Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: An interim analysis of a prospective observational 3+ year study, embedded within the US Corrona Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) registry (14 years and ongoing), was initiated to evaluate the safety of tofacitinib (tofa) after US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval on 6 November 2012. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Rates of adverse events (AEs) are calculated and reported quarterly.
Methods: Interim results from a planned 5 year study (6 Nov 2012–29 Feb 2016, ~3 years and 3 months) are presented evaluating rates of targeted AEs in 3 populations 1) initiators of tofa 2) initiators of a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) and 3) initiators of a conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD). Patients who had at least one visit after initiation were included in this analysis. AE data are captured from prescribing physicians during follow-up. Standardized rates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using the age and gender distribution of tofa initiators as the reference population.
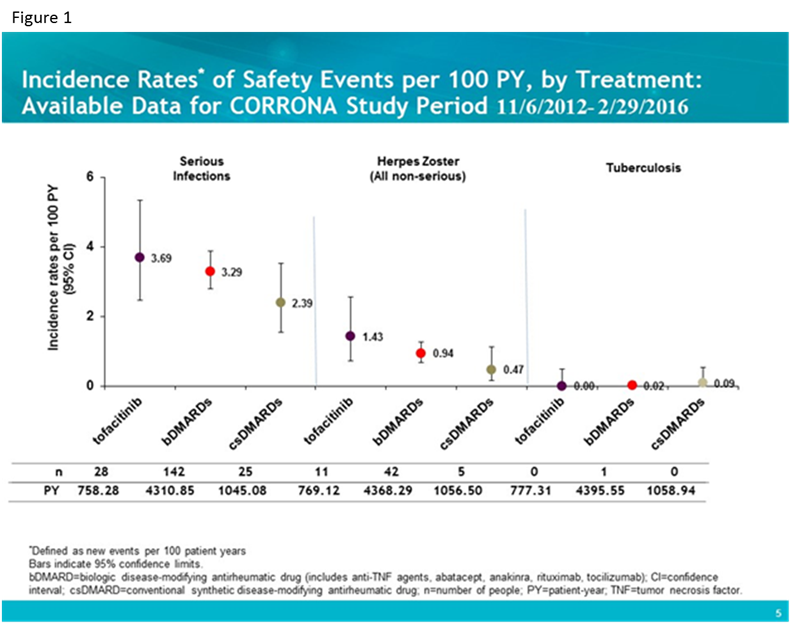
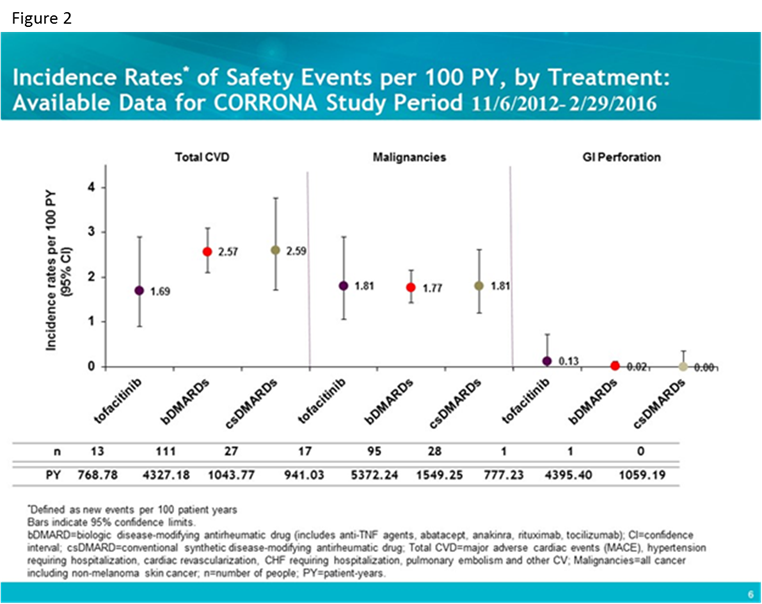
Results: Standardized incident AE rates (i.e., new events per 100 patient-years) were calculated for 760 tofa, 4,628 bDMARD and 1,328 csDMARD initiators with 777.31 person-years (PY), 4395.55 PY, and 1059.19 PY respectively. Baseline characteristics were examined; number of years disease duration was longer for tofa patients (mean [SD] 13.4 [9.99] vs. bDMARD 10.1 [9.85] and nbDMARD 4.77 [7.49]) and number of prior bDMARDs as well as number prior anti-TNFs were higher in tofa patients (mean [SD] 2.79 [1.81] and 1.79 [1.19] respectively) as compared to the bDMARD group (1.41 [1.34] and 1.09 [1.01]) and csDMARD group (0 by definition). Standardized incident rates for infections (figure 1) and cardiovascular disease (CVD), malignancies and gastrointestinal (GI) perforation (figure 2) are shown for the three groups.
Conclusion: In this interim analysis, despite some differences in baseline characteristics, patients initiating tofa, bDMARDs and csDMARDs for the treatment of RA experienced comparable age and gender adjusted rates of serious infections, cardiovascular events and malignancies overall.
References: Curtis JR et al. The validity of physician-reported hospitalized infections in an observational US arthritis registry. Rheumatology 2009:48(10); 1269-72. Fisher MC et al. Malignancy validation in a United States registry of rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders; 2012 May 31; 13:85. Solomon DH et al. Explaining the cardiovascular risk associated with rheumatoid arthritis: traditional risk factors versus markers of rheumatoid arthritis severity. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69(11): 1920-5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kavanaugh AF, Geier J, Bingham C III, Chen C, Reed GW, Saunders KC, Chen Y, Koenig A, Cappelli L, Greenberg JD, Kremer JM. Real World Results from a Post-Approval Safety Surveillance of Tofacitinib (Xeljanz): Over 3 Year Results from an Ongoing US-Based Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-results-from-a-post-approval-safety-surveillance-of-tofacitinib-xeljanz-over-3-year-results-from-an-ongoing-us-based-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-results-from-a-post-approval-safety-surveillance-of-tofacitinib-xeljanz-over-3-year-results-from-an-ongoing-us-based-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/