Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease with increased mortality. Little national-level data is available on inpatient mortality in RA patients. In this report, we use a large Unites States (U.S) population-based database to analyze the principal discharge diagnosis for RA patients experiencing inpatient mortality.
Methods: Data were abstracted from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database. This is the largest inpatient hospitalization database in the U.S. It is a nationally representative sample of 20% of hospitalizations from approximately 1000 hospitals. The numbers in the databases are weighted to optimize national estimates. The NIS was searched for hospitalizations in 2017 with an ICD-10 RA codes M05 and M06 as the principal or secondary diagnosis. The total number of RA discharges, number of in-hospital deaths, percentage of in-hospital deaths, length of stay (LOS), total hospital charges were recorded. The “principal discharge diagnosis” in RA patients experiencing in-hospital death was divided into 19 ICD 10 code categories.
Results: There were over 30 million discharges included in the 2017 NIS database. Of those, 565,440 hospitalizations were for patients aged 18 years or above, who had either a principal or secondary ICD 10 code for RA. 13,285 of these patients (2.35%) experienced in-hospital mortality. These patients were mainly female 70.19%, whites 64.85%, average age of 74.31 years, average LOS of 7.04 days and mean total hospital charges of $101,210. The top 5 principal discharge ICD 10 code categories in RA patients experiencing inpatient mortality in descending order of frequency were as follows (see table 1 and figure 1): infections 4810 (36.20%), cardiovascular 2605 (19.60%), respiratory 2045 (15.39%), digestive system 875 (6.59%), hematology/oncology 865 (6.51%). The most common principal diagnoses in RA patients with in-hospital mortality were sepsis, followed by acute and chronic hypoxic respiratory failure, aspiration pneumonitis, non-ST segment myocardial infarction, and acute kidney injury in descending order of frequency.
Conclusion: For adult RA patients experiencing in-hospital mortality, infections were the most common ICD 10 code category, and sepsis was the most common specific ICD 10 code principal diagnosis of hospitalization. Preventive measures, prompt diagnosis, and management of sepsis are needed to reduce the rate of inpatient mortality for RA patients.
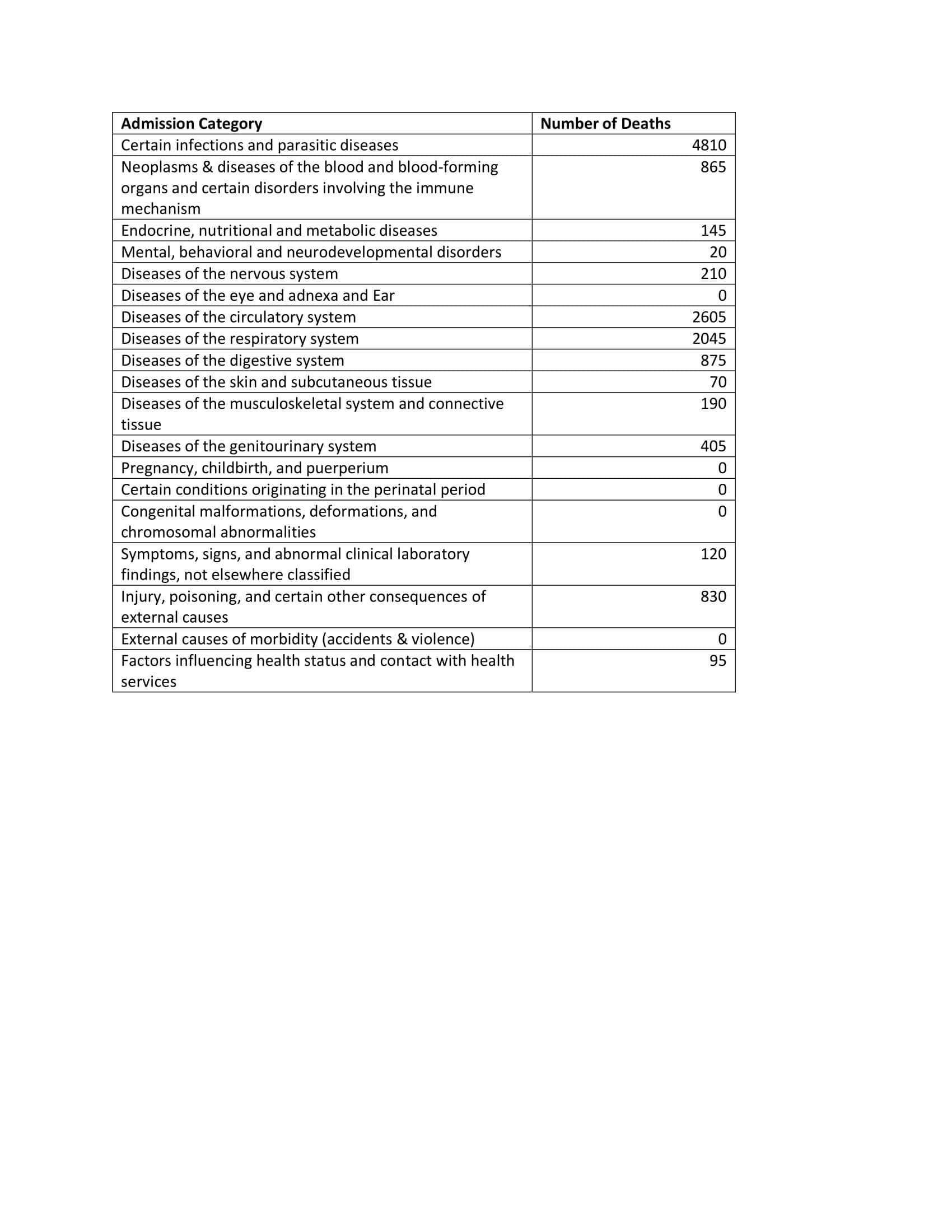 Table 1: ICD-10 code admission category for Rheumatoid arthritis hospitalizations with inpatient mortality
Table 1: ICD-10 code admission category for Rheumatoid arthritis hospitalizations with inpatient mortality
 Figure 1: Clustered column chart of ICD 10 admission category for RA hospitalizations with inpatient mortality
Figure 1: Clustered column chart of ICD 10 admission category for RA hospitalizations with inpatient mortality
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Edigin E, Eseaton P, Manadan A. Rheumatoid Arthritis Inpatient Mortality: An Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-inpatient-mortality-an-analysis-of-the-national-inpatient-sample/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-inpatient-mortality-an-analysis-of-the-national-inpatient-sample/
