Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The introduction of Mepolizumab treatment has revolutionized the therapy of EGPA and has promoted the search for biomarkers predictive of response to treatment. However, few data are available on proinflammatory mediators involved in the disease, particularly during Mepolizumab therapy. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of Mepolizumab on serum levels of cytokines/chemokines potentially involved in EGPA and to correlate them with the clinical and biohumoral profile of patients.
Methods: Patients with a diagnosis of EGPA, made according to ACR/EULAR 2022 classification criteria, followed at our center for at least 1 year and candidates for therapy with Mepolizumab 300 mg/4 weeks were included. Data on demographic, clinical, spirometry, and routine blood chemistry variables were collected before (T0) and after 6 months (T1) of therapy with Mepolizumab. On peripheral venous blood, we quantified serum levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, GM-CSF, Eotaxin-1, -2, -3 by ELISA. Patients were stratified by disease phenotype according to the presence/absence of ANCA-MPO and atopy (defined as the presence of allergic asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis and food allergies). The study received approval from the local Ethics Committee and was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
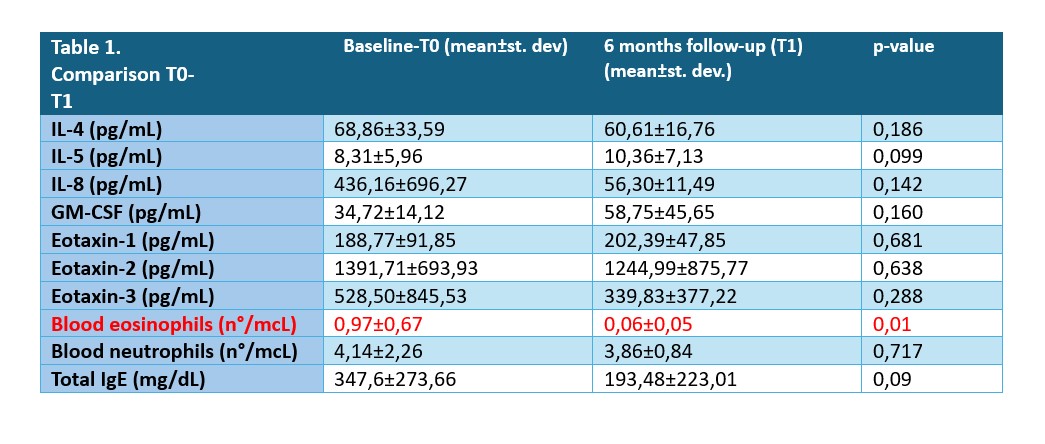
Results: Seventeen patients with EGPA were enrolled, 52.9% male. They showed a mean age of 56.12±8.34 years and an average disease duration of 5.92±3.49 years. 29.4% of cases (5 out of 17) were ANCA-MPO positive. All patients were asthmatic; asthma had a late onset in 41.2% (7/17) of them. 94.1% (16/17) had nasal polyposis and 64.7% (11/17) were atopic. 58.8% (10/17) were taking prednisone therapy with an average dose at T0 of 6.37±5.62 mg. Mean Sino-Nasal Outcome Test – 22 (SNOT-22) and Asthma Control Test (ACT) values at T0 were 45.88±16.95 and 18±4.04, respectively, with FEV1 of 2.14±0.5 L and Total Nasal Polyps Score (TNPS) of 3±1.87. Mean values of eosinophils, neutrophils, total IgE and cytokines/chemokines at T0 and T1 are shown in Table 1.
At T1, the levels of cytokines/chemokines, neutrophils, total IgE did not change, while the number of eosinophils decreased significantly (p=0.01), as did the daily dose of prednisone (2.11±2.12 mg, p=0.001). There was a decrease in SNOT-22 (25.38±16.16, p=0.001) and TNPS (1±1.22 p=0.002) and a parallel increase in ACT (21.6±3.24, p=0.018) at T1. The values of FEV1 remained unchanged.
Comparing patients by presence/absence of atopy and ANCA-MPO negativity/positivity, cytokine/chemokine levels did not differ between groups at T0 or even comparing T0 and T1, except in ANCA-MPO negative patients, where IL-5 values were found to be increased at T1 (7.69±7.5 vs 11.9±8.69, p=0.013).
Conclusion: This study confirms the effect of Mepolizumab on the control of peripheral eosinophilia and the improvement of asthma and nasal polyposis and shows that measurement of IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, GM-CSF, Eotaxin-1, -2, -3 levels does not appear useful for monitoring response to therapy. Further studies with larger samples are needed to evaluate changes in IL-5 levels during Mepolizumab therapy in ANCA-negative patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moretti M, Ferro F, Martelli I, Pistone F, Greco G, Di Cianni F, Italiano N, TALARICO R, Seccia V, Baldini C, Puxeddu I, Mosca M. Response to Mepolizumab Therapy in a Single-center Cohort of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Patients: Characterization of Cytokine/Chemokine Pattern and Phenotypic Stratification [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-mepolizumab-therapy-in-a-single-center-cohort-of-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-patients-characterization-of-cytokine-chemokine-pattern-and-phenotypic-stratification/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-mepolizumab-therapy-in-a-single-center-cohort-of-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-patients-characterization-of-cytokine-chemokine-pattern-and-phenotypic-stratification/