents in the rheumatology learning community. Therefore, in this analysis we seek to understand these learners’ experiences in the 2021 and 2022 RheumMadness tournaments.
Methods: Participants were emailed a survey at the completion of the 2021 and 2022 tournaments. For this analysis, we aggregated responses from early learners (medical students and residents) and advanced learners (attendings and fellows). Incomplete survey responses were excluded. Surveys assessed participants’ self-reported engagement with each curricular element according to a 5-point scale (1=never, 5=a great deal/every day). Learner experience was assessed according to Community of Inquiry (CoI) presences and sub-domains, as follows: cognitive (triggering, exploration, integration, and resolution), social (affective expression, open communication, group cohesion), and teaching (course design, facilitation, and direct instruction), according to a 5-point scale (1=strongly disagree, 5=strongly agree). Early learners were asked what impact RheumMadness had on their interest in rheumatology, with social media posts and survey comments from early learners reviewed to further explore their experiences. Survey responses from early versus advanced learners were compared with unpaired T-tests.
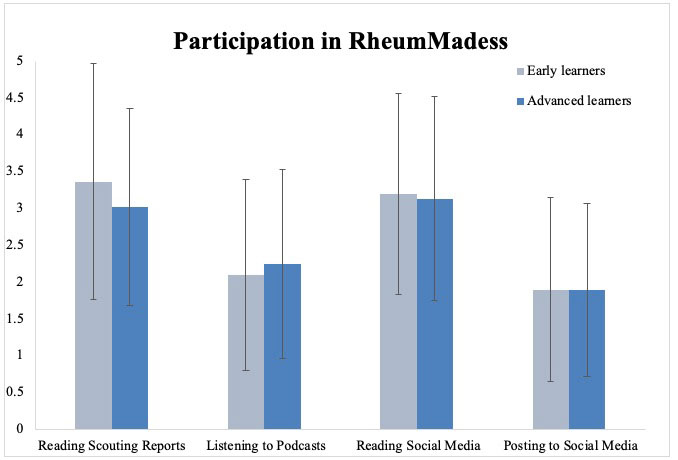
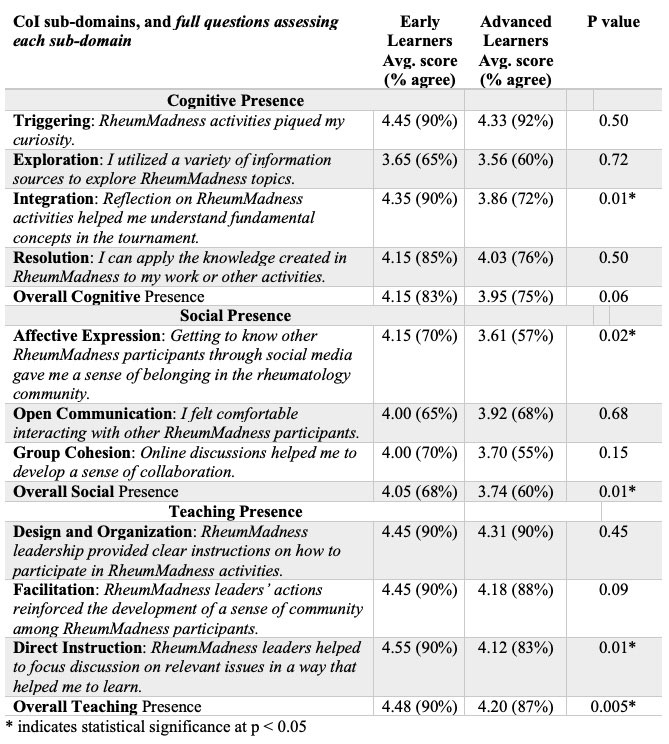
Results: Of 116 included respondents in 2021 and 2022, 17% (20/116) were early learners (4 medical students and 16 residents) and 83% (96/116) were advanced (50 attendings and 46 fellows). There was no significant difference between early and advanced learners in self-reported engagement with RheumMadness scouting reports, podcasts, or social media (Figure 1). Early learners reported stronger learning experiences in knowledge integration (p=0.01), affective expression (p=0.02), the overall social presence (p=0.01), direct instruction (p=0.01), and the overall teaching presence (p=0.005), (Table 1). Early learners’ interest in rheumatology was impacted by RheumMadness as follows: 17 (85%) increased, 3 (15%) no change, 0 (0%) decreased. Social media posts and survey comments further illustrate early learners’ experiences (Table 2).
Conclusion: Early and advanced learners had similar patterns of engagement in RheumMadness. However, early learners indicated that RheumMadness helped them understand fundamental concepts in the tournament (knowledge integration) and gave them a sense of belonging in the rheumatology community (affective expression) more than advanced learners. Thus, RheumMadness is a useful tool for increasing interest in rheumatology and connecting interested trainees to this specialty.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He L, Kellogg B, Macklin M, Bair C, Katz G, Garren A, Sparks m, Criscione-Schreiber L, leverenz d. RheumMadness: Early Learner Experience and Impact [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheummadness-early-learner-experience-and-impact/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheummadness-early-learner-experience-and-impact/