Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: We previously reported that markers of complement activation, specifically elevated C4d levels and positive modified HAM (mHAM) test, are associated with a higher risk of new thrombosis in our multi-center cohort of antiphospholipid antibody (aPL)-positive patients (Arthritis Rheumatol 2023; 75 [suppl 9]). This follow-up study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of rare germline variants in complement regulatory genes in these aPL-positive patients with or without new (first or recurrent) thrombosis, given that another cohort analysis previously demonstrated high rates of rare germline variants in catastrophic APS patients (60%), compared with APS patients (22%) or normal controls (24%) (Chatuverdi et al Blood. 2020;135:239).
Methods: APS ACTION registry inclusion criteria are positive aPL based on the Revised Sapporo APS Classification Criteria, tested at least twice within one year prior to enrollment. Patients are prospectively followed every 12±3m with clinical data and blood collection. Among North American APS ACTION centers, we identified patients with new thrombosis during follow-up, and controls without new thrombosis, matched (1:1) for gender, age (±5 years), history of thrombosis, and associated systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease. Complement split product assessments and functional analysis of complement activation based on mHam assay were previously described. As a follow-up, we performed a genetic analysis of complement regulatory genes by next generation sequencing, using a custom panel of genes (ADAMTS13, VWF, CFH, CFB, CFI, CFD, CFP, CFHR1, CFHR2, CFHR3, CFHR4, CFHR5, C3, C5, MCP, THBD, CR1, and DGKE), based on baseline registry samples.
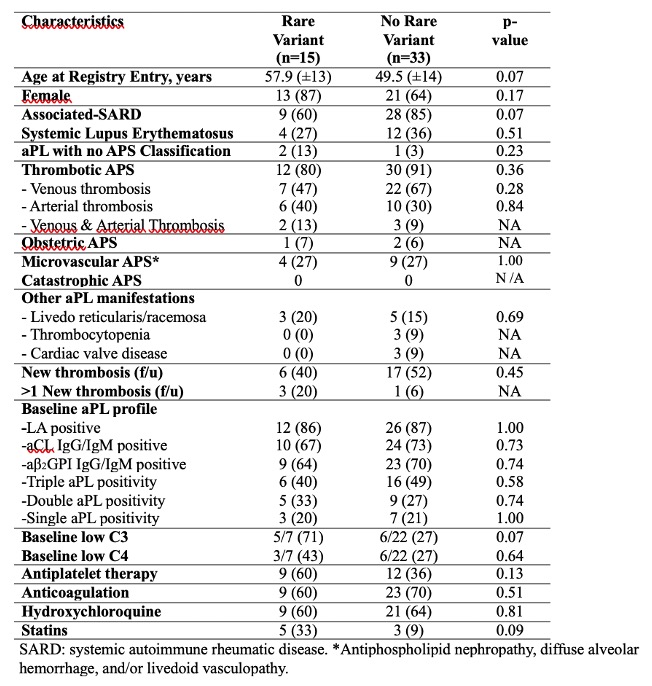
Results: As of May 2022, 365 aPL-positive patients from North American APS ACTION centers were included in the registry; 27 (7%) patients had a new thrombosis during the prospective follow-up, and were matched with 25 patients without new thrombosis. Among 52 patients, 48 had available samples for genetic analysis; at least one rare germline variant in complement regulatory genes was identified in 15 (31%) patients (2/15 had two different variants). These variants were located on ADAMTS13 gene (n:5), CR1 (n:3), C5 (n:2), CFP (n:2), CFHR4 or 5 (n:2), CFI (n:1), DGKE (n:1), and THBD (n:1). When we compared aPL-positive patients with (n:15) or without (n:33) germline variants, we found no difference among baseline characteristics (Table), the frequency of new thrombosis during the follow-up [6 (40%) vs 17 (52%), p:0.45], complement split products plasma levels (C4d, Bb, sC5b-9), and the number of patients with positive mHAM (3 [20%] vs 5 [15%], p:0.69].
Conclusion: Although one-third of our persistently aPL-positive patients have rare germline variants in complement regulatory genes, we did not observe any association with APS manifestations or other markers of complement activation. Future analysis of the entire cohort, including evaluating the functional significance of these variants, may help further understand the interaction between autoantibodies, genes, and the environmental triggers in APS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yelnik C, chaturvedi s, Labreuche J, Pan X, Belmont H, Kello N, Fortin P, Branch D, Zuo Y, Willis R, Brodsky R, Salmon J, Bertolaccini M, Cohen H, Petri M, Erkan D. Rare Germline Variants in Complement Regulatory Genes in Antiphospholipid Antibody Positive Patients: Prospective Results from AntiPhospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Networking (APS ACTION) Clinical Database and Repository (“Registry”) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rare-germline-variants-in-complement-regulatory-genes-in-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-prospective-results-from-antiphospholipid-syndrome-alliance-for-clinical-trials-and-international/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rare-germline-variants-in-complement-regulatory-genes-in-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-prospective-results-from-antiphospholipid-syndrome-alliance-for-clinical-trials-and-international/