Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) affects approximately 50% of patients and is a major determinant in the survival and prognosis of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We investigated the prognostic factors associated with the progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and death among LN patients.
Methods: Of 1,497 Korean patients with SLE in a prospective lupus cohort, we included 599 patients with biopsy-proven proliferative and membranous LN. Baseline demographics, renal histology, and clinical features were collected. The disease activity measured by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index-2K (SLEDAI-2K) and organ damage score using Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/ACR Damage Index total score (SDI) were annually assessed.
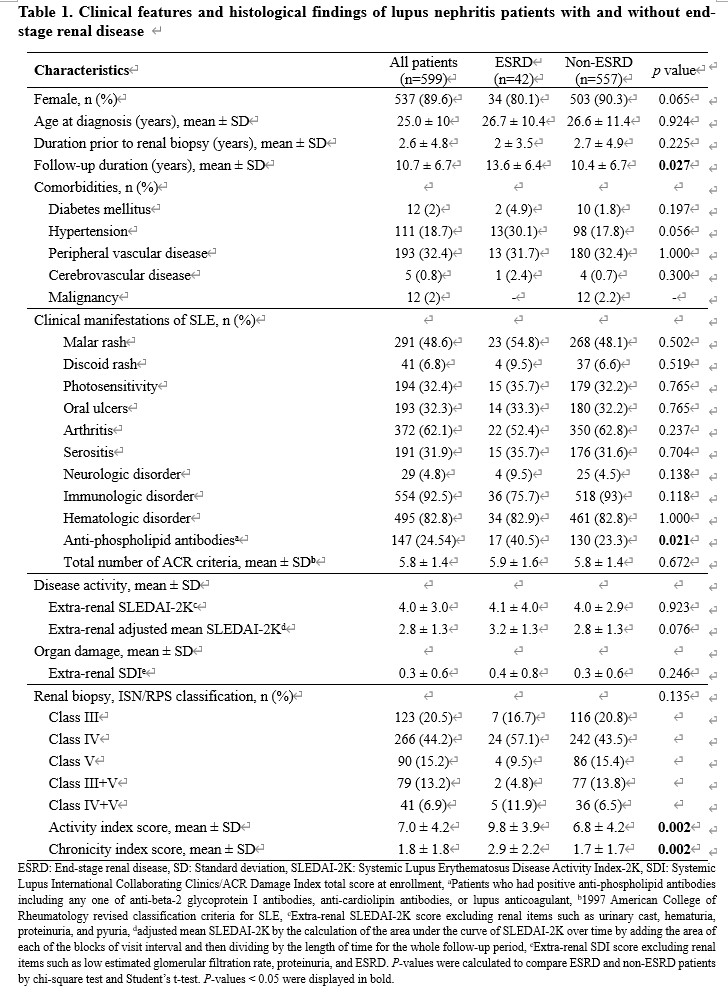
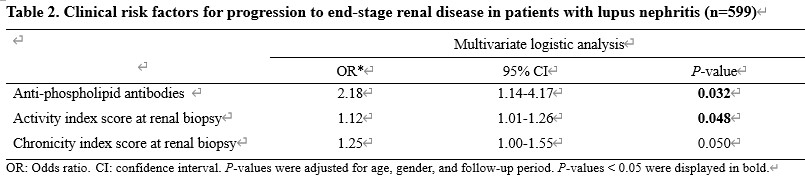
Results: The SLE patients with proliferative LN (class III or IV/±V, n=509) and membranous LN (class V, n=90) were followed for a mean of 10.7 years (Table 1). Among these patients, 7.0% developed ESRD. Anti-phospholipid antibodies (OR 2.18, P=0.032) and a high activity index score at renal biopsy (OR 1.12, P=0.048) were found to be independent predictors of ESRD after adjusting for age, gender, and follow-up duration by a multivariate logistic regression analysis (Table 2). During the follow-up period, a total of 31 patients died. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that non-ESRD patients had a better survival rate than ESRD patients (P=0.03). Additionally, we found that a higher extra-renal adjusted mean SLEDAI-2K (hazard ratio [HR] 1.83, P < 0.001) was significantly associated with increased overall mortality by a multivariate Cox-proportional hazard analysis.
Conclusion: Our study identified that anti-phospholipid antibodies and the activity index in renal histology are crucial predictors of ESRD in LN patients, with high disease activity indicating an increased risk of death. This emphasizes the importance of strict disease control to prevent mortality in high-risk LN patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shin J, Lee J, Lee H, Bae S, Bang S. Renal Survival and Mortality in Patients with Proliferative and Membranous Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/renal-survival-and-mortality-in-patients-with-proliferative-and-membranous-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/renal-survival-and-mortality-in-patients-with-proliferative-and-membranous-lupus-nephritis/