Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a chronic neurological disorder associated with brain iron metabolism. Although RLS has been linked to various immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, such as psoriatic arthritis (PsA), little is known about the influence of inflammation on this association or the impact of RLS on disease activity, disease burden, and other comorbidities. The objective is to evaluate the prevalence of restless legs syndrome (RLS) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and its association with clinical, inflammatory, functional characteristics, and comorbidities.
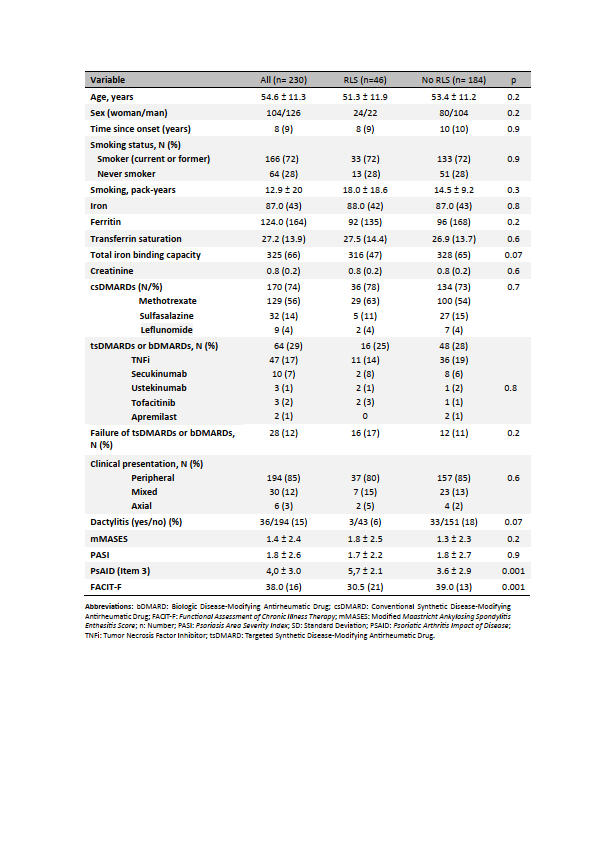
Methods: This is a cross-sectional observational study including 230 PsA patients. RLS screening was performed using the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group questionnaire, with diagnostic confirmation by a neurologist. Demographic data, disease activity (measured by DAPSA), functionality (measured by HAQ), disease impact (measured by PsAID), and comorbidities (anxiety, depression, sleep quality, obesity, and fibromyalgia) were collected.
Results: RLS was confirmed in 46 patients (20%). Patients with RLS showed a higher frequency of polyarthritis (27% vs. 6%; p< 0.001), a greater number of swollen joints (2.0 vs. 1.4; p=0.04), increased fatigue (p< 0.001), higher disease activity (p< 0.001), greater disease impact (p< 0.001), and poorer functionality (p=0.01). RLS was associated with higher rates of anxiety, depression, and poor sleep quality (all p< 0.001).In the regression analysis, polyarthritis (OR: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.00–1.9; p=0.04) and skin problems (OR: 1.4; 95% CI: 1.03–2.0; p=0.03) were significantly associated with the presence of RLS.
Conclusion: RLS is common in patients with PsA and is associated with poorer functionality, higher disease burden, increased fatigue, anxiety, depression, and worse sleep quality. Inflammation and psoriasis-related symptoms could be related to the presence of RLS in these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Toledano E, Villegas C, Chacón C, Hidalgo Calleja C, Miguel B, Blanco L, Turrión A, Compán O, Martín M, Gómez S, Montilla C. Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Association with Inflammatory, Clinical Parameters, and Comorbidities [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/restless-legs-syndrome-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-association-with-inflammatory-clinical-parameters-and-comorbidities/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/restless-legs-syndrome-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-association-with-inflammatory-clinical-parameters-and-comorbidities/