Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders I: Clinical Trials
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: The most effective treatment for Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) are glucocorticoids (GC), but these are associated with toxicity. Three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) suggest methotrexate (MTX) might have GC sparing effects [1-3]. However, the RCTs are limited by small sample sizes, a maximum dose of MTX 10mg/week, and suboptimal quality due to high dropout and lack of blinding in some studies. The aim of this trial is to study the efficacy of MTX 25mg/week in recently diagnosed PMR patients (PMR MODE study) [4].
Methods: In a 52-week placebo-controlled RCT, patients with recently diagnosed PMR fulfilling the 2012 EULAR/ACR criteria and treated with GC for less than 8 weeks were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either MTX 25mg/week or matching placebo, stratified by sex and inflammatory markers (ESR 70 mm/h and/or CRP ≥ 25 mg/L). Patients and physicians remained blinded throughout the trial, and analysis was also conducted blinded. The primary outcome was GC-free remission (PMR-activity score < 10) at week 52, tested with a one-sided Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test with stratification taken into account. Secondary outcomes were the proportion of patients with relapse and incidence rate of relapse, adverse event incidence rate, cumulative GC dose, and MTX/placebo dose adjustments.
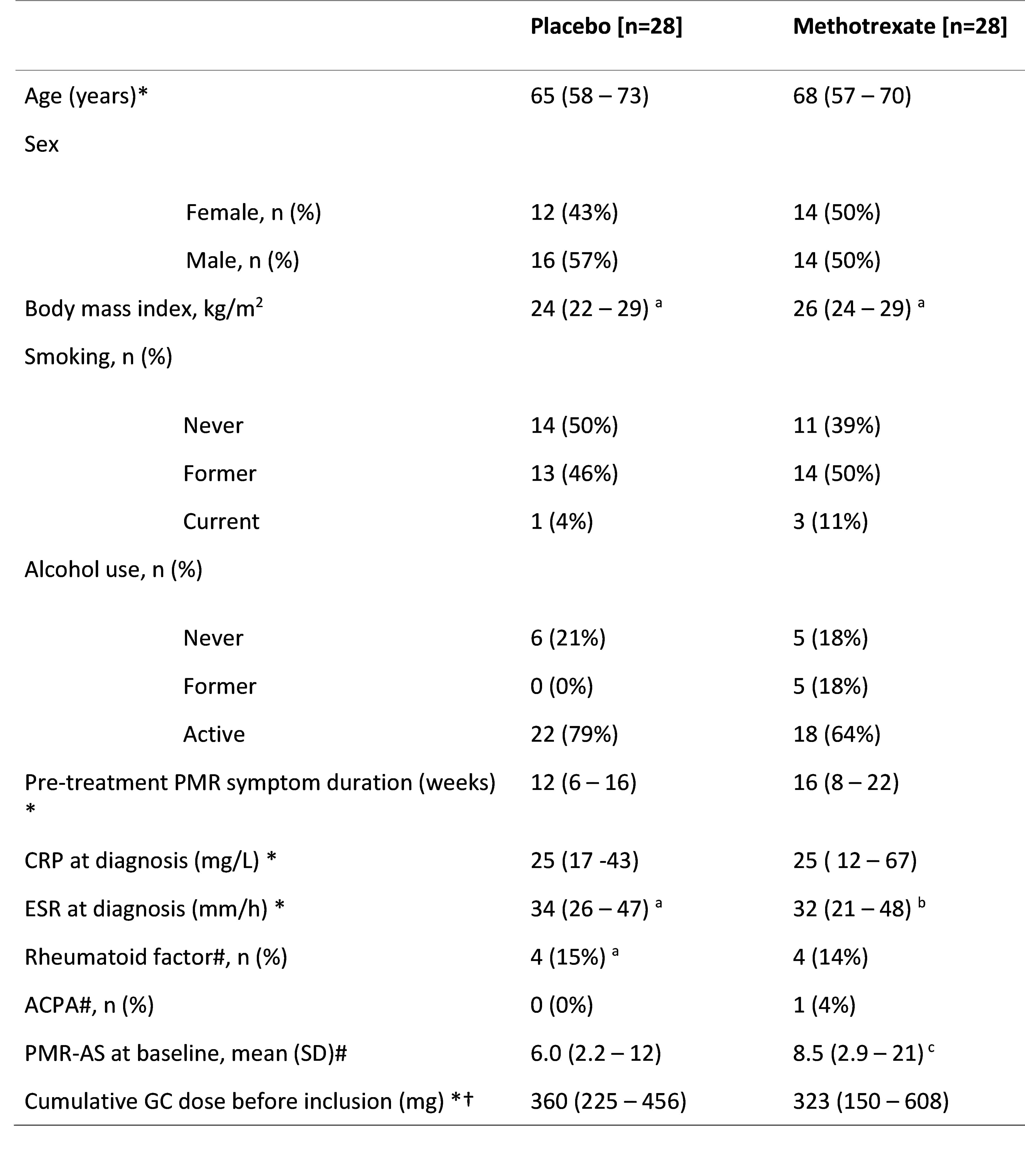
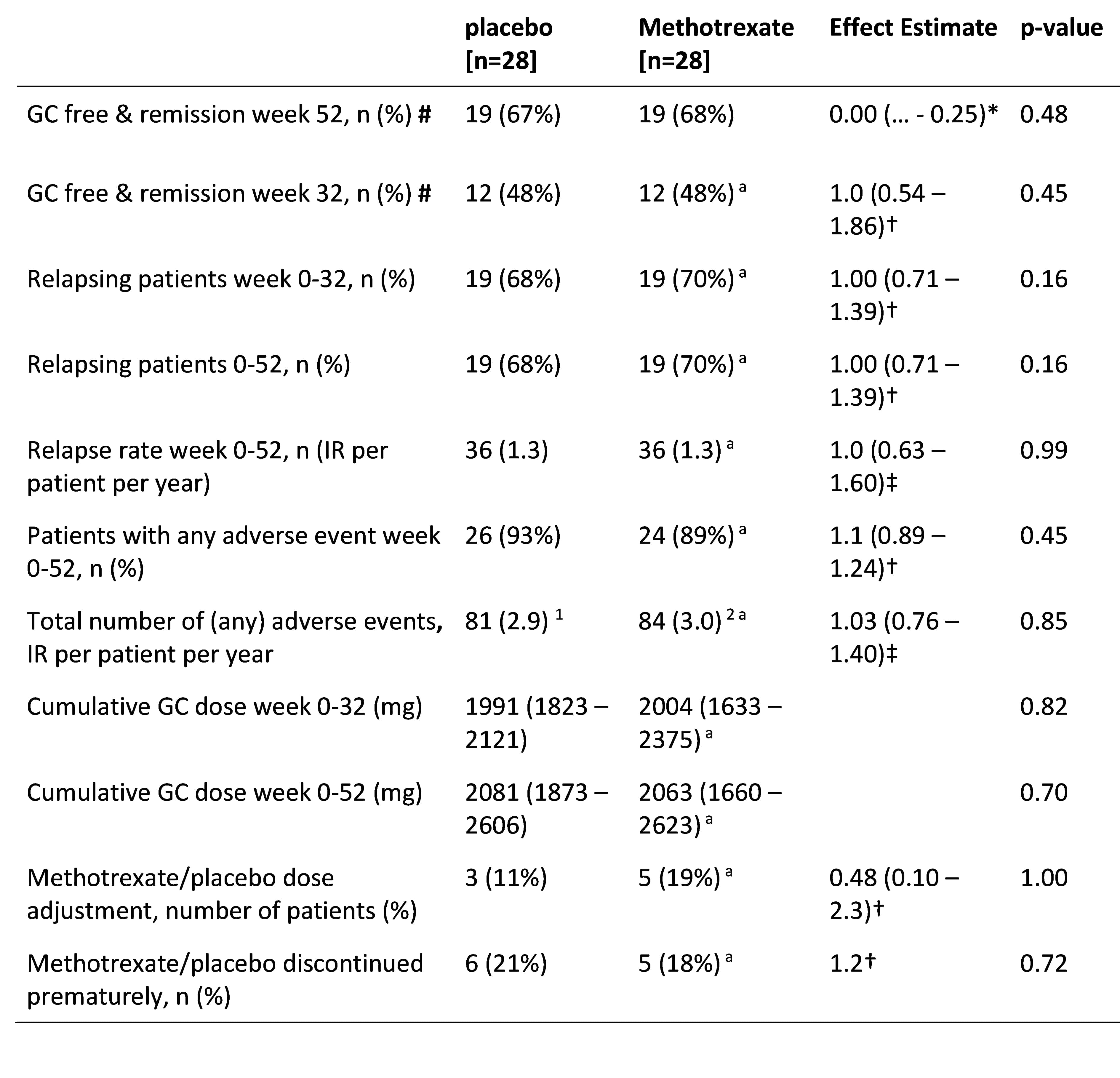
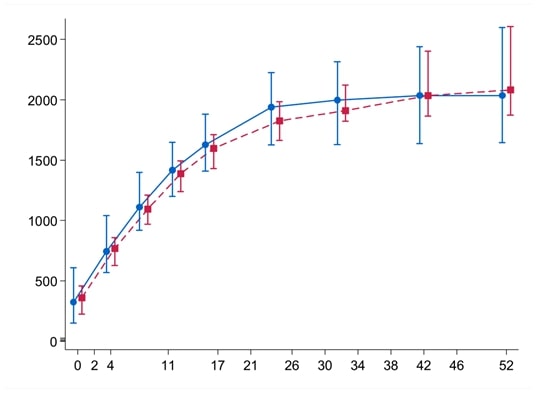
Results: Sixtyfour patients were recruited, of whom 56 are included in the final analysis, (table 1). The proportion of patients in GC free remission did not differ significantly between groups, placebo (67%) compared to MTX (68%), adjusted difference 0.00 (95%-CI upper limit 0.25), p = 0.48). Secondary outcomes (table 2) also did not show significant differences, with similar number and proportion of patients with relapse, adverse event incidence rate, GC use, and MTX/placebo dose adjustment and discontinuation between groups.
Conclusion: This small but high quality RCT could not show any significant effect of MTX in recently diagnosed PMR patients on GC free remission at one year. The confidence interval makes clinically relevant effects unlikely. In light of current availability of other GC sparing agents, the position of MTX in PMR may be revised.
Trial registration: Dutch trial register NL-OMON22681, EudraCT 2019-002413-18
Funding: Dutch Arthritis Society project 18-2-401
References.
1) Ferraccioli et al. Methotrexate in polymyalgia rheumatica: preliminary results of an open, randomized study. J Rheumatology. 1996
2) Caporali et al. Prednisone plus methotrexate for polymyalgia rheumatica: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004
3) Van Der Veen et al. Can methotrexate be used as a steroid sparing agent in the treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 1996
4) Marsman et al. PolyMyalgia Rheumatica treatment with Methotrexate in Optimal Dose in an Early disease phase (PMR MODE): study protocol for a multicenter double-blind placebo controlled trial. Trials. 2022
Notes. * Displayed as median (interquartile range). # Based on ≤ 14 U/ml and < 16 for Rheumatoid factor and ACPA respectively. The PMR-AS is calculated as follows: CRP (mg/dL) + (morning stiffness (in minutes) * 0.1) + elevation of upper limbs (ranging 0_3) + VAS for pain (ranging 0_10) + VAS physician’s global (ranging 0_10). † converted to prednisolone dose equivalent.
Abbreviations. CRP, C-reactive protein; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; PMR, polymyalgia rheumatica; ACPA, Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; PMR-AS, PMR activity-score; GC, glucocorticoid; kg, kilogram; m, meter
a: n = 27; b: n = 26; c: n = 23
Notes. For continuous outcomes medians (interquartile ranges) are reported.
* Risk difference and one sided 95% CI
† Risk ratio and two-sided 95% CI
‡ Incidence rate ratio and two-sided 95% CI
# Remission is based on the PMR-AS, which is calculated by CRP (mg/dL) + (morning stiffness (in minutes) * 0.1) + elevation of upper limbs (ranging 0_3) + VAS for pain (ranging 0_10) + VAS physician’s global (ranging 0_10). A PMR-AS < 10 was considered in remission or low disease-activity.
Abbreviations. GC, glucocorticoid; PMR-AS, PMR activity-score; CRP, C-reactive protein; VAS, visual analogue scale; AE, adverse events.
1 from which 3 serious adverse events (pulmonary embolism, ischemic cerebrovascular event, and right humeral fracture); 2 from which 1 serious adverse event (suspected methotrexate pneumonitis).
a: n = 27
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bolhuis T, Kooijman N, Marsman D, Snijders G, den Broeder A, den Broeder N, Van der maas A. Results of a One Year Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial with Methotrexate 25mg Per Week for Recently Diagnosed PolyMyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-of-a-one-year-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-with-methotrexate-25mg-per-week-for-recently-diagnosed-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/results-of-a-one-year-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-with-methotrexate-25mg-per-week-for-recently-diagnosed-polymyalgia-rheumatica/