Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rapid onset of clinical improvement is an important attribute of treatment success for patients with PsA. These analyses evaluate the speed of onset of clinical improvement in patients with active PsA treated with the IL-17A selective monoclonal antibody ixekizumab (IXE) compared with placebo (PBO) and include populations naïve to biologic treatment or with a previous inadequate response to TNF inhibitors.
Methods: Data were integrated from two Phase III, multicenter, double-blind, PBO- controlled trials. Patients with active PsA either naïve to biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (SPIRIT-P1) or with prior lack of efficacy or intolerance to TNF-inhibitor(s) (SPIRIT-P2) were randomized to placebo (PBO, N=224), 80 mg IXE every 4 weeks (IXE Q4W, N=229) or every 2 weeks (IXE Q2W, N=226), after a 160 mg starting dose. Continuous data were analyzed using mixed-effects model for repeated measures; categorical data, using a logistic regression model with missing values imputed by nonresponder imputation.
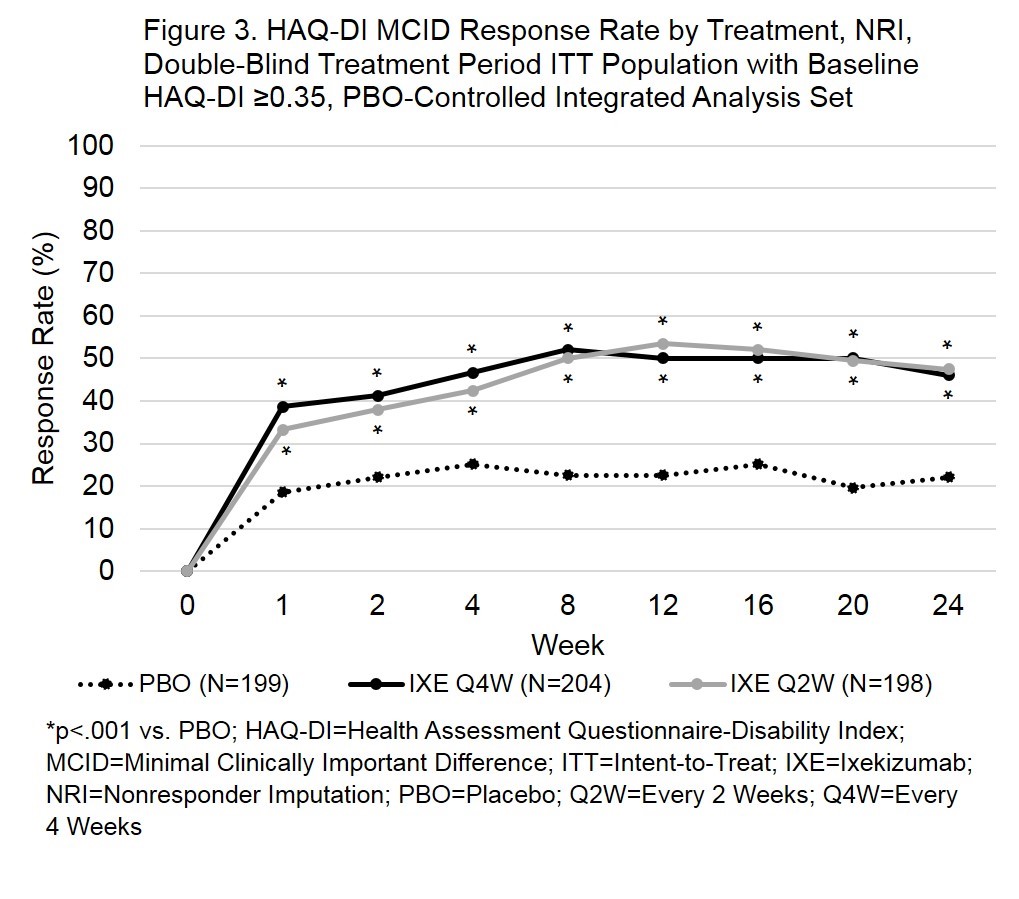
Results: ACR20 response rates were significantly greater for both IXE doses (p<.001) at week 1 (Fig 1). ACR50 response rates were significantly greater by week 2 for IXEQ4W (p=.013) and week 1 for IXEQ2W (p=.030). ACR70 response rates were significantly greater by week 4 (IXE Q4W, p=.039) or week 2 (IXE Q2W, p=.002). With the exception of the IXEQ2W ACR70 response rate at week 4 (p=.176), response rates for ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 remained statistically significant compared to PBO through the 24-week, double-blind study period. In patients with plaque psoriasis (≥3% body surface area) at baseline, both IXE dosing regimens achieved significant improvements in psoriasis area and severity index total score compared to PBO by week 1 (Fig 2). Patients with HAQ-DI ≥ 0.35 at baseline demonstrated significantly improved physical function by week 1, as measured by HAQ-DI minimal clinically important difference (≥0.35) response rates (p<.001) for both doses of IXE (Fig 3).
Conclusion: Patients achieved significantly greater improvements in PsA, skin conditions, and physical function with both IXE dose regimens compared to PBO. Statistically significant improvements in multiple clinical measures occurred as early as week 1 and remained statistically significant through 24-weeks.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar AA, Papp KA, Shuler C, Park SY, Kvien TK. Rapid Onset of Efficacy in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Ixekizumab: A Pooled Analysis of Data from Two Phase III Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-onset-of-efficacy-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-a-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-two-phase-iii-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-onset-of-efficacy-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-a-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-two-phase-iii-clinical-trials/