Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is usually accompanied by metabolic diseases including obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Obesity has been confirmed as a risk factor for gout. This study aims to explore the clinical and renal uric acid excretion features in gout patients with obesity.
Methods: Primary gout patients hospitalized from 2013 to 2017 were included. The diagnosis of gout fulfilled the 1977 ACR gout classification criteria or the 2015 ACR/EULAR classification criteria. The patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30ml/min/1.73m2 and secondary gout were excluded. Baseline characteristics, fasting blood biochemical indexes, incidence of comorbid diseases were collected. The 24h urinary uric acid (UUA) and urinary creatinine excretion (UCr) were evaluated on unrestricted diet, which were used for the calculation of renal uric acid excretion variables. Obesity was defined as body mass index (BMI) ≥28 kg/m2.
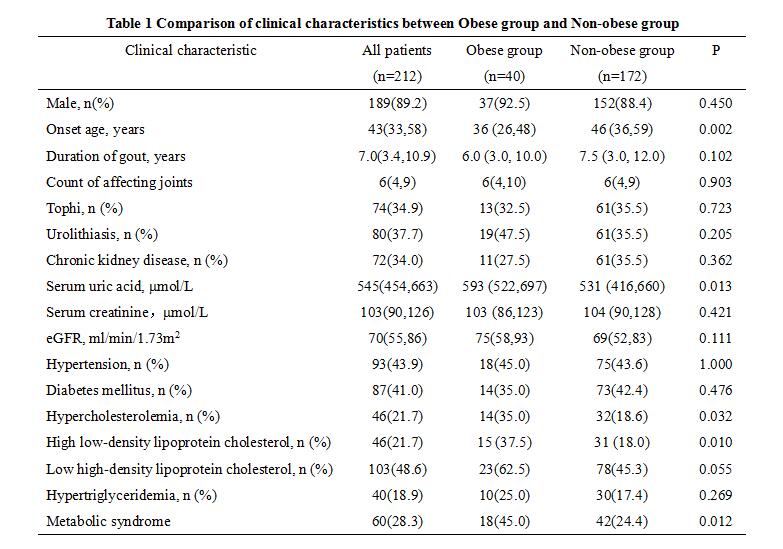
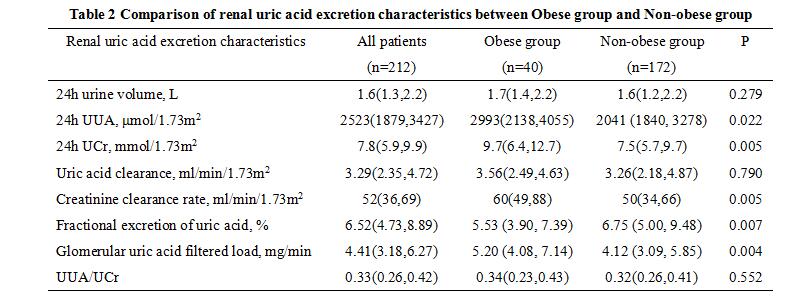
Results: ①Among 212 recruited patients, 89.2% were male, the median age of onset was 43(33,58) years old and median serum uric acid (sUA) was 545 (454,663) μmmol/L, 40 patients (18.9% ) had obesity. ②Compared with non-obese group (n=172), the obese group presented a younger onset age [36 (26,48) years vs. 46 (36,59) years], significantly higher level of sUA [593 (522,697) μmol/L vs. 531 (416,660) μmol/L], higher incidence of hypercholesterolemia (35.0% vs. 18.6%), high low-density lipoproteinemia (37.5% vs. 18.0%), and metabolic syndrome (45.0% vs. 24.4%, all P<0.05). There were no significant difference between two groups in gender, duration of gout, count of affecting joints, levels of serum creatinine and eGFR, and incidence of tophi, urolithiasis, chronic kidney disease, hypertention, diabetes mellitus, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and hypertriglyceridemia (all P>0.05, Table 1). ③ The glomerular uric acid filtered load [5.20 (4.08, 7.14) mg/min vs 4.12 (3.09, 5.85) mg/min] was significantly higher in the obese group. Although the 24h UUA excretion was significantly higher [2993 (2138, 4055) μmol vs. 2041 (1840, 3278) μmol], the fractional excretion of uric acid in the obese group was significantly lower [5.53 (3.90, 7.39) % vs. 6.75 (5.00, 9.48)%, Table 2].
Conclusion: High uric acid load of serum and glomerular filtration in gout patients with obesity may due to the relative insufficiency of renal uric acid excretion.
Acknowledgement: The present study was supported by Guangdong Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant No. 2014A030310086) .
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liang JJ, Li QH, Mo YQ, Wei XN, Zheng DH, Dai L. Relative Insufficiency of Renal Uric Acid Excretion in Gout Patients with Obesity Leads to High Serum and Glomerular Filtration Load of Uric Acid [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relative-insufficiency-of-renal-uric-acid-excretion-in-gout-patients-with-obesity-leads-to-high-serum-and-glomerular-filtration-load-of-uric-acid/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relative-insufficiency-of-renal-uric-acid-excretion-in-gout-patients-with-obesity-leads-to-high-serum-and-glomerular-filtration-load-of-uric-acid/