Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Plenary II
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:30AM-1:00PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a systemic autoimmune disease of unknown etiology characterized by B-cell hyperactivation, lymphoid infiltration, progressive destruction of exocrine glands, and various extraglandular manifestations.1 Patients with SS have a 15- to 20-fold elevated risk of developing B-cell lymphoma as a life-threatening complication.2 Remibrutinib is an oral, covalent, and highly specific inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK).3 BTK is expressed in cells of both adaptive and innate immune system including B cells, and is indispensable for B‑cell receptor and Fc receptor signaling. Here we report 24-week safety and efficacy results from a phase 2 proof-of-concept trial of remibrutinib in patients with primary SS.
Methods: This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 study enrolled patients with moderate to severe SS with a baseline EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index (ESSDAI) score of ≥5, EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) of ≥5, anti-Ro/SSA antibody positivity ≤3 months prior to screening, and unstimulated whole salivary flow rate of >0 mL/min. Safety of remibrutinib in patients with SS and its effect on change from baseline in ESSDAI, salivary flow, and patient reported outcomes (PRO) were evaluated.
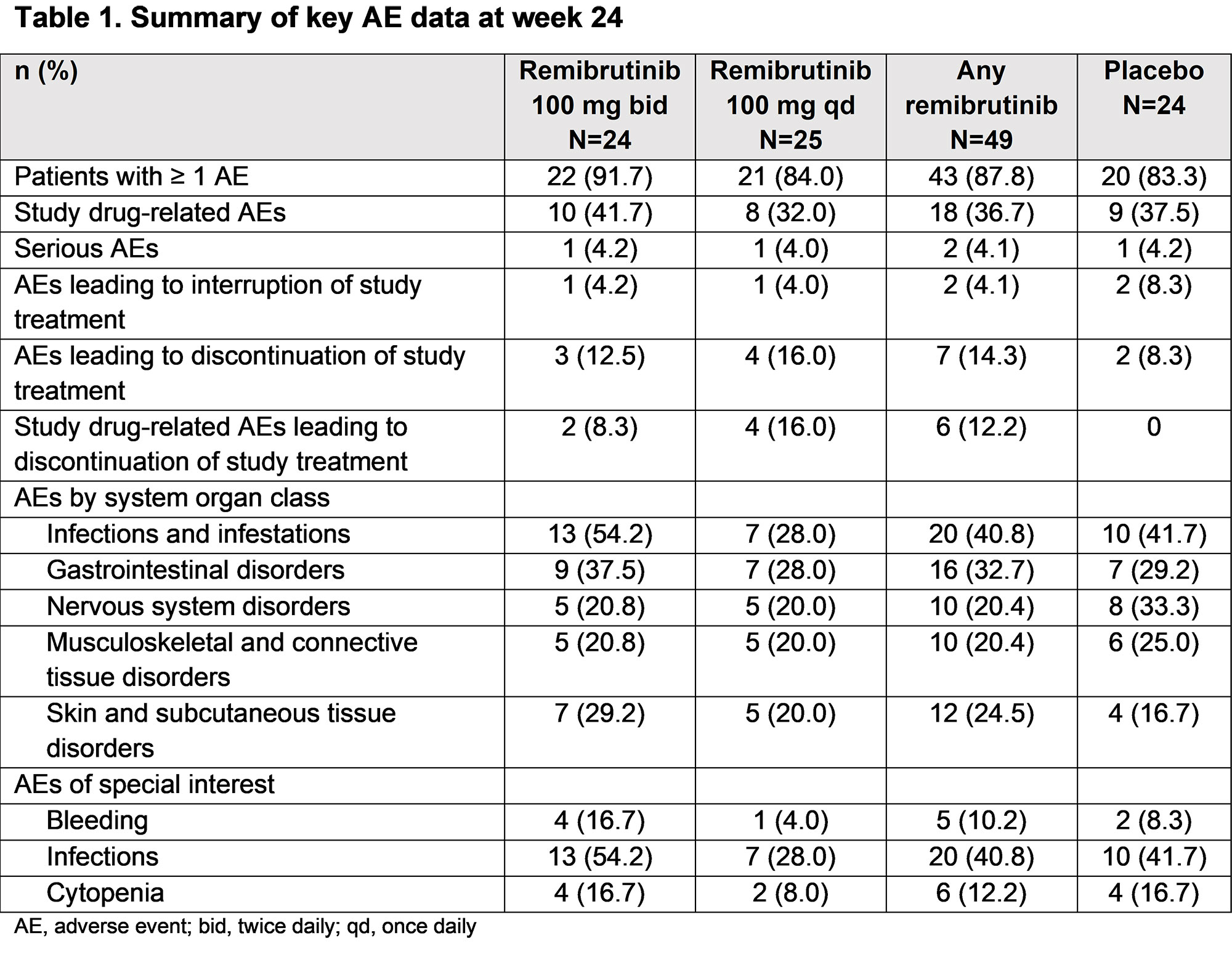
Results: Overall, 73 patients were randomized to receive remibrutinib 100 mg bid (n=24), 100 mg qd (n=25), or placebo (n=24) between Aug 2019 and May 2021. Only 2 patients were men. Mean (SD) age was 51.8 (13.34) years. Groups were generally balanced for demographic and disease-related baseline parameters. Incidence of adverse events (AEs) was similar across groups. No severe AE was reported. Infections were the most frequently reported AE by system organ class, with similar rates in remibrutinib and placebo groups (40.8% and 41.7%; Table 1). No notable liver abnormalities were reported in any group. Remibrutinib resulted in a statistically significant improvement in ESSDAI score compared with placebo at week 24 (DESSDAI −2.86, P=0.003 [two-sided; for both regimens combined]) with numerical improvement over placebo at all time points (Figure 1). Unstimulated salivary flow showed a tendency for improvement with remibrutinib compared to placebo (Figure 2). Total serum IgG and IgM, but not IgA, declined from baseline but remained in normal range. Anti-SS-A and -SS-B autoantibodies followed the trend of total IgG. PROs, including ESSPRI, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, and EuroQol-5 Dimension were similar in remibrutinib and placebo groups.
Conclusion: Remibrutinib had a favorable safety profile; was well-tolerated over 24 weeks in patients with SS. ESSDAI, salivary flow, and pathologically elevated immunoglobulins as signatures of activity improved. These results suggest BTK inhibition with remibrutinib as the first effective oral disease-modifying therapy for SS. PROs, including ESSPRI, may need longer duration to demonstrate benefits. Additional studies are warranted to confirm the benefit of remibrutinib treatment in SS.
References
- Brito-Zeron P, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16047
- Mariette X, et al. N Engl J Med.2018;378(10):931–939
- Kaul M, et al. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(5):1756–1768
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dörner T, Szántó A, Tseng J, Kaul M, Pylvaenaeinen I, Hanser M, Abdallah N, Cenni B, Siegel R. Remibrutinib (LOU064) in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Safety and Efficacy Results from a 24‑Week Placebo-controlled Proof-of-Concept Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remibrutinib-lou064-in-sjogrens-syndrome-safety-and-efficacy-results-from-a-24%e2%80%91week-placebo-controlled-proof-of-concept-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remibrutinib-lou064-in-sjogrens-syndrome-safety-and-efficacy-results-from-a-24%e2%80%91week-placebo-controlled-proof-of-concept-study/