Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: 18F-fluodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) is useful to establish the presence and extent of large vessel vasculitis (LVV). Tocilizumab (TCZ) has shown efficacy in the management of LVV. However, it is unknown if the extent of FDG vascular uptake may influence the clinical response to TCZ.
Our aim was to assess whether the extent of baseline FDG vascular uptake in PET/CT scans correlates to clinical and serological evolution in patients with LVV under TCZ therapy.
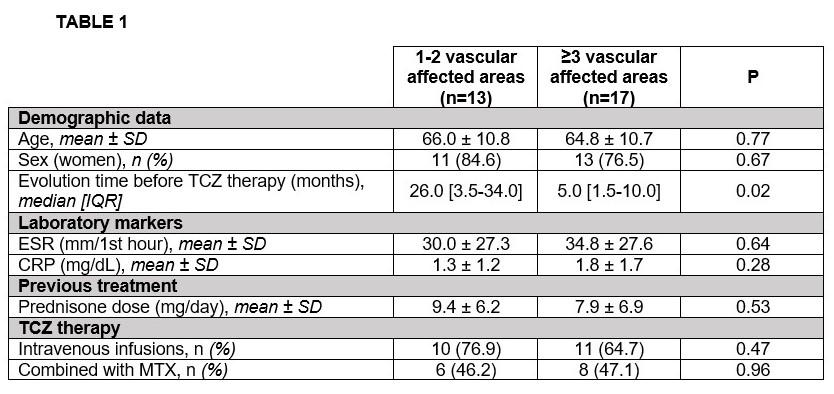
Methods: Comparative single-center study of 30 patients with LVV treated with TCZ who were divided into two groups depending on the extent of FDG vascular uptake in the baseline PET/CT scan: a) 1-2 affected areas, b) ≥affected 3 areas. Vascular FDG uptake was qualitatively assessed by two experienced nuclear medicine physicians in five areas (supra aortic trunks, thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta, iliac arteries, femorotibial arteries). We assessed clinical improvement (no improvement/partial/complete), normalization of acute phase reactants (CRP ≤0.5mg/dL and/or ESR ≤ 20 mm/1st hour) and reduction of prednisone dose (mg/day).
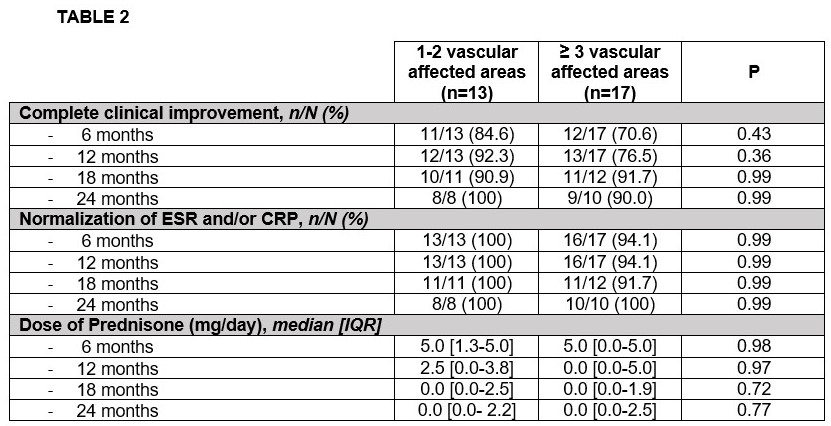
Results: We included 30 (24 women/6 men); mean age 65.3±10.6 years. 13 patients exhibited FDG vascular uptake in < 3 areas whereas 17 patients had ≥3 affected areas. There was a trend to higher ESR/CRP and shorter evolution of clinical symptoms before TCZ onset in patients with ≥3 affected areas (TABLE 1). Most of the patients received TCZ as intravenous infusions and almost half of them received combined therapy with MTX in both groups. Clinical and serological evolution and reduction of prednisone dose is shown in the TABLE 2. No statistical differences were found between both groups. However, patients with ≥ 3 affected areas tended to experience a slower clinical response.
Conclusion: TCZ therapy was effective in patients with LVV regardless the extent of FDG vascular uptake in the baseline PET/CT scan. However, a trend to a slower clinical response was observed in patients with ≥3 affected areas.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sanchez-Bilbao L, Prieto-Peña D, Gonzalez-Mazon I, Martinez-Lopez D, Calderon-Goercke M, Martínez-Rodríguez I, Banzo I, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Response to Tocilizumab in Large Vessel Vasculitis According to the Extent of Baseline 18F-FDG Vascular Uptake [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-tocilizumab-in-large-vessel-vasculitis-according-to-the-extent-of-baseline-18f-fdg-vascular-uptake/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-tocilizumab-in-large-vessel-vasculitis-according-to-the-extent-of-baseline-18f-fdg-vascular-uptake/