Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The Hospital Anxiety
and Depression Scale (HADs) is a generic measure of psychological status
comprising anxiety and depression subscales. The aim of this study was to assess the psychometric
properties of HADs in psoriatic arthritis (PsA), to calibrate the scale, and to
provide interval-level scale for use in parametric analyses when required.
Methods:
We
used HADS data from patients with PsA recruited in PRESTA trial. [1] The data
was subjected to Rasch analysis to determine fit to
the Rasch model (implying construct validity and unidimensionality), reliability and targeting in subjects with
PsA.
Results:
The number
of evaluable subjects was 740 at baseline, 701 at week 12, and 653 at week 24. Both
the anxiety subscale and the depression subscale satisfied the expectation of
the Rasch model (table 1). The overall scale was
shown to fit the Rasch model (item-by-severity interaction
Chi-Square = 15.878, p = 0.601) and had excellent reliability (person
separation index = 0.888). Validity and reliability of HADS were confirmed at baseline
and both follow-up visits.
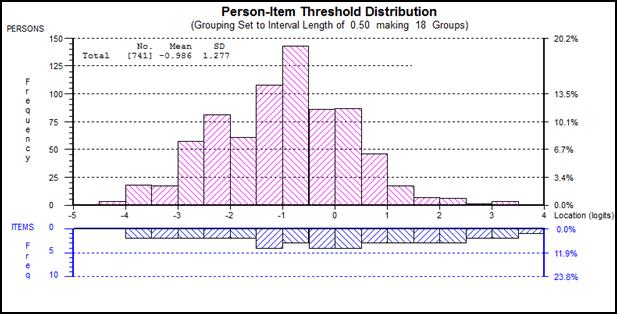
Figure 1 presents person location relative to all items (logarithmically
transformed scores) along the same scale (logits). The top plot
representing ‘persons severity’; those with higher scores (impaired
psychological status) on the right of the scale and those with lower scores
(better psychological status) on the left. The bottom plot presents relative
‘difficulty’ of the items. HADS appears to be well targeted across all ‘severity’
levels, providing for calibration of the scale by transforming raw scores into
interval-level (Rasch-transformed) scores.
Conclusion:
The
validity and reliability of the HADS are confirmed in PsA and continues to be a
useful psychological status instrument to use in PsA clinical studies. Raw
scores can be Rasch-transformed into interval scores
for use alongside other outcomes in parametric analyses.
Table
1. Fit Statistics for the Anxiety
and Depression Subscales
in PsA (Baseline).
|
Subscale |
Location |
SE |
Item Fit Residuals |
Chi-Square |
DF |
p-value |
|
Anxiety |
-0.120 |
0.021 |
-0.074 |
6.494 |
9 |
0.690 |
|
Depression |
0.120 |
0.022 |
0.356 |
9.384 |
9 |
0.403 |
SE, Standard error; DF, Degrees of
freedom, Non-significant p-value for Chi-Square suggests fit to Rasch model
Figure
1. Person-item Threshold Distribution Showing
Targeting of the HADS (Baseline Data)
References:
1. Sterry W, et al. Comparison
of two etanercept regimens for treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis:
PRESTA randomised double blind multicentre trial. BMJ 2010;340(c147)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ndosi M, Hsu MA, Cappelleri J, Jones H, Chhabra A, Helliwell PS. Rasch Analysis of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale in Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from the Presta Study. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rasch-analysis-of-the-hospital-anxiety-and-depression-scale-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-presta-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rasch-analysis-of-the-hospital-anxiety-and-depression-scale-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-presta-study/