Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Placebo-controlled clinical trials are the gold standard to provide the highest-quality evidence of treatment efficacy; however, in early SSc, requiring participants to take long-term placebo raises feasibility and ethical concerns. Studies may allow immunosuppressive rescue therapy when a participant’s condition worsens. Statistically, adjusting for rescue therapy to derive appropriate conclusions about treatment efficacy is complicated. We applied several analytic approaches to address rescue therapy in a recently-completed trial.
Methods: ASSET was a multicenter double-blind, randomized placebo (PBO)-controlled trial of abatacept (ABA; NCT02161406). Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to 12 months ABA or matching PBO, stratified by duration of dcSSc (≤18 vs >18 to ≤36 months). After 6 months of treatment, investigators were given a choice to add rescue therapy for worsening signs or symptoms.
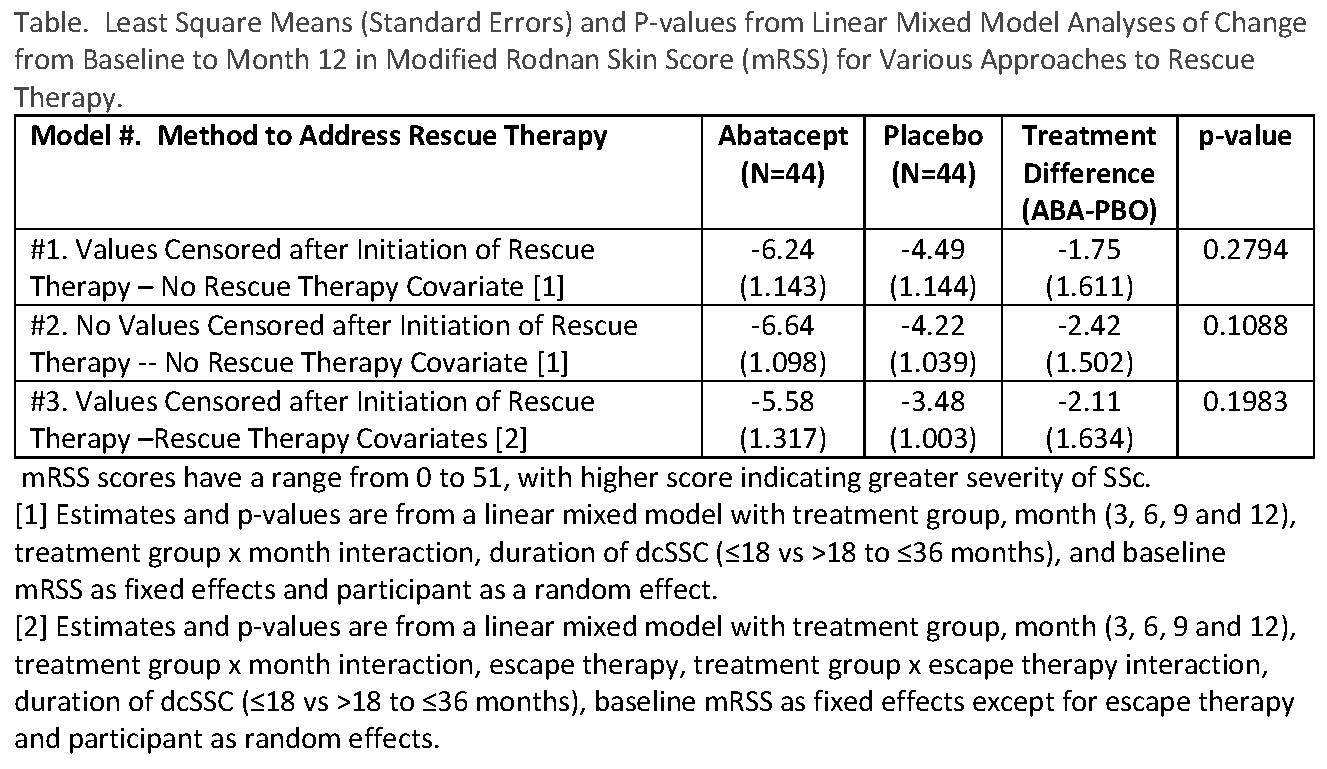
Our primary analytic strategy for treatment comparisons for the primary (change from baseline to month 12 in mRSS) and secondary endpoints was based on the ITT principle for inclusion of participants, but to eliminate data after the onset of rescue therapy using linear mixed models. We also applied the “standard” approach of performing a strict ITT analysis and including all observations (i.e., including post-rescue therapy values). In addition to censoring, we used two models to deal with rescue therapy – inclusion and exclusion of terms for rescue therapy and treatment group X rescue therapy interaction.
Results: 44 ABA and 44 PBO were randomized. 7 (16%) ABA and 16 (36%) PBO participants began rescue therapy (p=0.03). By eliminating observations after the start of rescue therapy and not incorporating rescue therapy into the model, the smallest mean treatment difference occurred (see Table, #1). As might be expected with twice as many PBO participants starting rescue therapy, the largest mean treatment difference occurred when all observations were included in the analysis and rescue therapy was not incorporated into the model (See Table, #2). Censoring observations after the start of rescue therapy and incorporating rescue therapy as a covariate resulted in an intermediate estimate. No statistically significant treatment differences were observed from any model.
Conclusion: Although there was differential use of rescue therapy in our study, several simple approaches to handling rescue therapy resulted in comparable conclusions, providing confidence in our results. More sophisticated analytic methods, such as jointly modeling the primary endpoint and the probability of rescue therapy, may be useful, as well as consideration of the choice of estimand during the design of the trial which will help focus analytic efforts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Spino C, Parker RA, Khanna D. Rescuing Standard Analyses of Immunosuppresive Rescue Therapy in Randomized Controlled Trials: Alternative Approaches in a Scleroderma Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rescuing-standard-analyses-of-immunosuppresive-rescue-therapy-in-randomized-controlled-trials-alternative-approaches-in-a-scleroderma-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rescuing-standard-analyses-of-immunosuppresive-rescue-therapy-in-randomized-controlled-trials-alternative-approaches-in-a-scleroderma-clinical-trial/