Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease leading to joint destruction. Although many
studies have addressed correlates associated with the speed of joint
destruction, less attention has been paid to the distribution of joint destruction
in RA. Here, we divided hand bone destruction into fingers and non-fingers in
patients with RA and analyzed which factor is associated with finger joint
destruction.
Methods: We recruited a total of 1,215 Japanese subjects with RA as
two different sets. We assessed the degree of joint destruction by total sharp
score (TSS). TSS of fingers and non-fingers were used as a dependent variable
and a covariate, respectively. Age, sex, disease duration, smoking, C-reactive
protein, RA treatment, positivity and levels of anti-citrullinated
peptide antibody (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) were used as candidates of
correlates. We assessed overall effect in meta-analysis. We further tested
findings in Japanese subjects for their associations in 157 Dutch RA patients
in the BeSt study in which treatment regimens were
strictly specified. The association was also analyzed between finger TSS and
HLA-DRB1 alleles or genetic risk scores based on haplotypes of amino acid
residues associated with RA susceptibility. We also extended the analyses
to TSS in the foot joints.
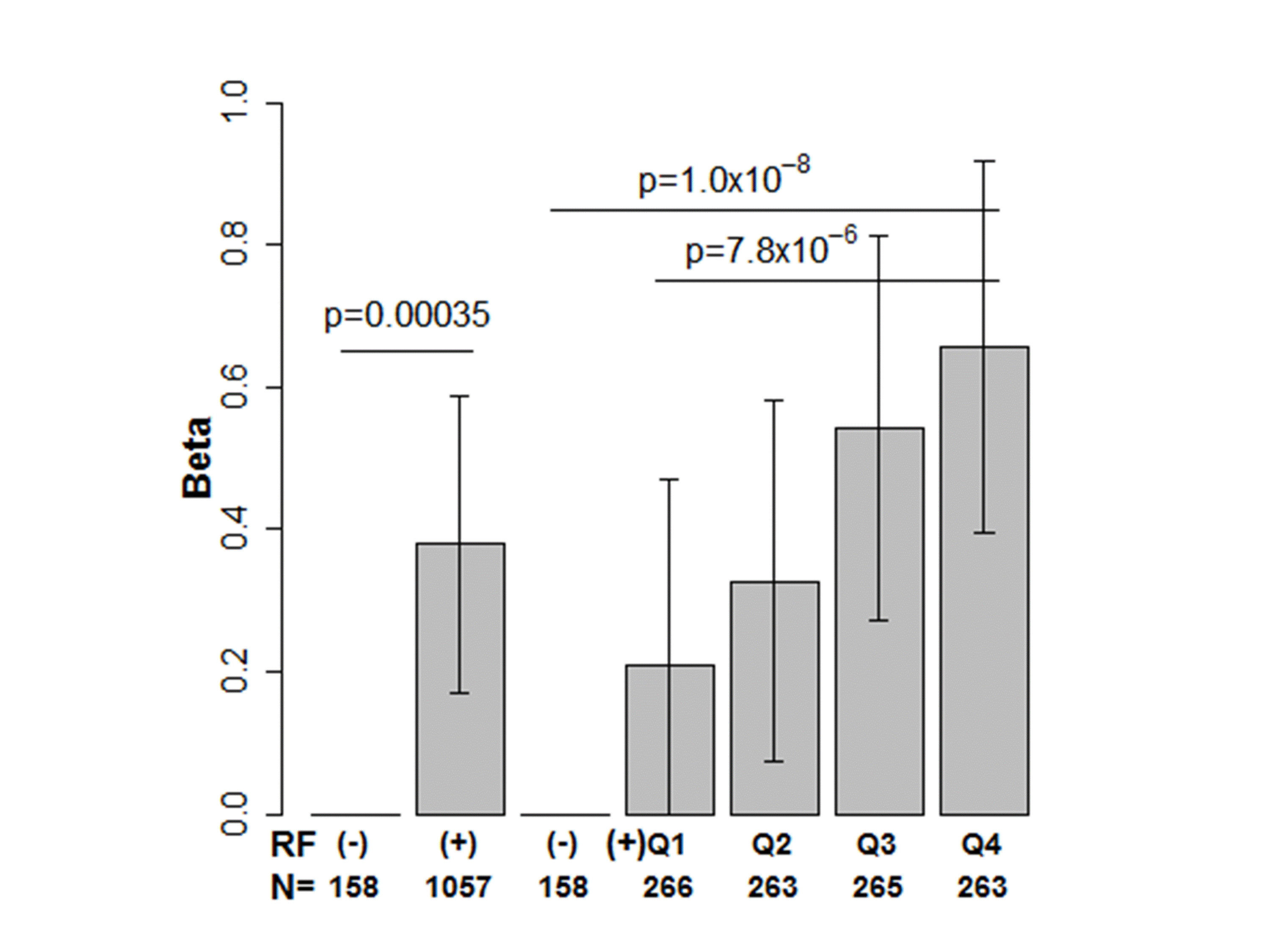
Results: Unsurprisingly, disease duration was associated with
finger TSS (p≤0.00037). RF positivity and levels showed significant
associations with finger TSS after adjusting for covariates (p=0.0022 and
8.1×10-7, respectively). These associations were true to
time-averaged finger TSS. We observed association between RF positivity and
finger TSS in the BeSt study (p=0.049). We did
not find associations between finger TSS and positivity or levels of ACPA. ACPA(-)RF(+) subjects were found to explain the difference
between RF and ACPA. No associations of HLA-DRB1 alleles or genetic risk scores
were observed. RF positivity and levels also showed a significant association
with foot TSS or combination of foot and finger TSS.
Conclusion: RF
positivity and levels are associated with finger joint destruction
independently from non-finger joint destruction and covariates. Our findings
might suggest different mechanisms between joint destruction of finger and
non-finger joints in RA.
Figure. Associations between finger
TSS and positivity or levels of rheumatoid factor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Terao C, Yamakawa N, Yano K, Markusse IM, Ikari K, Yoshida S, Furu M, Hashimoto M, Ito H, Fujii T, Ohmura K, Murakami K, Takahashi M, Hamaguchi M, Tabara Y, Taniguchi A, Momohara S, Raychaudhuri S, Allaart CF, Yamanaka H, Mimori T, Matsuda F. Rheumatoid Factor Is Associated with the Distribution of Hand Joint Destruction in a Dose-Dependent Manner [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-is-associated-with-the-distribution-of-hand-joint-destruction-in-a-dose-dependent-manner/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-is-associated-with-the-distribution-of-hand-joint-destruction-in-a-dose-dependent-manner/