Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: : In the context of an expanding therapeutic landscape and absence of head-to-head trials in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), data on direct comparison of effectiveness between the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (TOFA) and other advanced therapies (AT), i.e., inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor (TNFi) and interleukin-17 (IL-17i) in patients (pts) with axSpA is lacking. To compare real-world effectiveness of TOFA, TNFi, and IL-17i using an adapted version of a claims-based treatment (tx) effectiveness algorithm applied to the Komodo Healthcare Map®, a large US administrative claims database.
Methods: Adults with axSpA who initiated ≥1 selected AT on/after Dec 14 2021 (tofacitinib FDA approval date for ankylosing spondylitis) were selected and required to have continuous healthcare enrollment for >12 months before and >6 months after the index date (date of AT initiation). Pts could contribute multiple tx episodes of the analysis (i.e. multiple index dates) if they switched to a different AT over the study period. Pts with >1 AT administered/prescribed on the index date were excluded. Pts were classified into cohorts based on the AT initiated on each index date: (1) TOFA (2) TNFi (adalimumab, golimumab, infliximab, etanercept, certolizumab) and (3) IL-17i (ixekizumab, secukinumab). Propensity score weighting (PSW) was used to adjust for baseline confounders. The proportion of pts fulfilling all effectiveness criteria over the 6-month study period was reported. Lack of effectiveness (i.e. not meeting all 8 effectiveness criteria) was compared between TOFA vs TNFi and TOFA vs IL-17i cohorts using Cox Proportional Hazards model with robust variance estimator to account for within patient correlation (multiple tx episodes). Results were reported as weighted hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals.
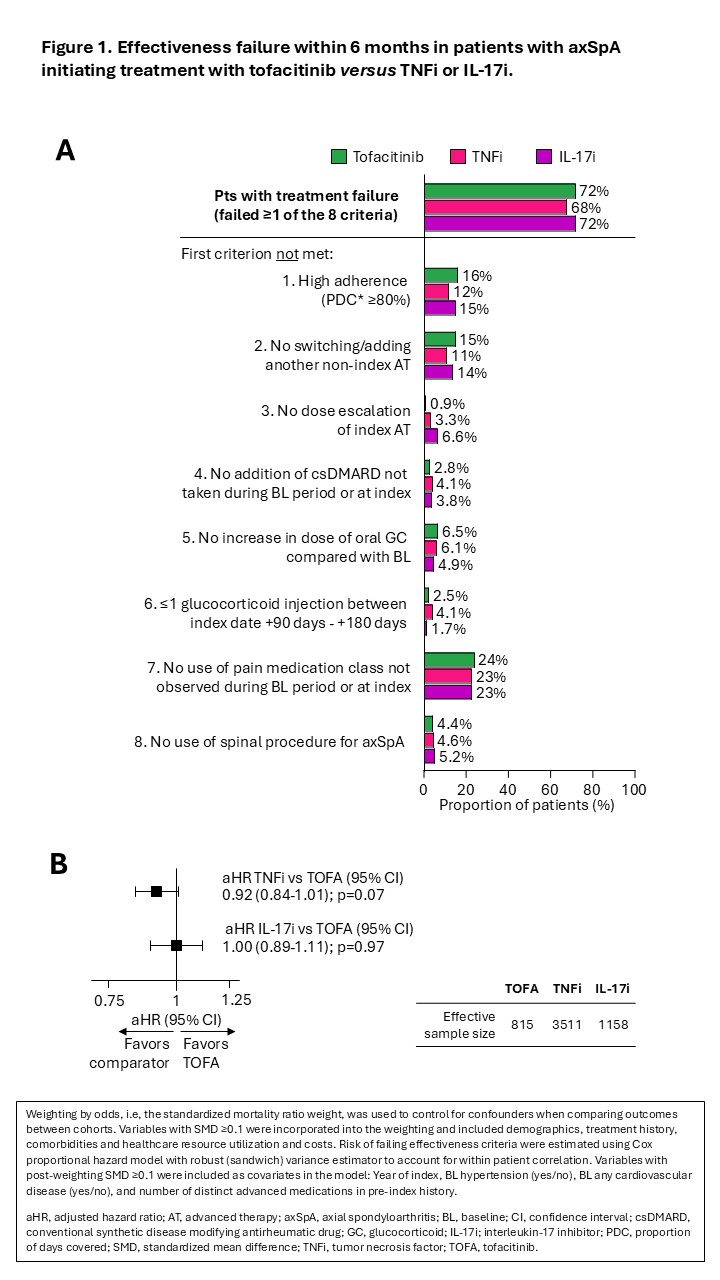
Results: A total of 829 TOFA, 14,056 TNF and 4,472 IL-17i pts were included. Mean age at index ranged from 47 to 48 years; proportion of female range from 65% to 69%. In the pre-index period, 60% of TOFA pts had used >2 prior ATs, vs. 14% for the TNFi and 40% for the IL-17i cohort. Prior to PS weighting, use of steroid, opioid, non-opioid pain medications and csDMARDs at baseline was higher in the TOFA vs the TNFi and IL-17i cohorts. After PS weighting, 28%, 32%, and 28% of pts in the TOFA, TNFi, and IL-17i cohorts met all effectiveness criteria. No difference in risk of effectiveness failure was found between cohorts: TNFi vs TOFA: HR=0.92 (0.84-1.01); IL-17i vs TOFA: HR=1.00 (0.89-1.11). Most common events associated with effectiveness failure were: use of a new pain medication class, low adherence to index tx, and switching/adding another non-index AT for axSpA.
Conclusion: In this study using real-world data, pts with axSpA who initiated TOFA, TNFi, or IL-17i had similar effectiveness within the first 6 months of tx initiation. Overall response rate to TOFA in this real-world cohort, assessed using a claims-based effectiveness algorithm, was comparable ASDAS major improvement rates and numerically lower than ASAS40 response rates observed in published tofacitinib AS clinical trials. Longer term follow-up will allow confirmation of the robustness of these conclusions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Gauthier G, Fallon L, Gruben D, Ling Y, Brouillette M, Yndestad A, hong Y, Kelkar M. Real-world comparative effectiveness of tofacitinib, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, and interleukin-17 inhibitors among patients with axial spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-and-interleukin-17-inhibitors-among-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-and-interleukin-17-inhibitors-among-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/