Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Information regarding response rate and sustained remission in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), in Hispanics with non-biological treatment is scarce. We performed a study to estimate the response rates and sustained remission during the disease course of patients with IIM treated with conventional immunosuppressive agents.
Methods: A retrospective longitudinal study from medical records of patients with MII at a single rheumatology reference center in Mexico was performed. Medical records were reviewed to determine clinical presentation, serum creatine kinase (CK) levels, initial treatment and outcome measures such as the muscle strength assessed by the manual muscle testing of 8 muscle groups (MMT8), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability index (HAQ-Di) during follow-up. The primary outcome was time to achieve sustained remission, defined as no evidence of active myositis for ≥ 6 months while not receiving glucocorticoids and the presence of all of the following: 1) improvement of muscle strength; 2) normal muscle enzyme levels; 3) tapering immunosuppressive agents or withdrawal. Interval between first remission and first relapse was recorded. Additionally, status of remission was reported at the end of follow up for each patient.
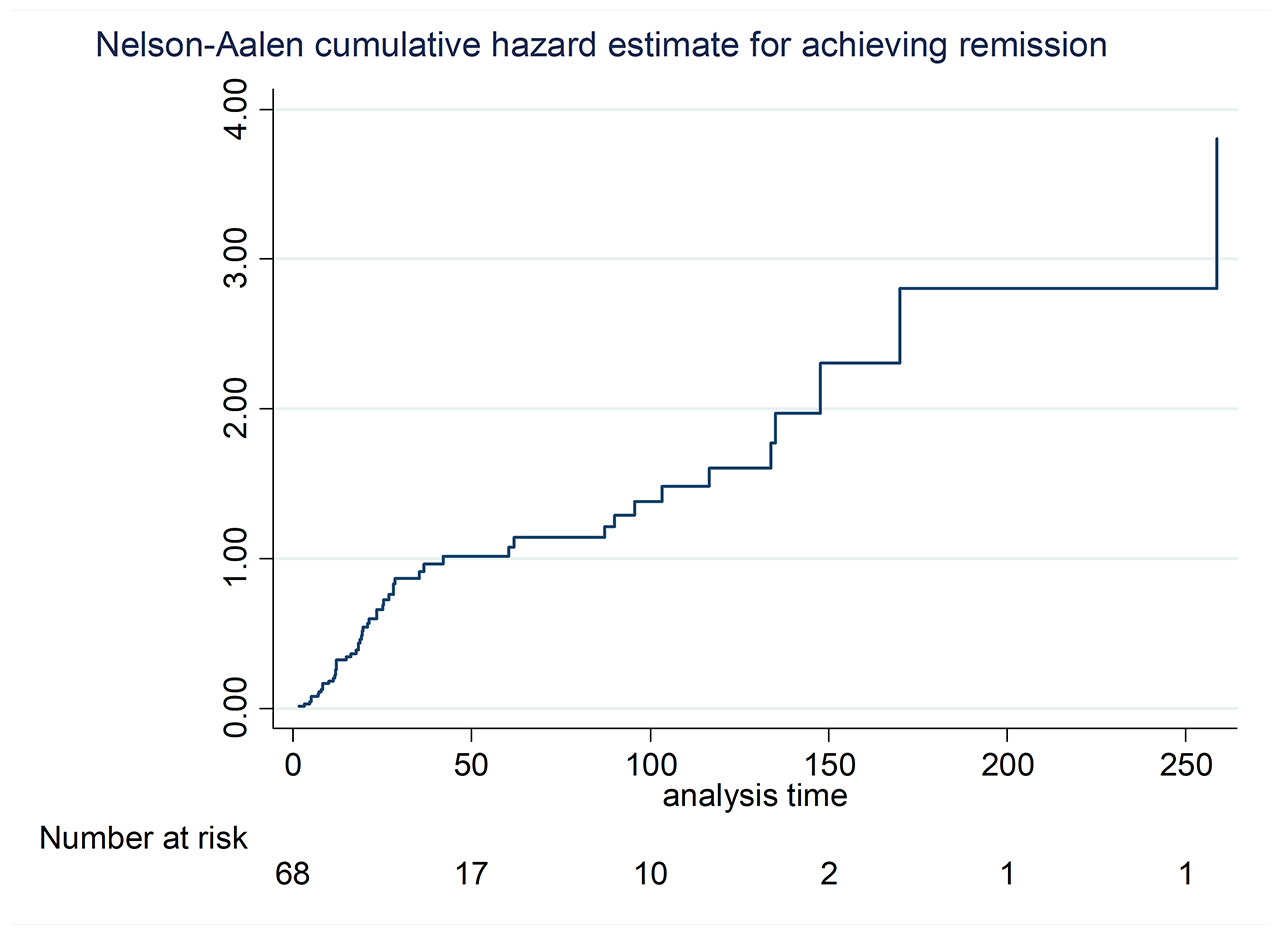
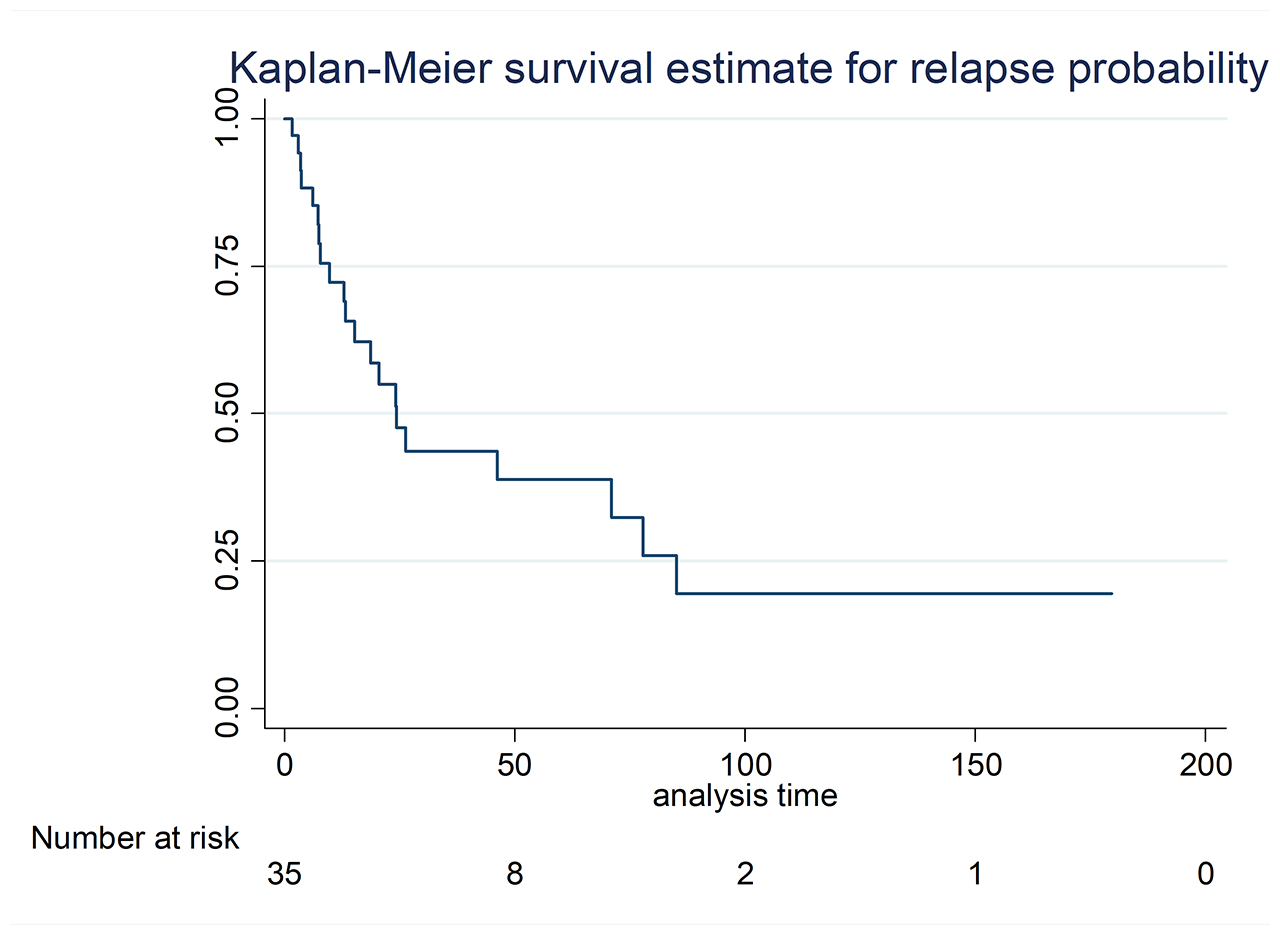
Results: Data from 76 patients, which 81.4% had DM and 14.6% had PM; female 8.26%, mean age of 39 (SD ± 12.6) years; Interval between symptom onset and first assessment showed a median of 185 (RIQ 64 – 518) days; All patients received a standardized stepwise treatment with glucocorticoids and either a single or combined therapy with methotrexate (MTX) or azathioprine (AZA) until remission was achieved; Remission was observed in 68.42%, with a median time required for achieving remission of 22.2 (RIQ 11 – 46) months. From the sub group of patients achieving remission 78.85% had sustained remission and 41.18% showed relapses with a median of relapse-free survival time of 15.16 (RIQ 6 – 32) months during follow up. The median follow-up period for the entire cohort was 38 (RIQ 21 – 108) months; During final visit, the proportion of subjects in remission were 55.3%, normal muscle strength 58.9%, chronic muscular damage in 16.1%, normal CPK and muscle enzymes in 75%; Treatment with glucocorticoids in 46.4% and any immunosuppressive agent in 82.1% With median of HAQ-Di score of 0 (RIQ 0 – 0.35).
Conclusion: Treatment of IIM with conventional immunosuppressive agents results in a high rate of subjects achieving remission, however, most subjects required prolonged time with continued immunosuppressive therapy and relapses are frequent, which may account in significative muscle damage burden during follow up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sánchez-Rodríguez A, Gómez-Ruiz C, Montes-Yanes A, Medrano-Ramírez G. Response Rate and Sustained Remission in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Receiving Conventional Immunosuppressive Stepwise Management [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-rate-and-sustained-remission-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-receiving-conventional-immunosuppressive-stepwise-management/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-rate-and-sustained-remission-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-receiving-conventional-immunosuppressive-stepwise-management/