Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0554–0592) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IL-17A and IL-17F are the key inflammatory mediators in the IL-17 cytokine family (IL-17A to IL-17F). IL-17A is the widely recognized inflammatory cytokine in this family. IL-17F has drawn increasing attention for its functional similarity with IL-17A and its clinical efficacy in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Like IL-17A, IL-17F utilizes IL-17RA/RC receptor. Limited studies are available on IL-17F in human diseases. The objective of this study was to evaluate the significance of IL-17F in the pathognomonic ‘pannus’ formation in PsA and to compare that with the contributing role of IL-17A.
Methods: Here we determined functional role IL-17F on Synovial fibroblasts (FLS) proliferation and on induction of inflammatory cytokines/endopeptidase (IL-6, IL-8, MMP3) related with pannus formation. A. FLS isolated from PsA (n=5) were cultured with rIL-17F (100 ng/ml) for 5 days. For proliferation assay MTT/CFSE dilution assays were done. To determine the effect of IL-17F on the production of relevant cytokines/chemokines the PsA-FLS culture supernatants were evaluated for IL-6, IL-8, and MMP3 by specific ELISA kits. Similar experiments were done with rIL-17A (100 ng/ml), rIL-22 (100 ng/ml), TNF-α (20ng/mL). Concentrations of rIL-17 A/F, rIL-22, TNF-α were selected by doing dose curves.B. As IL-17F and IL-17A shares ~50% homology, we evaluated additive or synergistic effect of these cytokine combinations on FLS proliferation and cytokine/chemokine production in PsA-FLS. C. By Flow cytometric studies of T cells derived from PsA synovial fluid (SF) (n=10) we identified the expression of IL-17A and IL-17F in the effector memory T (TEM) cells.
Results: In MTT assay we observed rIL-17F induced significant proliferation in PsA FLS (OD: 1.49+0.05) compared to unstimulated (OD: 0.19+0.04; p < 0.001). Treatment with rIL-17A (OD: 1.85+0.07) induced significantly more proliferation than rIL-17F and rIL-22 (1.49+0.05; p < 0.05, 1.48+0.02; p < 0.001, respectively). However, compared to rIL-17A alone (OD:1.85+0.07) stimulation with rIL-17A+rIL-17F induced significantly more proliferation in PsA FLS (OD: 2.05+0.09; p < 0.001). Furthermore, PsA FLS treated with TNF-α+rIL-17A+rIL-17F had highest proliferation (OD 1.85+0.07). In CFSE proliferation assay the results were similar (Fig 1).PsA FLS stimulated with rIL-17A, rIL-17F and TNF-α produced significantly more IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 compared to media (p < 0.001). However, compared to IL-17F upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 were significantly higher with IL-17 A (p < 0.001) as shown in Fig 2. In the SF of PsA patients the level of IL-17A was higher than IL-17F (Fig 3). In SF derived T cells with Hi-D FACS studies we identified (i) CD4+ TEM cells secreted IL-17A and IL-17F (ii) IL-17A+ TEM cells were more than IL-17F (Fig 3B, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: IL-17A is more in the PsA synovium and functionally more potent than IL-17F in respect to its regulatory role on pannus formation. That explains the success of anti-IL-17A mab therapy in PsA. There is moderate level of synergism with IL-17A and IL-17F in respect to FLS proliferation and upregulations of FLS secreted inflammatory cytokines. This substantiates the combined role of IL-17A/F in the pathogenesis of PsA.
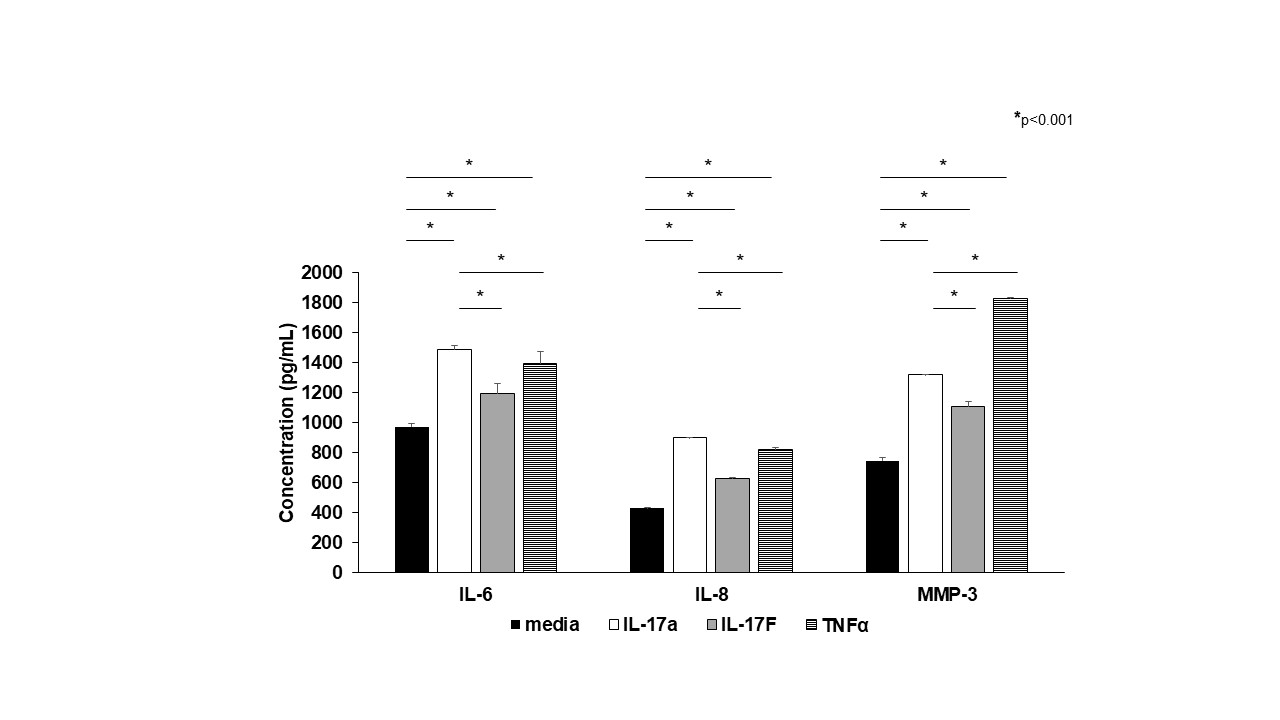 Figure 1. Comparative effect of IL-17A and IL-17F and their synergism on proliferation of synovial cells (FLS) of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). All experiments were done in triplicate.
Figure 1. Comparative effect of IL-17A and IL-17F and their synergism on proliferation of synovial cells (FLS) of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). All experiments were done in triplicate.
Fig 1 A. Effect of IL-17F on Fibroblast proliferation. Representative histograms showing proliferation of PsA FLS cells stimulated with rIL-17A, rIL-17F, and rIL-22 on left. Bar diagram on right shows significant increase of proliferation of PsA FLS with rIL-17A compared to rIL-17F or rIL-22 (p < 0.001). All experiments were done in triplicate.
Fig 1B. Synergistic effect of IL-17F with IL-17A and/or with TNF-α on PSA FLS proliferation. On left side representative histograms showing proliferation of PsA FLS cells stimulated with rIL-17F, rIL-17A and TNF-α. Bar diagram on right showing the significant synergistic effect of IL-17F with IL-17A and with TNF-α on PsA FLS proliferation (p < 0.001).
.jpg) Figure 2. Effect of rIL-17F on IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-3 Expression. Bar diagrams of the average concentration (pg/mL) of cytokines in cell culture supernatant of PsA FLS treated with rIL-17A, rIL-17F or TNF-α. Compared to rIL-17F upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 were significantly higher with rIL-17 A (p < 0.001) All experiments were done in triplicate.
Figure 2. Effect of rIL-17F on IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-3 Expression. Bar diagrams of the average concentration (pg/mL) of cytokines in cell culture supernatant of PsA FLS treated with rIL-17A, rIL-17F or TNF-α. Compared to rIL-17F upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 were significantly higher with rIL-17 A (p < 0.001) All experiments were done in triplicate.
.jpg) Figure 3. Source of IL-17A & IL-17F: Both in the synovial fluid (SF) of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and at single cell level of effector memory CD4+ T cells IL7A is the predominant cytokine compared to IL-17F.
Figure 3. Source of IL-17A & IL-17F: Both in the synovial fluid (SF) of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and at single cell level of effector memory CD4+ T cells IL7A is the predominant cytokine compared to IL-17F.
Fig 3A. Bar diagrams demonstrating average concentration (pg/mL) of IL-17A and IL-17F in synovial fluid and plasma of PsA and osteoarthritis (OA) patients. IL-17A levels were significantly higher than IL-17F (p < 0.001). All experiments were done in triplicate
Fig 3B. Expression of IL-17A is significantly higher compared to IL-17F in activated CD4+ T memory T cells in synovial fluid T cells of psoriatic arthritis patients. A representative flow plot showing expression of IL-17A and IL-17F in CD4+ memory T cells. Bar diagram showing significantly higher numbers of IL-17A+ CD4+ memory T cells compared to IL-17F (p < 0.001) in PsA and RA in synovial fluid derived T cells. All experiments were done in triplicate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Abria C, Raychaudhuri S. Regulatory Role of IL17 F in the Pannus Formation of Psoriatic Arthritis: A Comparative Study with IL-17A [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-il17-f-in-the-pannus-formation-of-psoriatic-arthritis-a-comparative-study-with-il-17a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-il17-f-in-the-pannus-formation-of-psoriatic-arthritis-a-comparative-study-with-il-17a/
