Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex inflammatory disorder in which autoantibodies play a prominent role. Several types of autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factors (RFs) – primarily IgM antibodies binding to the Fc-domain of IgG- and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) have predictive value for RA onset and severity. Interestingly, the combined presence of both types of antibodies is a better marker for a more severe disease than the presence of only RFs or only ACPAs. While pathogenic properties of both RF and ACPA in isolation have been studied in detail, few studies have investigated the combination.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the interactions between RFs and ACPAs using well-defined recombinant monoclonal RFs and ACPAs in a biosensor system (IBIS). Monoclonal ACPAs (100nM) with or without 25nM monoclonal IgM-RFs were flowed over sensor-spots to which six different citrullinated peptides or their arginine controls were coupled. Changes in refractive index caused by binding of molecules were measured and plotted as response units against flowing time in sensorgrams.
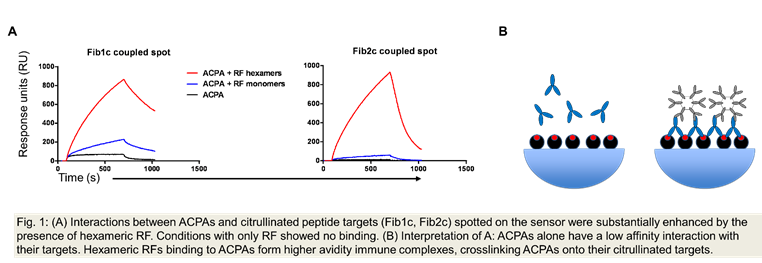
Results: We observed that interactions between ACPAs and citrullinated peptide targets were substantially enhanced by the presence of hexameric RF (Figure 1A). The observed increase in RU was mathematically greater than could be explained by a 1:1 or even a 1:2 interaction between ACPAs and RF. This suggests that the RFs enhance the binding of ACPAs to their targets by crosslinking them (Figure 1B). These results could be replicated using RF and ACPA from RA patients’ serum. RF+ ACPA+ sera treated with Dithiothreitol (DTT) to reduce the IgM-RF showed a decreased binding of ACPAs to the citrullinated peptide targets.
Conclusion: We hypothesize that RFs may contribute to pathogenesis in RA by potentiating immune complex formation of ACPAs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Falkenburg WJJ, van Schaardenburg D, Koers J, Ooijevaar-de Heer P, Wolbink G, Bentlage AEH, Vidarsson G, Rispens T. Rheumatoid Factors May Potentiate Immune Complex Formation of Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factors-may-potentiate-immune-complex-formation-of-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factors-may-potentiate-immune-complex-formation-of-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies/