Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:There are no valid followup parameters in the assessment of disease activity in Takayasu arteritis(TA).We investigated the impact of incorporation of vascular imaging into ITAS in the assessment of disease activity in TA
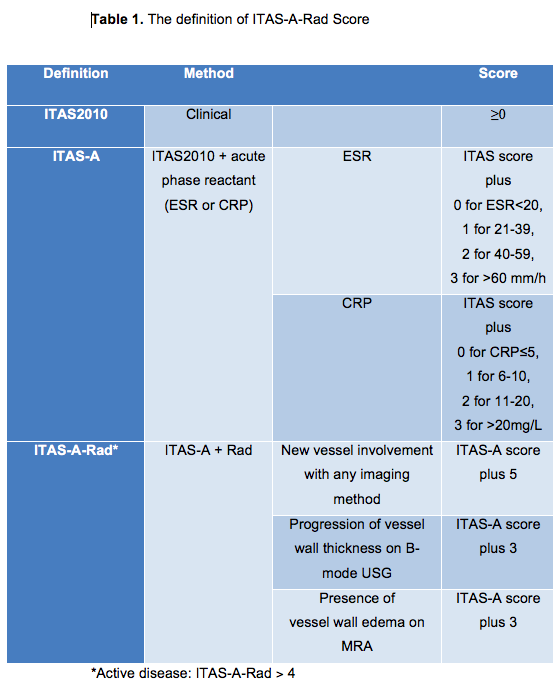
Methods: 52 patients who fulfilled the ACR criteria were included. Physician global assessment(PGA),Kerr,et alÕs criteria(K,eC) and ITAS2010/ITAS-A scores were evaluated in all patients(1,2).All the patients were followed using 3-6 monthly USG and 6-12 monthly MR angiography (MRA). Radiological activity(Rad) was defined based on the presence of any of the 3 parameters including new vessel involvement by any imaging technique(5 points), the increase in vessel wall thickness USG (3 points) and vessel wall edema on MRA(3 points). Then we incorporated these scores with ITAS-A to obtain a composite disease activity index (ITAS-A-Rad)(table1).
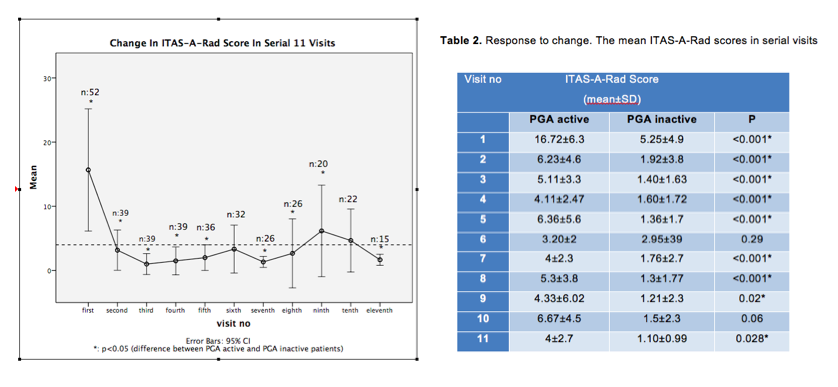
Results: Total 410 visits of 52 TA patients(mean age 50.7, F:92.3%, mean followup duration: 6.4 ± 2.9 yrs) were evaluated.Radiological assessment was done in 359 visits.Patients were categorized as having active disease in 194 visits (47.4%) according to PGA and 72 visits (17.5%) according to K,eC.The agreement between them was fair (66%,_:0.29).Rad parameters were determined in 105 out of 359 visits.The total agreement was found to be 83% (_:0.58) between the radiological disease activity and K,eC and 76% (_:0.52) between the RAD and PGA.Mean ITAS-A-Rad scores were significantly higher in visits with active disease compared to visits with inactive disease according to both PGA and K,eC(table2).The ITAS-A-Rad was significantly correlated with all the other activity parameters including ITAS2010, ITAS-A, and APRs.There were 43 visits with new vessel involvement by any of the two imaging techniques;all visits included patients with active disease based on both PGA and Kerr et al criteria. The agreement between ITAS2010 and PGA was fair (69%,_0.38).When acute phase reactant was added (ITAS-A), it did not improve (68%,_0.34). But the agreement between ITAS-A-Rad and PGA (72%,_0.50) and also K,eC(82%,_:0.56)was found to be moderate. When only ITAS-A-USGor only ITAS-A-MRAwas used, the agreement with PGA remained unchanged (73%,_0.45 and 76%,_0.52 respectively).When responsiveness to change of ITAS-A-Rad score was evaluated by serial visits of patients,it was found that the mean value of the score was discriminative for disease activity according to PGA in 9 of 11 visits(Figure1)
Conclusion: This study suggest that ITAS A Rad, a modified ITAS2010 score may be used to be a valuable foIlow-up parameter in the assessment of disease activity in TA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kenar G, Karaman S, Cetin P, Yarkan H, Zengin B, Can G, Birlik M, Onen F. Radiological Disease Activity Is the Major Determinant for Physicians While Deciding Active Disease in Takayasu Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiological-disease-activity-is-the-major-determinant-for-physicians-while-deciding-active-disease-in-takayasu-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiological-disease-activity-is-the-major-determinant-for-physicians-while-deciding-active-disease-in-takayasu-arteritis/