Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Macrophages are pivotal to rheumatoid pathogenesis and their inflammatory products drive many of the signs and symptoms of disease. Mavrilimumab inhibits macrophage activation and survival via blockade of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-α (GM-CSFRα) and has previously shown a rapid (2 week) and sustained clinical benefit in patients with RA. We present data from the EARTH EXPLORER 1 study examining speed of clinical response to mavrilimumab, and effect on the multi-biomarker disease activity (MBDA) score after week 1 (1 dose).
Methods
This was a Phase 2b, 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study (NCT01706926). Patients with adult-onset RA (18–80 years; DAS28-CRP >3.2; ≥4 swollen joints; inadequate response to ≥1 DMARD) received mavrilimumab (30, 100, or 150 mg) or PBO, administered subcutaneously every 2 weeks + methotrexate (7.5–25.0 mg/week). Efficacy assessments included DAS28-CRP, ACR responses, CRP, ESR, swollen joint count (SJC), tender joint count (TJC) and pain. MBDA score was calculated using the validated Vectra®DA algorithm, based on serum concentration of 12 biomarkers, to track the effect of mavrilimumab on disease over time. Additional assessments were conducted on MBDA biomarker components.
Results
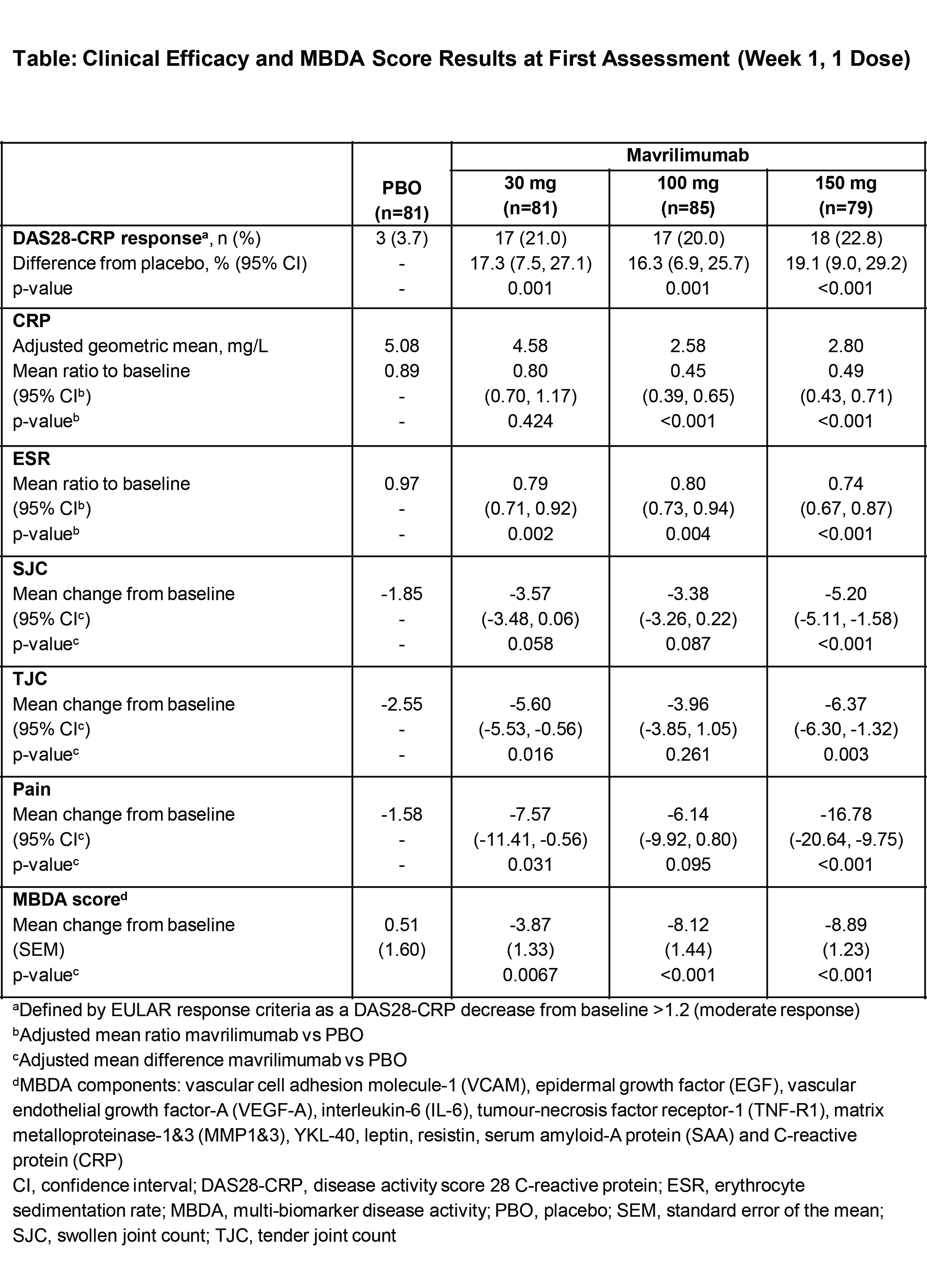
Overall, 326 patients with mean (SD) DAS28-CRP 5.8 (0.9) were randomized to mavrilimumab (30, 100, or 150 mg) or PBO (n=81, 85, 79, and 81, respectively). At week 1 (first assessment), all mavrilimumab doses showed significant reductions from baseline in DAS28-CRP (p<0.001 vs PBO; Figure A), with treatment benefit increasing to week 12. Significant improvements for 150 mg vs PBO were seen at week 1 for CRP, ESR, SJC, TJC, and pain (Table). Effects of mavrilimumab 150 mg were near maximal vs PBO for CRP, ESR, and pain at week 1, and sustained (week 24). SJC and TJC for 150 mg improved from baseline (week 1) and continued to improve (week 12); this was sustained until week 24. Rapid onset of clinical benefit was paralleled with reduction in MBDA score; 100 and 150 mg showed early (week 1) and sustained (week 24) significant changes in MBDA score vs PBO (p<0.01; Figure B), with greater decreases in DAS28-CRP responders vs non-responders (week 12). Approximately ≥50% decreases in serum IL-6, CRP, and serum amyloid-A protein levels were observed at week 1 and maintained during treatment.
Conclusion
By targeting activated macrophages via inhibition of GM-CSFRα, mavrilimumab substantially reduced patients’ RA disease activity from first (week 1; 1 dose) to final assessment, evaluated by multiple clinical endpoints and biomarkers.
Disclosure:
I. B. McInnes,
MedImmune,
5,
MedImmune, AstraZeneca,
5;
G. Burmester,
Medimmune,
5;
J. M. Kremer,
Corrona,
1,
AbbVie, Amgen, Genentech, Lilly, Pfizer,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Genentech, Lilly, Pfizer, BMS,
5,
Corrona,
3;
P. Miranda,
Medimmune,
2;
M. Korkosz,
None;
J. Vencovsky,
None;
A. Rubbert-Roth,
None;
E. Mysler,
Medimmune,
2;
D. Close,
Medimmune,
3;
M. A. Sleeman,
AstraZeneca,
1,
Medimmune,
3;
A. Godwood,
AstraZeneca,
1,
Medimmune,
3;
S. Sandbach,
Medimmune,
3;
P. C. Ryan,
Medimmune/AstraZeneca,
1,
Medimmune,
3;
D. Sinibaldi,
Medimmune,
1,
Medimmune,
3;
W. White,
Medimmune,
3;
N. A. Defranoux,
Crescendo Bioscience,
1,
Crescendo Bioscience,
3;
M. Weinblatt,
BMS, UCB, Crescendo Bioscience,
2,
Medimmune, AstraZeneca, Amgen, AbbVie, BMS, UCB, Crescendo Bioscience, Lilley, Pfizer, Roche,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rapid-onset-of-clinical-benefit-is-associated-with-a-reduction-in-validated-biomarkers-of-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-mavrilimumab-a-human-monoclonal-antibody-targeting/