Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2015–2051) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Combination therapy with two biologic agents (bDMARDs) or a biologic plus a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) is rarely used in rheumatology due to safety concerns and limited supporting evidence. However, it may be considered for selected patients with refractory disease or those with multiple immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). This case series describes the efficacy and safety of dual targeted therapy in patients with rheumatic conditions, including those requiring treatment for concurrent IMIDs or non-rheumatic comorbidities.
Methods: Patients treated in the Rheumatology Department of a district hospital who received at least two biologic agents or a combination of a bDMARD and a JAKi, dispensed by the hospital pharmacy, were retrospectively reviewed. Patients were categorized into two groups:Group A: both agents for IMIDs, (eg., spondyloarthritis [Spa] and inflammatory bowel disease [IBD]).Group B: one treatment for a rheumatic inflammatory disease and the other for a non-rheumatic condition (eg., migraine, asthma).Demographics, indications, duration of dual therapy, clinical response (Group A), acute-phase reactants, and adverse events (both groups) were collected. Clinical efficacy was assessed globally (‘yes,’ ‘partial,’ ‘no’) due to population heterogeneity.
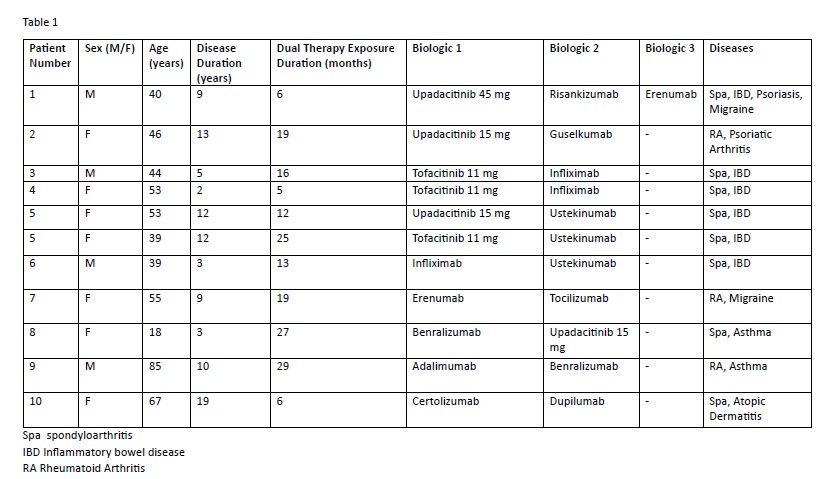
Results: 10 patients were included: 6 in Group A and 4 in Group B. One patient in Group A received two different dual therapy regimens over time (both included) and one was in both groups due to triple therapy. Among the 10 patients, 4 were male and 6 female, with a mean age of 48.6 ± 18.1 years and a mean disease duration of 8.5 ± 5.4 years. Therapy characteristics and drug combinations appear in Table 1, with the most frequent being JAK inhibitor plus an IL-23 inhibitor. Mean duration of dual therapy was 17.5 months (range: 5–29).In Group A, 5/6 patients had Spa + IBD, one had psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The average number of prior biologic treatments was 3.83 ± 1.47. Among 7 drug combinations, 2 patients showed clinical improvement, 4 partial improvement and 1 failed. One case led to treatment switch, resulting in partial benefit. The mean reduction in CRP was 7.85 ± 2.3 mg/L and in ESR 9.33 ± 15.14 mm/h. No serious adverse events were observed. Two patients experienced mild infections while on tofacitinib combinations, which resolved with dose reduction; treatment continued. In Group B, non-rheumatic comorbidities included migraine (n=2), asthma (n=2), and atopic dermatitis (n=1). The median duration of treatment was 27 months (range 6–29). Four patients were still receiving treatment at the time of data collection and one patient discontinued due to lack of efficacy for migraine. No major adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: The expanding use of biologic therapies across multiple diseases has led to combination regimens involving biologic and targeted synthetic drugs. In our series the most frequent combination was JAKi with IL-23 inhibitor. Patients needing dual therapy often had Spa and IBD, but others with IMIDs or comorbidities like asthma or migraine also benefited. Despite the clinical complexity of these cases, dual therapy has shown a favorable safety and efficacy profile.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aguilar Zamora M, Arévalo Ruales K, Garijo Bufort m, Pastor Orduña M, Aparicio Rubio C, Cornejo Uixeda S, Borrás Blasco J. Real-World Use of Dual Targeted Therapy in Rheumatic Disease: A Single-Center Case Series [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-use-of-dual-targeted-therapy-in-rheumatic-disease-a-single-center-case-series/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-use-of-dual-targeted-therapy-in-rheumatic-disease-a-single-center-case-series/