Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients receiving immunosuppressive therapies are known to have a higher risk of herpes zoster and subsequent complications compared to the general population. The recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix, hereafter referred to as “RZV”) has been shown to be both safe and efficacious among such patients. In 2021, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) updated their recommendations and approval for the administration of RZV to include all immunosuppressed adults (any age). We assessed patient characteristics associated with RZV vaccination rates among U.S. veterans.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional observational study using national Veterans Affairs (VA) data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse. The study population included all VA patients aged ≥ 18 who were prescribed at least one immunosuppressive medication (including conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs, biologics, and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs) for ≥ 90 days between 2017 and 2023. We identified patients with one or more doses of RZV documented. We examined whether demographic and clinical characteristics (age, sex, race, ethnicity, rurality of residence, medication type, rheumatology specialty care) were associated with receiving RZV using multivariate logistic regression, accounting for clustering by facility and report the predicted marginal proportions of patients vaccinated.
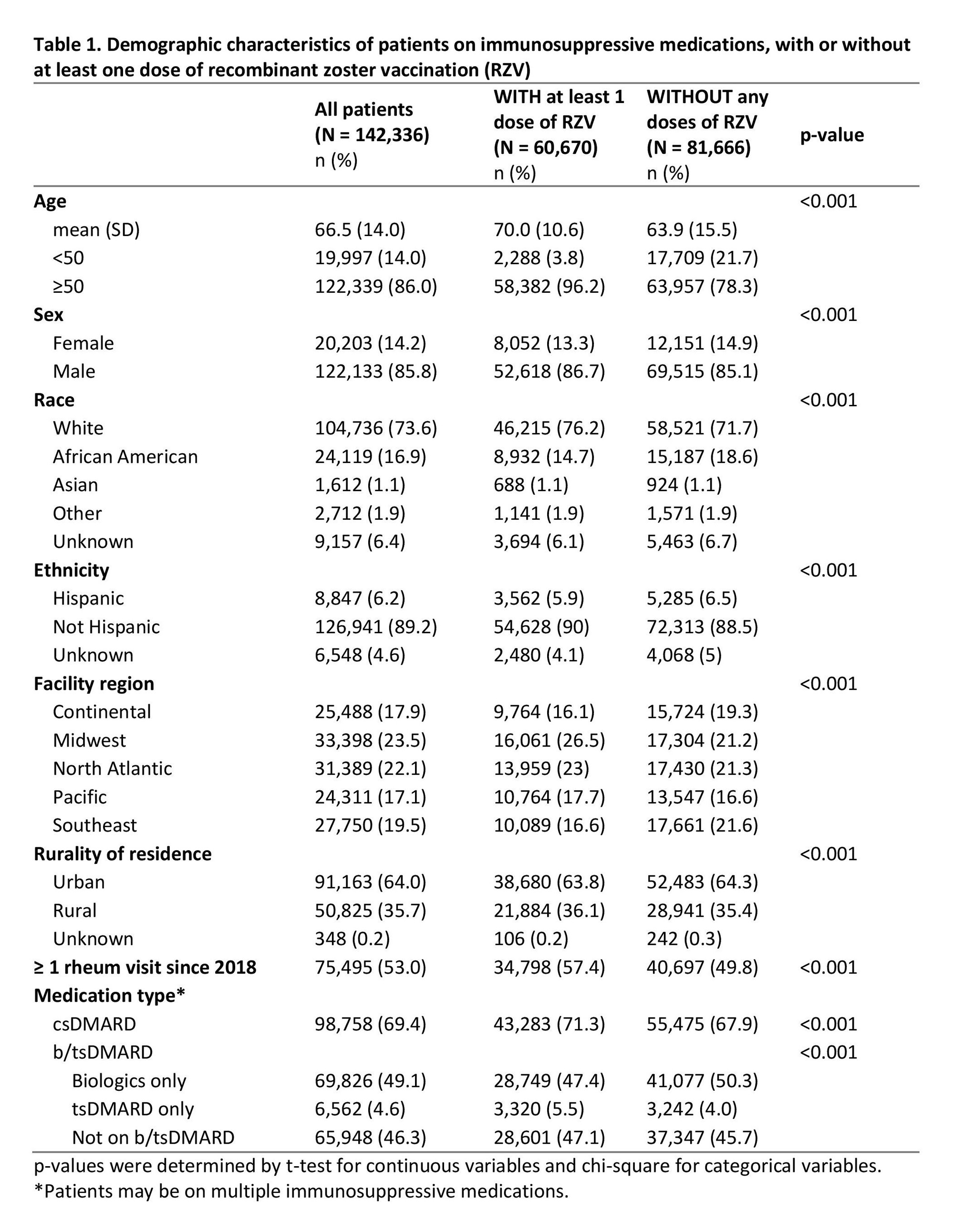
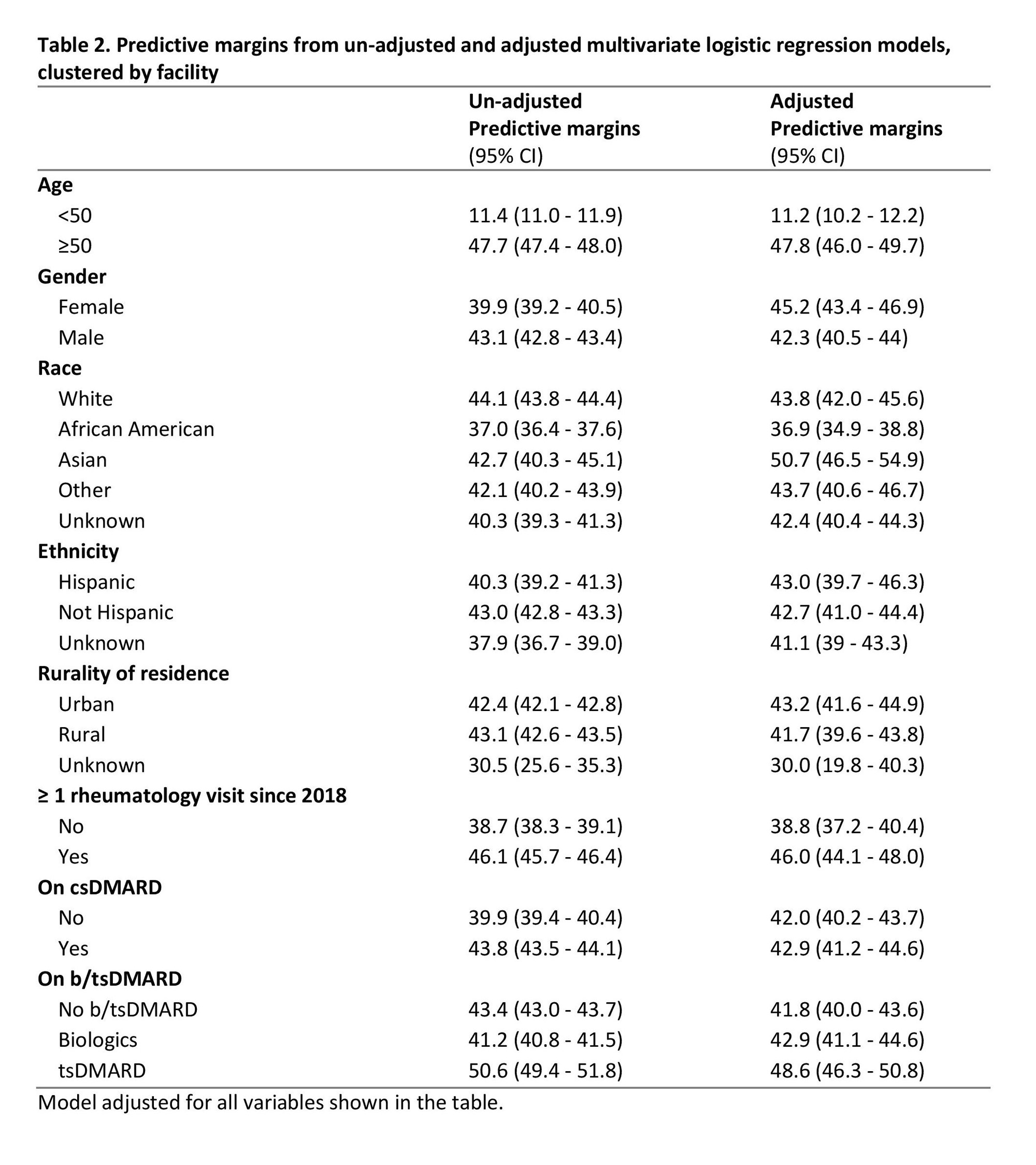
Results: We identified 142,336 veterans across 130 facilities as prevalent users of csDMARDs, biologics, or tsDMARDs between 2017 and 2023 (Table 1). Most patients were male (85.8%), white (73.6%), non-Hispanic (89.2%), and lived in urban areas (64.0%). Mean age (SD) was 66.5 (14.0) years. Of these patients, 34.8% had received at least two doses of RZV (fully immunized), 7.7% had received 1 dose of RZV, and 57.4% had not received any doses of RZV. Multivariate logistic regression revealed the largest differences in vaccination rates were for patients < 50 years vs ≥ 50 years (11.2% vs 47.8%, p < 0.05), African American vs white patients (36.9% vs 43.8%, p < 0.05), and those without a recent visit with a rheumatologist vs those with at least one rheumatology visit since 2018 (38.8% vs 46.0%, p < 0.05; Table 2). Patients receiving tsDMARDs (vs receiving neither a biologic nor tsDMARD) were more likely to receive at least 1 dose of RZV (48.6% vs 41.8%, p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Among adult U.S. veterans receiving immunosuppressive medications, less than half have received at least one dose of RZV. Patients under 50 years old were least likely to have received RZV, likely reflecting a lag in implementing updated CDC guidance for this group. Quality improvement efforts should specifically focus on younger patients and African American patients. Future work should explore the development of population-health management tools (such as clinical dashboards in electronic medical records) to support quality improvement in RZV administration rates for immunosuppressed patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abada S, Li J, Tarasovsky G, Wilson C, Yazdany J, Whooley M, Schmajuk G. Recombinant Zoster Vaccination Among U.S. Veterans Receiving Immunosuppressive Medications 2017-2023 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/recombinant-zoster-vaccination-among-u-s-veterans-receiving-immunosuppressive-medications-2017-2023/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/recombinant-zoster-vaccination-among-u-s-veterans-receiving-immunosuppressive-medications-2017-2023/