Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory autoimmune disease that can present with glandular swelling, chronic pancreatitis, sclerosing cholangitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis, amongst others. Along with a supporting clinical history, diagnosis is typically established by biopsy of affected tissue showing hallmark histopathologic findings. Many patients demonstrate elevated serum IgG4 levels and checking levels is often part of the initial workup when considering IgG4-RD. At Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, IgG4 levels can be checked by ordering IgG subclass levels or IgG4 levels. However, we have frequently observed the filarial IgG4 antibody test erroneously ordered instead, even though the patient’s symptoms are not suggestive of filariasis or other tropical infectious disease. Inadvertent ordering of filarial IgG4 consumes healthcare dollars and may lead to delay in diagnosis of potential IgG4-RD. Our goal was to quantify how prevalent this issue is over the last 5 years (March 2017-March 2022) and institute a quality improvement (QI) intervention to significantly reduce inadvertent filarial IgG4 testing.
Methods: Using SlicerDicer on EPIC, we determined the number of patients who had ≥ 1 filarial IgG4 level ordered (date range 3/22/2017-3/21/2022). Using the patient’s medical record number (MRN), we individually reviewed the charts to determine whether such testing was indicated or done inadvertently while investigating a diagnosis of IgG4-RD. We designed a pop-up reminder that appears when a provider tries to order a filarial IgG4. The pop-up contained recommendations for alternative testing for IgG Subclass 4 or IgG Subclasses instead, and officially launched on 3/22/2022. To determine the efficacy of our intervention after a 1-year observation, we determined the number of patients who had ≥ 1 filarial IgG4 ordered between the dates 3/22/2022 and 3/21/2023.
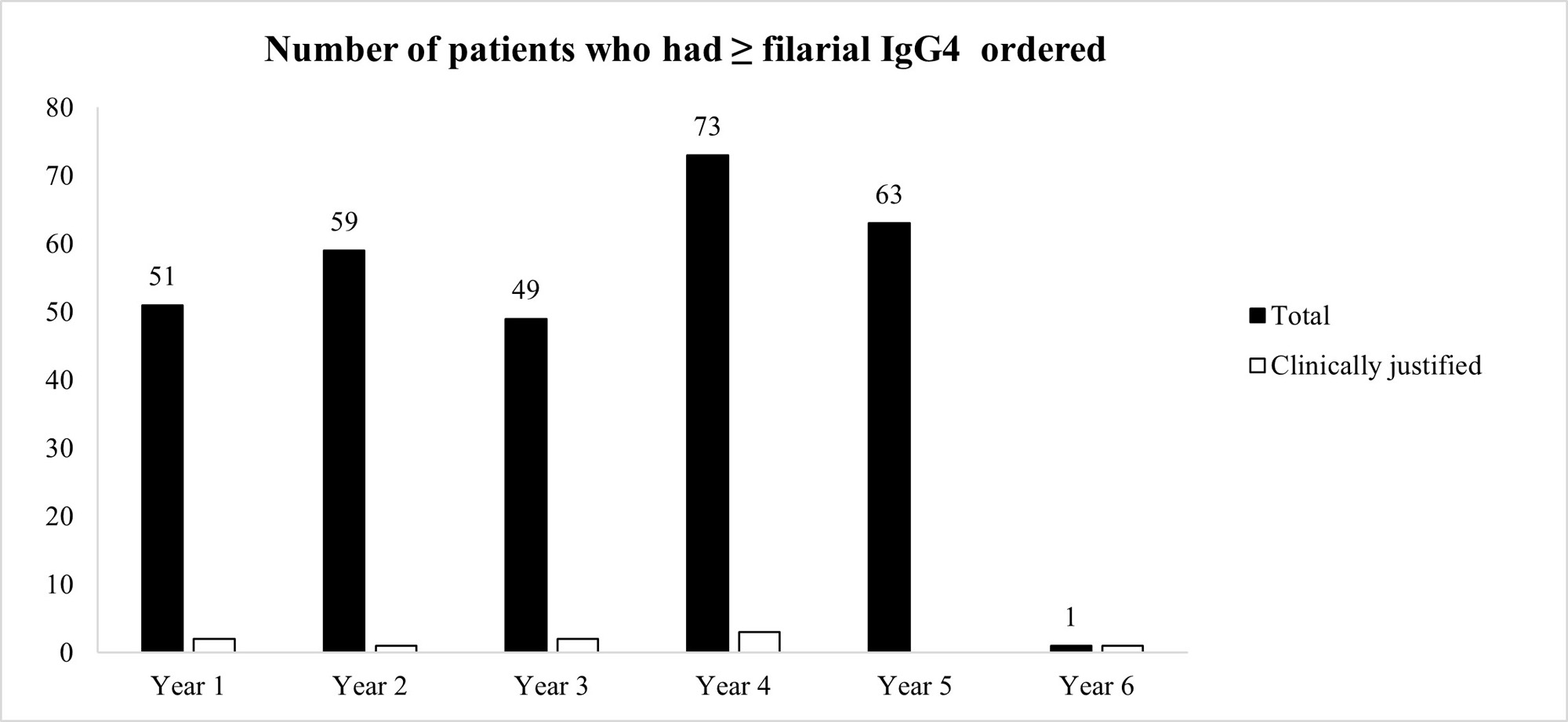
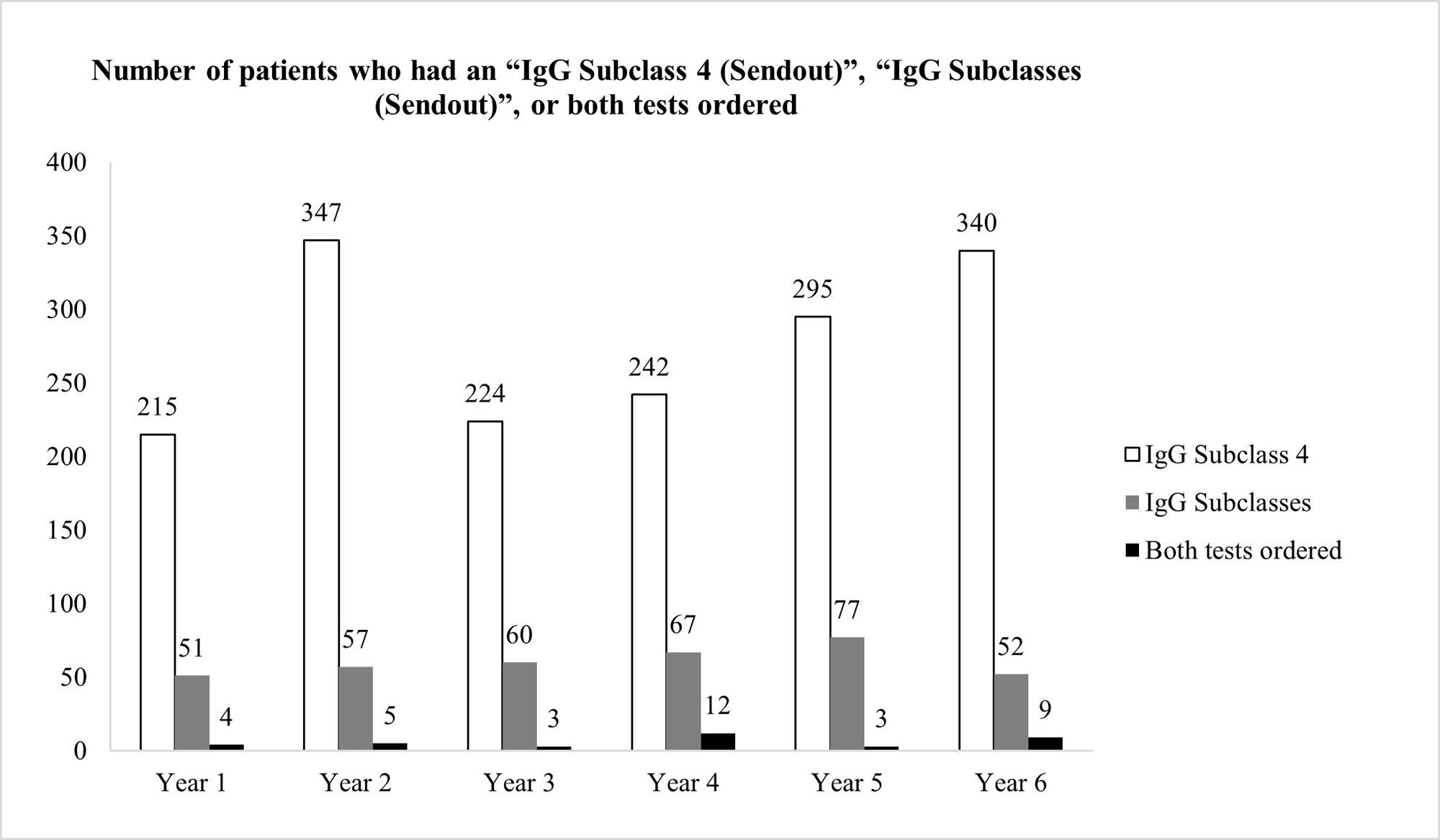
Results: 295 patients had ≥ 1 filarial IgG4 test ordered between 3/22/2017 and 3/21/2022 (average 59 patients per year). The vast majority of patients (97.3%) had unjustifiable reasons for ordering the test, after review of the patients’ charts (Figure 1) However, our pop-up intervention significantly reduced (100% reduction) inadvertent filarial IgG4 testing after a 1-year observation. Only 1 filarial IgG4 test was ordered during 3/22/2022-3/21/2023, and it was clinically indicated after chart review (Figure 1) Ordering of IgG4 Subclass 4 or IgG Subclasses was not negatively affected by the pop-up (Figure 2)
Conclusion: We instituted an effective QI intervention in the form of a pop-up reminder that effectively eliminated the inadvertent checking of filarial IgG4 when such testing was not justified.It was selective against filarial IgG4 orders, and did not create an undue burden on providers who tried to order potentially justifiable IgG4 or IgG subclass testing. Since each filarial IgG4 test costs $288.75 at Labcorp (821383), our intervention could potentially reduce health expenditures by $17,000 per year at our institution. This strategy could be applied at other medical centers if a similar problem with filarial IgG4 exists and can also be applied to other lab tests that are often checked inadvertently.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vu K, Choi J, Golenbiewski J. Reducing Inadvertent Antifilarial Antibody Testing at an Academic Medical Center: A Quality Improvement Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reducing-inadvertent-antifilarial-antibody-testing-at-an-academic-medical-center-a-quality-improvement-project/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reducing-inadvertent-antifilarial-antibody-testing-at-an-academic-medical-center-a-quality-improvement-project/