Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of autoimmune diseases, though costs and payer restrictions have limited who are treated and when these agents are used. Potentially lower cost biosimilars have been developed and FDA-approved, although only 2 TNF inhibitors have been made available to pts. Here, we describe utilization and characteristics of pts receiving IFX and its biosimilars in US community rheumatology practices.
Methods: Electronic medical records data from the American Rheumatology Network (ARN) – Trio Health Rheumatology registry was used for the study. The ARN is a physician-led and owned organization with over 200 practicing rheumatologists that supports some of the largest independent practices in the US. Pts with RA diagnosis who initiated or switched to IFX or biosimilars since December 2016 were selected for analysis. Differences between treatment groups were assessed using t-test for continuous variables and chi-square test for categorical variables. Logistic regression model was used to evaluate outcome remission/low disease activity at 6 mo accounting for demographic and treatment characteristics. Time to treatment discontinuation was assessed using Kaplan-Meier method.
Results: 3156 pts met study criteria; 1972 (62%) were on IFX (775 [39%] as monotherapy) and 1184 (38%) received biosimilars (306 [26%] as monotherapy). Of pts on biosimilars, 350 (30%) switched between different biosimilars or IFX and were removed from the analysis. The remaining 834 pts were treated with infliximab-dyyb (574 [69%]) or infliximab-abda (260 [31%]).
There were no differences by age and gender between IFX and each biosimilar group [Table 1]. Compared to pts on biosimilars, pts receiving IFX had longer follow-up, fewer prior DMARD or biologic regimens, and longer duration of treatment with IFX. Pts on biosimilars were less likely to be commercially insured and more likely to be on Medicaid compared to IFX. IFX pts were more likely to be in remission/low disease activity at treatment initiation and at 6 mo since treatment initiation compared to pts on biosimilars; there were no differences between biosimilar groups. IFX pts had smaller improvement from baseline (BSL) to 6-mo CDAI compared to pts on biosimilars.
Accounting for age, payer, regimen, steroid use, duration of therapy, number of prior regimens, and BSL disease activity status, variables significantly impacting the outcome were BSL disease activity, regimen duration, and use of steroids but not choice of a biologic [Table 2].
Median time to treatment discontinuation was not statistically different among groups [Figure 1].
Conclusion: Among RA pts treated with IFX and its biosimilars there were differences in demographic and BSL clinical characteristics. IFX was used earlier in the treatment journey than biosimilars with higher proportion of pts in remission at BSL and last observation. Time to treatment discontinuation was similar among groups. After accounting for other pt and treatment characteristics, regimen choice (use of a particular biosimilar vs IFX) was not significantly associated with treatment success at 6 mo since regimen initiation.
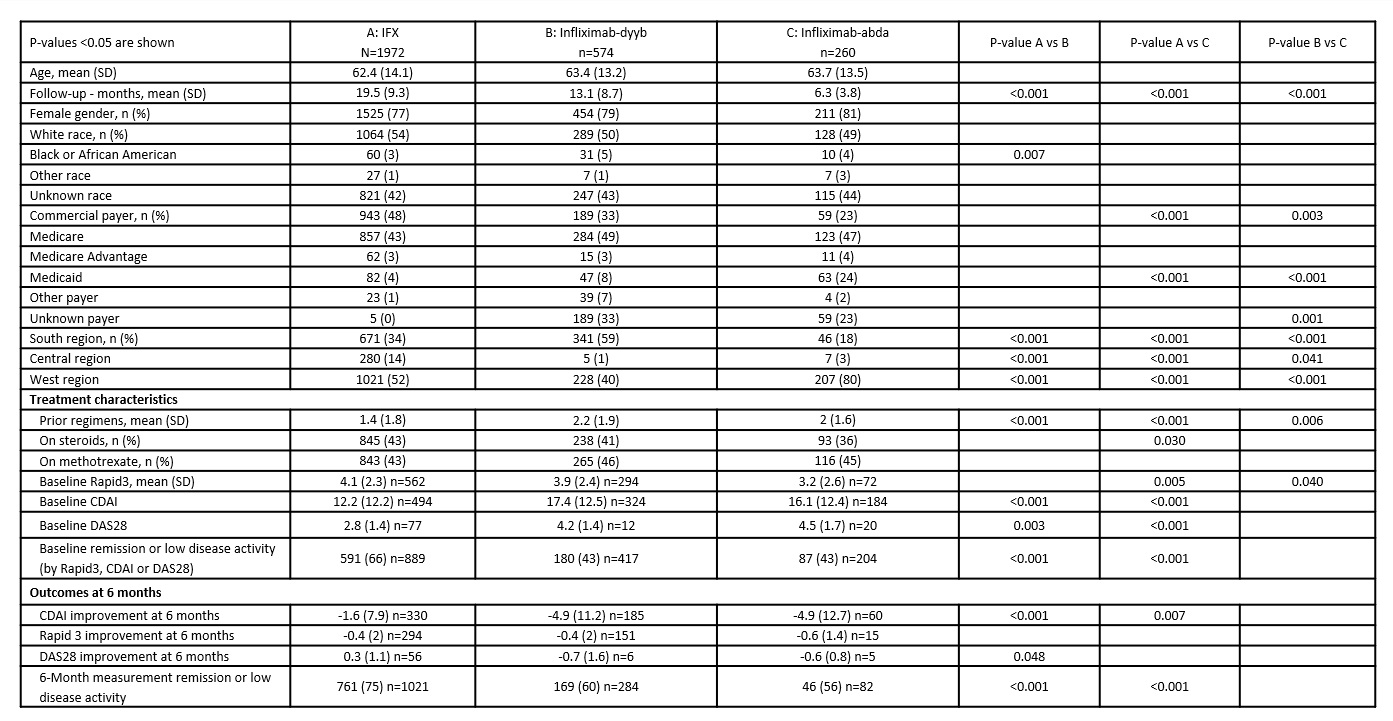 Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics
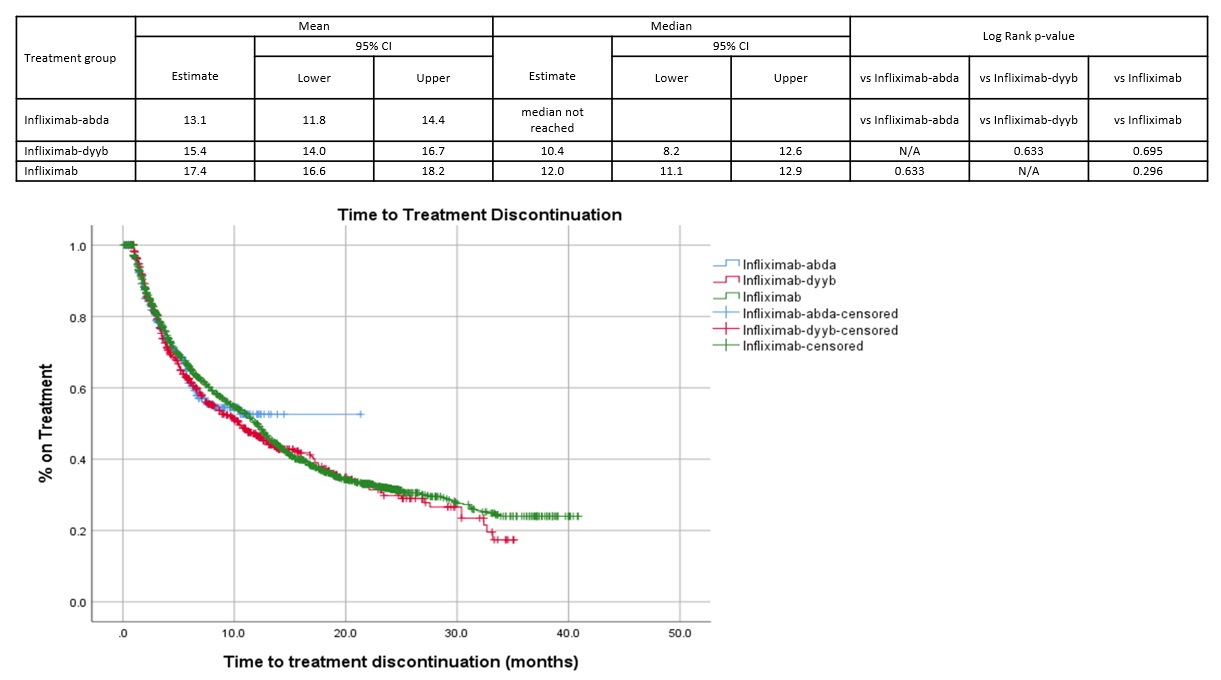 Figure 1. Time to Treatment Discontinuation (months)
Figure 1. Time to Treatment Discontinuation (months)
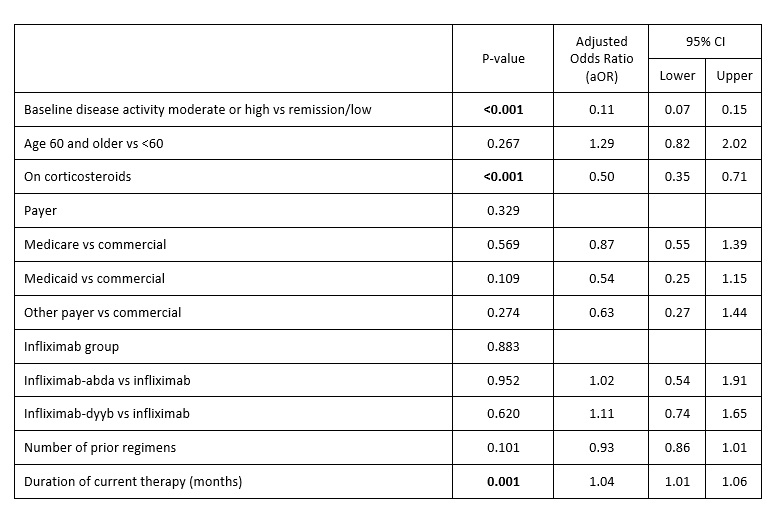 Table 2. Logistic regression results: outcome remission/low disease activity at 6 months since regimen initiation
Table 2. Logistic regression results: outcome remission/low disease activity at 6 months since regimen initiation
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Helfgott S, Radtchenko J, Soloman N, Huston K, Singh J, Edgerton C. Real-World Utilization of Infliximab (IFX) and Its Biosimilars in Patients (Pts) with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Since the First Biosimilar Approval in the US [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-utilization-of-infliximab-ifx-and-its-biosimilars-in-patients-pts-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-since-the-first-biosimilar-approval-in-the-us/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-utilization-of-infliximab-ifx-and-its-biosimilars-in-patients-pts-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-since-the-first-biosimilar-approval-in-the-us/
