Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the real-world, long-term effectiveness of rituximab (RTX) as rescue therapy in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome-associated interstitial lung disease (pSS-ILD).
Methods: Multicentre observational retrospective longitudinal study of a cohort of pSS-ILD patients who initiated RTX due to progressive or refractory ILD despite treatment with glucocorticoids and conventional immunosuppressants.
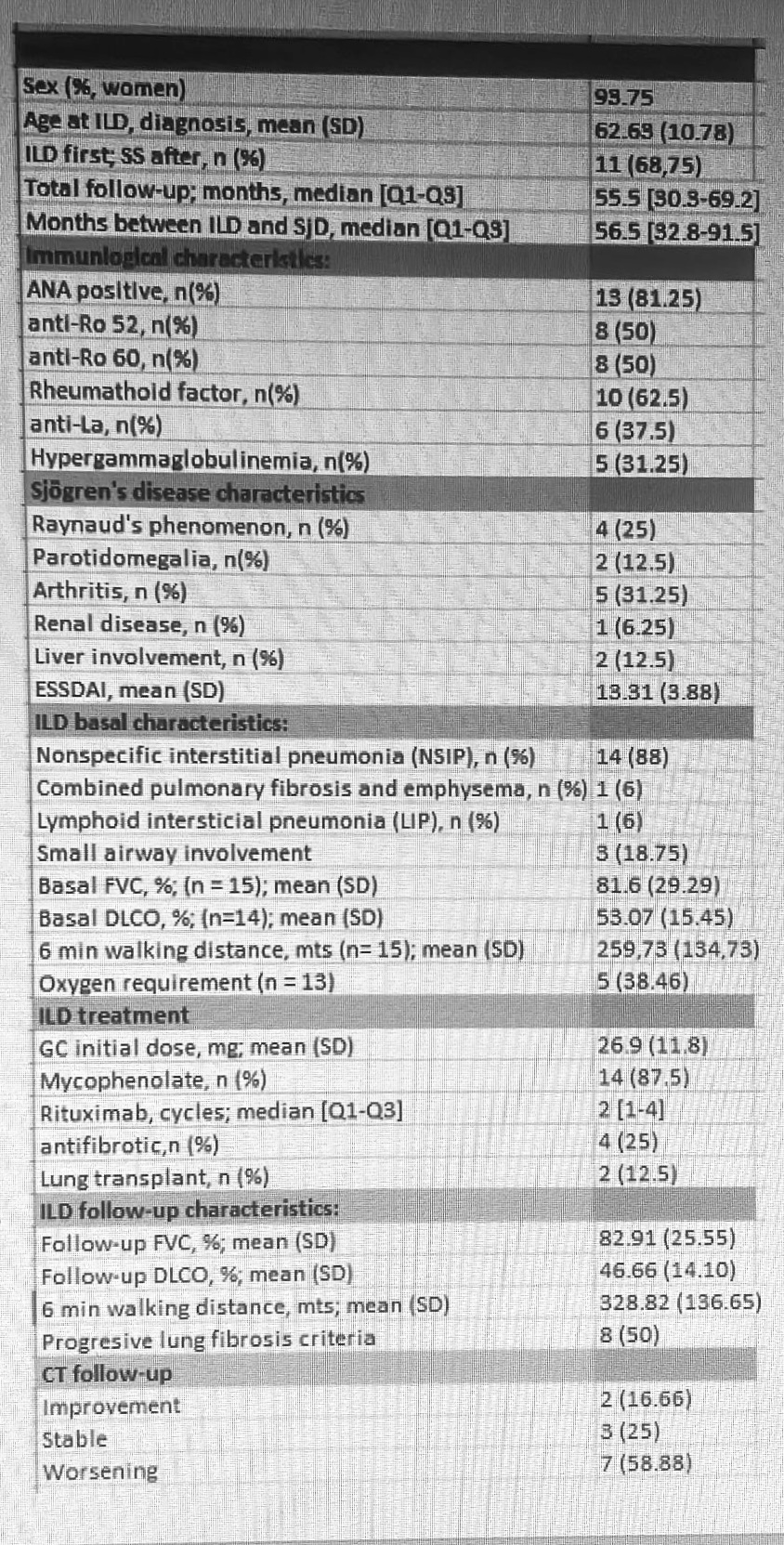
Results: To date, 16 patients have been treated with RTX. The main demographic, clinical, functional, serological, and therapeutic characteristics of the entire cohort are summarised in Table 1.The most frequent ILD pattern on high resolution CT-scan was Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) (88%), while lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) and combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema were each observed in one patient (6%). The median follow-up from ILD diagnosis to the last visit was 55.2 months (IQR: 30.3–69.2).RTX was administered in combination with mycophenolate mofetil (31%), azathioprine (19%), or tacrolimus (13%), while one patient (6%) received RTX as monotherapy. Four patients (25%) were treated concurrently with antifibrotic agents (nintedanib, n=3; pirfenidone, n=1).At last follow-up, 7 patients (44%) remained on RTX. Treatment was discontinued in 9 patients (56%) due to lack of efficacy (n=3; 19%), death (n=3; 19%), lung transplantation (n=2; 13%), or adverse events (n=1; 6%).Among patients who continued RTX, mean declines in %FVC and %DLCO from ILD diagnosis to RTX initiation were –11.7% and –11.4%, respectively, followed by mean improvements of +7.8% (FVC) and +6.3% (DLCO) from RTX initiation to the last available follow-up. However, these improvements did not reach statistical significance (p=0.31 for FVC; p=0.34 for DLCO). Adverse events were reported in 5 patients (31%), mostly consisting of non-severe infections.
Conclusion: RTX achieved stabilisation or improvement in only 44% of patients, indicating limited overall effectiveness and underscoring the need for more effective therapeutic strategies in progressive pSS-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Estrada-Alarcón P, Reina D, ALEGRE SANCHO J, Roig Kim M, Aguilar-Coll m, De Daniel Bisbe L, Fabregat A, Cubells M, Narváez J. Real-world clinical effectiveness of rituximab rescue therapy in patients with progressive interstitial lung disease associated with primary sjögren’s syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-clinical-effectiveness-of-rituximab-rescue-therapy-in-patients-with-progressive-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-clinical-effectiveness-of-rituximab-rescue-therapy-in-patients-with-progressive-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/