Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The physician global assessment of lung disease (PGALD) is a recently proposed disease activity measure for patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated lung disease (SJIA-LD) – a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in SJIA. This study evaluates the reliability and construct validity of the PGALD.
Methods: 20 SJIA-LD clinical vignettes were created, informed by historical patient encounters as templates. Vignettes included brief patient medical histories, physical examination findings, a list of prescribed medications, laboratory results, diagnostic imaging, pulmonary function test results, and biopsy results – when available. Fifty-seven pediatric rheumatologists and pulmonologists with experience caring for children with SJIA-LD were invited to rate vignettes utilizing the PGALD, a 10-point Likert scale (0 = inactive SJIA-LD; 10 = highly active SJIA-LD). Raters who completed the initial round of 20 vignettes were asked three days later to rate a subset of 8 repeat vignettes. Inter- and intra-rater reliability were assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC). Based on the 95% confidence interval of ICC estimates, values less than 0.5 indicated poor reliability, between 0.5-0.75 moderate-, between 0.76-0.9 good-, and >0.9 excellent reliability. SJIA-LD features influencing PGALD ratings were assessed in univariate analysis.
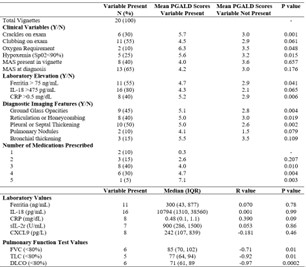
Results: The ICC for all raters was 0.678 (0.543, 0.819), indicating moderate to good inter-rater reliability. The intra-rater ICC was 0.863 (0.823, 0.893) indicating good intra-rater reliability. Factors associated with higher mean PGALD scores included the presence of crackles on auscultation (5.7 vs. 2.9; p=0.001), hypoxemia on pulse oximeter (5.6 vs. 3.2; p=0.01), current oxygen requirement (6.3 vs. 3.5; p=0.04), suggestive diagnostic imaging features (p≤0.01), and three or more prescribed medications for SJIA-LD (p≤0.01). Pulmonary function measures demonstrated significant negative correlations with mean PGALD scores, including forced vital capacity (r=−0.71; p=0.01), total lung capacity (r=−0.92; p=0.01), and diffusion capacity (r=−0.97; p=0.0002). Only the CRP was weak-to-moderately correlated with PGALD scores (r=0.39; p=0.09), while other laboratory values including ferritin, IL-18, CXCL9, and sIL2R were not significantly correlated.
Conclusion: The PGALD is a novel measure of SJIA-associated LD activity. Its initial validation suggests acceptable construct validity and reliability. Additional studies are needed to assess its responsiveness to change over time.
.jpg) Sp02 – Peripheral saturation of oxygen; MAS – macrophage activation syndrome; IL-18 – Interleukin 18; CRP – C-reactive protein; CXCL9 chemokine c-x-c-motif; FVC – forced vital capacity; TLC – Total Lung capacity; DLCO – lung diffusion capacity.
Sp02 – Peripheral saturation of oxygen; MAS – macrophage activation syndrome; IL-18 – Interleukin 18; CRP – C-reactive protein; CXCL9 chemokine c-x-c-motif; FVC – forced vital capacity; TLC – Total Lung capacity; DLCO – lung diffusion capacity.
Unpaired t test performed for Clinical Variables, Laboratory Elevation and Diagnostic Imaging Features; Pearson Correlation Coefficient performed for Laboratory Values and Pulmonary function Test Values; ANOVA performed for Number of Medications Prescribed.
.jpg) Association between clinical features and mean PGALD scores. A: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without supplemental oxygen. B: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without hypoxia. C: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without crackles on exam. D: Mean PGALD scores by number of medications (1-5) used to treat SJIA-LD. *p= < 0.05, **p= < 0.01
Association between clinical features and mean PGALD scores. A: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without supplemental oxygen. B: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without hypoxia. C: Mean PGALD scores in patients with vs. without crackles on exam. D: Mean PGALD scores by number of medications (1-5) used to treat SJIA-LD. *p= < 0.05, **p= < 0.01
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rife E, Zhai G, Altaye M, Andringa J, Brunner H, Canna S, Henderson L, Kimura Y, Lieberman S, Riskalla M, Vogel T, Wobma H, Schulert G. Reliability and Validation of the Physician’s Global Assessment of Lung Disease (PGALD) in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis -Associated Lung Disease (SJIA-LD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validation-of-the-physicians-global-assessment-of-lung-disease-pgald-in-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-lung-disease-sjia-ld/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validation-of-the-physicians-global-assessment-of-lung-disease-pgald-in-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-lung-disease-sjia-ld/