Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: For patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who are treated with etanercept (ETN) plus methotrexate (MTX), dosing down of ETN or withdrawal of MTX are options once treat-to-target has been achieved. In the COMET study1 (NCT00195494), patients with RA received combination therapy (50 mg/week ETN+MTX) for 52 weeks in Period (P) 1, and were then randomized to either continue combination therapy or discontinue MTX and receive ETN monotherapy for a further 52 weeks (P2). The purpose of this analysis was to compare Week 104 clinical, functional, and radiographic outcomes between treatment arms for each patient subgroup, classified by disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28) response (achievement or not of DAS28 low disease activity [LDA; DAS28 score ≤3.2] or remission [DAS28 score < 2.6]).
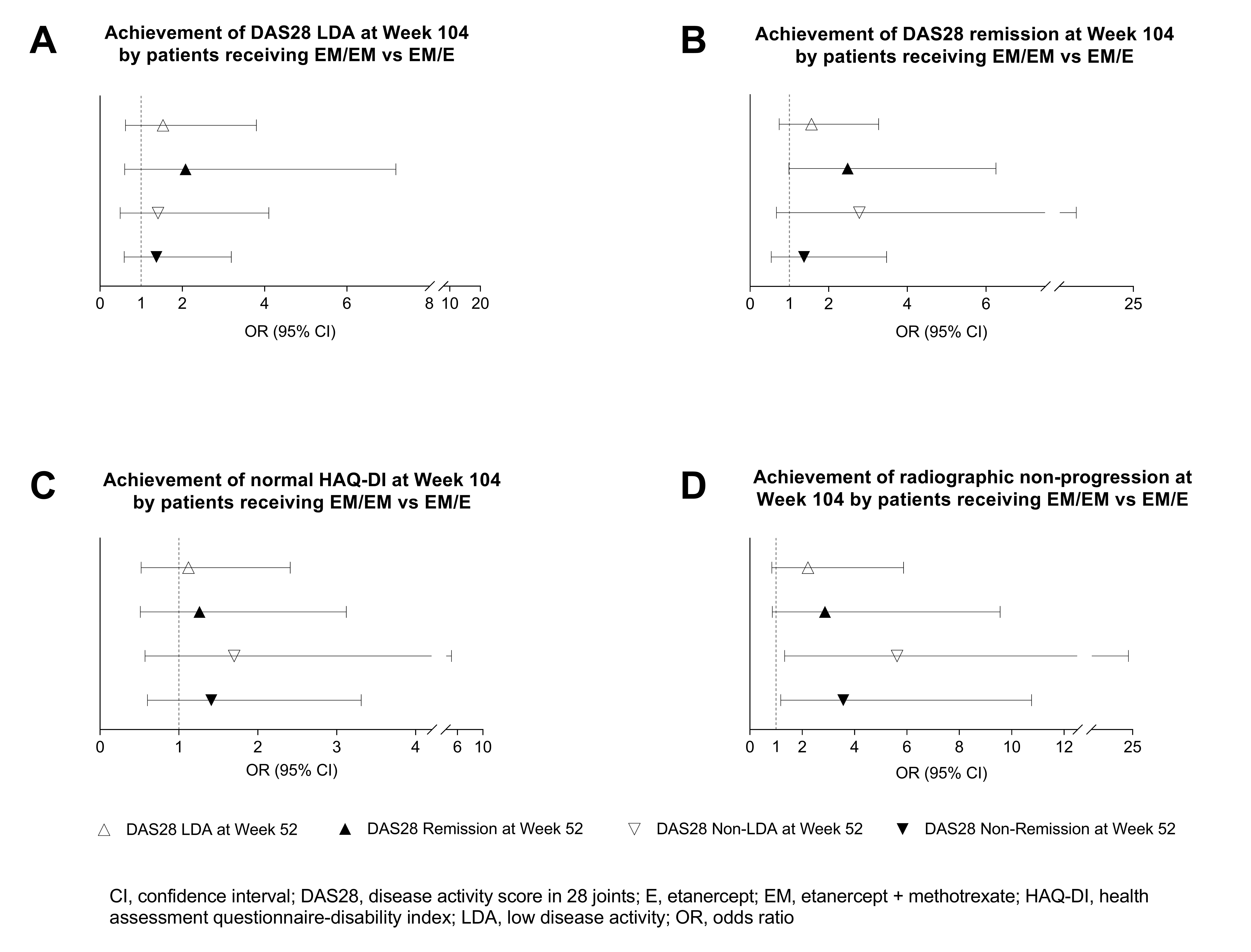
Methods: Odds ratios (ORs) comparing the ETN+MTX and ETN P2 treatment arms for each Week 52 DAS28 status were calculated from logistic regression models with treatment, Week 52 DAS28 status, and their interaction as predictors of achieving DAS28 LDA, DAS28 remission, normal Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score (score ≤0.5), and radiographic non-progression (change from Year 2 baseline in modified Total Sharp Score [mTSS] of ≤0.5) at Week 104.
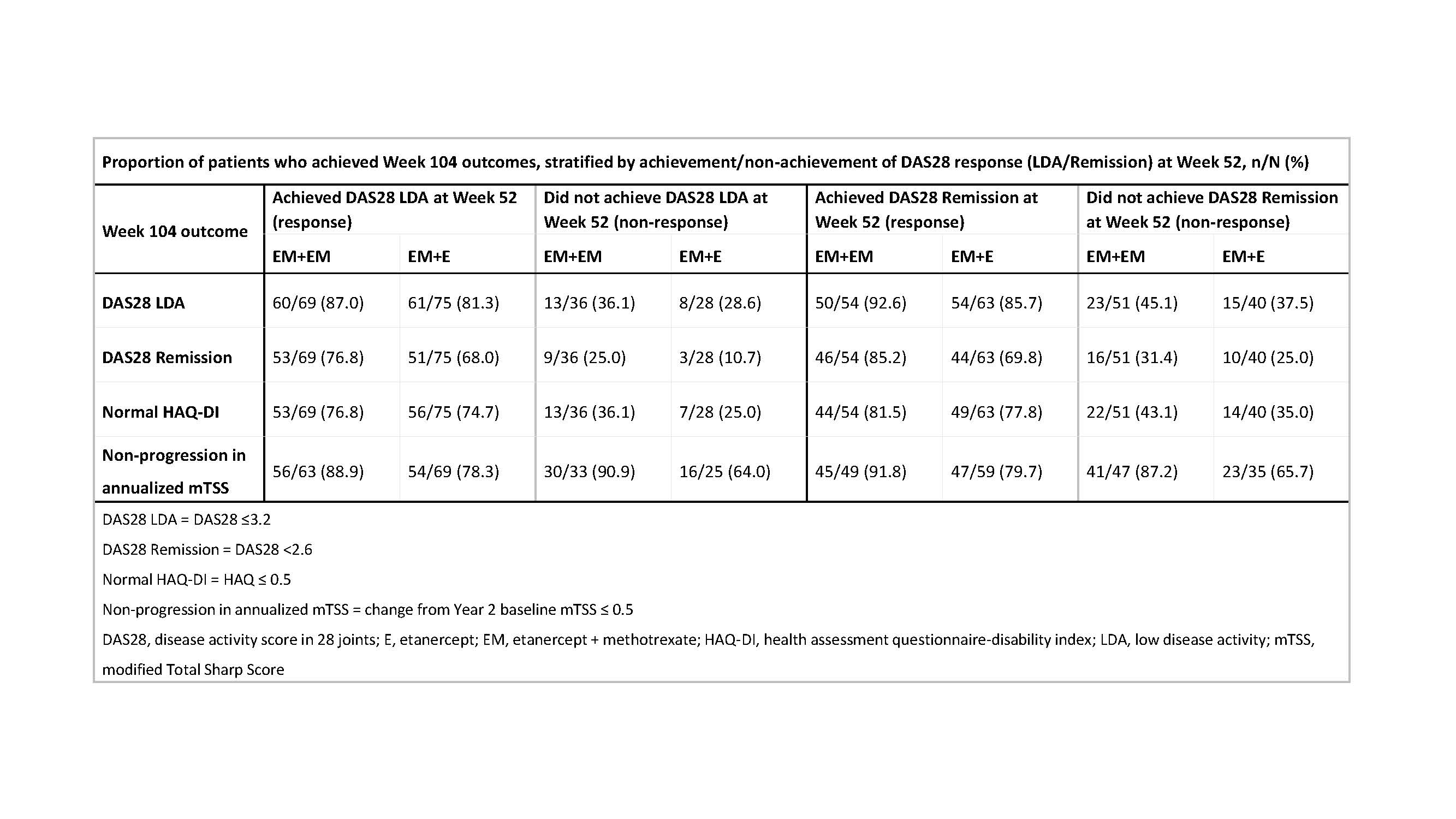
Results: A total of 208 patients (105 in the ETN+MTX and 103 in the ETN monotherapy P2 treatment arms, respectively) were included in this analysis. The odds of achieving DAS28 LDA, DAS28 remission, or normal HAQ-DI at Week 104 in patients who did or did not achieve a DAS28 response at Week 52 did not generally differ significantly between the treatment groups (Figure, Panels A-C), which could be attributed, at least in part, to lack of power to detect treatment differences due to small sample sizes (36 [ETN+MTX] and 28 [ETN] patients were in the Week 52 LDA non-response category while 51 [ETN+MTX] and 40 [ETN] patients were in the remission non-responder category). The only exception was the significantly higher odds of achieving radiographic non-progression in patients treated with ETN+MTX vs ETN monotherapy who did not achieve a DAS28 response at Week 52 (Figure, Panel D). Although the overall lack of significant ORs suggests that there were almost no differences between the two treatment arms, the ETN+MTX treatment arm had ~5-15% higher rates of response compared with ETN monotherapy for the DAS28 and HAQ outcomes (regardless of Week 52 DAS28 subgroup), and for radiographic outcomes for Week 52 DAS28 responders. A ~25% higher rate of response for the ETN+MTX vs the ETN monotherapy treatment arm was seen for radiographic outcomes in the Week 52 DAS28 non-response categories (Table). Week 52 DAS28 status did not modify treatment effect on outcomes, but did increase the ETN treatment effect on radiological efficacy from ~10% for Week 52 DAS28 responders to ~25% for Week 52 DAS28 non-responder.
Conclusion: For patients with RA receiving ETN+MTX who achieved DAS28 LDA or remission after 52 weeks, discontinuation of MTX at Week 52 may result in minimal loss of clinical, functional, and radiological efficacy after an additional 52 weeks of treatment with ETN monotherapy.
1 Emery P, et al. Lancet 2008;372:375-82.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emery P, Breedveld F, Pedersen R, Campos E, Szumski A, Hirose T. Relationships Between DAS28 Response and Clinical, Functional and Radiographic Outcomes in Year 2 of the COMET Study of Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-das28-response-and-clinical-functional-and-radiographic-outcomes-in-year-2-of-the-comet-study-of-etanercept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-das28-response-and-clinical-functional-and-radiographic-outcomes-in-year-2-of-the-comet-study-of-etanercept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/