Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The GO PRACTICE study was initiated following a demand by the French Health Authorities for long-term data on the real-life use of golimumab (GLM) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The primary objective was to assess the persistence of GLM over 2 years after initiation. Secondary objectives included evaluations of 1) clinical disease activity from baseline to 2 years, 2) changes in patient-reported disease activity, functional ability and quality of life (QoL), and 3) GLM clinical safety.
Methods: Observational, prospective, multicenter French study. Patients ≥18 years with RA, PsA and axSpA were included consecutively following GLM initiation, and followed-up for 2 years. Data were collected at baseline, year 1 and year 2. GLM persistence was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. Clinical disease activity was measured using the Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) for RA and PsA, and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) for axSpA. Patient-reported disease activity was measured with the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) for RA and PsA, and the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) for axSpA. Functional ability was assessed with the Health Assessement Questionnaire (HAQ) and QoL was assessed with the EQ-5D and SF-12 surveys.
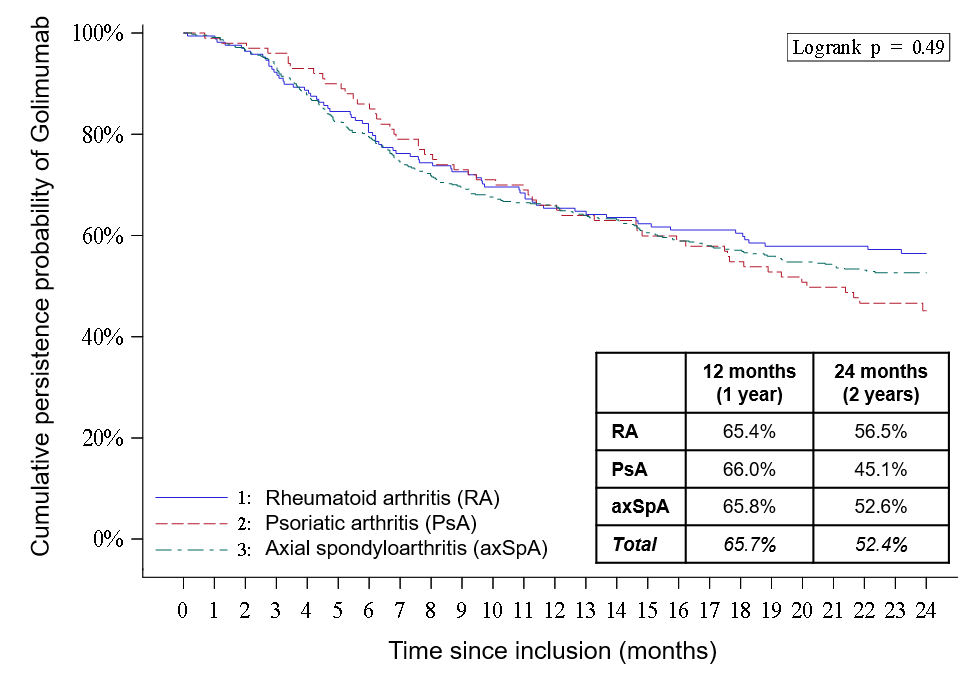
Results: From January 2015 to March 2016, 770 patients were selected at 134 sites, of which 754 were included in the analysis. Mean age was 46 years and 61% were female. Most had axSpA (63%), then RA (23%) and PsA (14%). Mean duration of rheumatic disease was 7.6 years; 37% had previously received biologics; the proportion of patients who received 1, 2, 3 and ≥4 biologics were 18%, 11%, 6% and 2%, respectively. Most patients were prescribed 50 mg GLM monthly (97%). Concomitant treatments included DMARDs (38%), corticosteroids (19%) and NSAIDs/analgesics (71%). GLM persistence at 2 years was 52.4% (56.5%, 45.1% and 52.6% in RA, PsA and axSpA, respectively). Disease activity showed clinically significant improvements from baseline to 2 years in patients persisting on GLM: for RA, mean DAS28-CRP from 4.3±1.1 to 2.3±0.8 (p < .0001), mean RAPID3 from 4.5±1.8 to 1.8±1.7 (p < .0001); for PsA, mean DAS28-CRP from 3.9±1.0 to 2.0±0.8 (p < .0001), mean RAPID3 from 5.3±1.4 to 2.8±2.2 (p < .0001); for axSpA, mean ASDAS-CRP from 3.2±0.8 to 1.7±1.0 (p < .0001), mean BASDAI from 5.5±1.6 to 2.8±1.9, (p < .0001). HAQ, EQ-5D and SF-12 scores also improved significantly over 2 years. GLM was discontinued by 67 (8.9%) patients due to intolerance or adverse event (AE); reported AEs were consistent with GLM’s known safety profile. Post-hoc multivariate analyses with patients’ sociodemographic and medical history variables showed that for GLM discontinuation over the 2 years, gastrointestinal disease was a risk factor in RA [HR 3.9, CI95% (2.0-7.6)] and being female was a risk factor in axSpA [HR 1.9, CI95% (1.4-2.6)]. GLM was re-prescribed to 338 (93.4%) of 362 patients who persisted on GLM at 2 years.
Conclusion: Real-life GLM persistence is satisfactory at 2 years and is accompanied by clinical improvements in RA, PsA and axSpA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flipo R, Tubach F, Ouaniche J, Goupille P, Lespessailles E, Gouyette N, Harid N, Sequiera S, Bertin P, Fautrel B. Real-Life Golimumab Persistence in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease: Results of the GO PRACTICE Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-life-golimumab-persistence-in-patients-with-chronic-inflammatory-rheumatic-disease-results-of-the-go-practice-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-life-golimumab-persistence-in-patients-with-chronic-inflammatory-rheumatic-disease-results-of-the-go-practice-study/