Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI) is an oral, reversible and selective Janus kinase 1 and 2 inhibitor. Treatment with once-daily oral BARI resulted in low rates of radiographic progression for up to 2 years in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of this paper is to evaluate radiographic progression of structural joint damage in patients with RA over 5 years of treatment with BARI.
Methods: This study included patients who completed three phase 3 trials, RA-BEGIN (DMARD-naïve), RA-BUILD (csDMARD-IR) or RA-BEAM (MTX-IR), and enrolled in the long-term extension study, RA-BEYOND. Patients receiving blinded BARI at the conclusion of phase 3 trials remained on that dose (2mg or 4mg, once daily) in RA-BEYOND. At 52 weeks, DMARD-naïve patients receiving methotrexate (MTX) or combination therapy (BARI 4mg + MTX) were switched to BARI 4mg monotherapy; MTX-IR patients receiving adalimumab (ADA) were switched to BARI 4mg on background MTX. At 24 weeks, csDMARD-IR patients receiving placebo (PBO) were switched to BARI 4mg on background csDMARD. Analysis population included patients who had baseline and at least one radiograph collected after 2 years. Radiographic progression of structural joint damage (Years 3-5) was determined by changes from baseline in van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score (ΔmTSS), erosion score, and joint space narrowing. Proportion of patients showing no progression was assessed based on change from baseline mTSS (Δ mTSS) from the originating study, using thresholds of 0.5 or the smallest detectable change (SDC). Mixed model repeated measures and logistic regression models were used to analyze continuous variables and categorical variables, respectively; linear extrapolation was used for imputation of missing data (maximum of 1 year).
Results: Overall, 82.6% (2125/2573) of patients entered the long-term extension study. Among DMARD-naïve patients, those on initial BARI monotherapy or in combination with MTX had significantly slower radiographic progression (ΔmTSS) compared to those on initial MTX at years 3, 4, and 5 (Table 1; p≤0.05). These patients also had significantly fewer erosions at these time points (p≤0.05). A greater proportion of patients who had received initial BARI therapy and BARI in combination with MTX had no radiographic progression compared to initial MTX monotherapy using thresholds of 0.5 (Table 2; p≤0.05). Among MTX-IR patients, patients on initial BARI treatment had slower radiographic progression compared to PBO and the results were comparable to those on initial adalimumab treatment at years 3, 4, and 5 (Table 1). A greater proportion of patients who had received initial BARI therapy had no radiographic progression compared to initial PBO using thresholds of SDC (Table 2; p≤0.05). Among csDMARD-IR patients, although differences between groups were small, patients on initial BARI 4mg had slowest radiographic progression compared to initial PBO and initial BARI 2mg (Table 1). At least 74% of the structure data used in the analyses are based on observed data.
Conclusion: Treatment with once-daily oral BARI maintained low rates of radiographic progression for up to 5 years in different patient populations with RA.
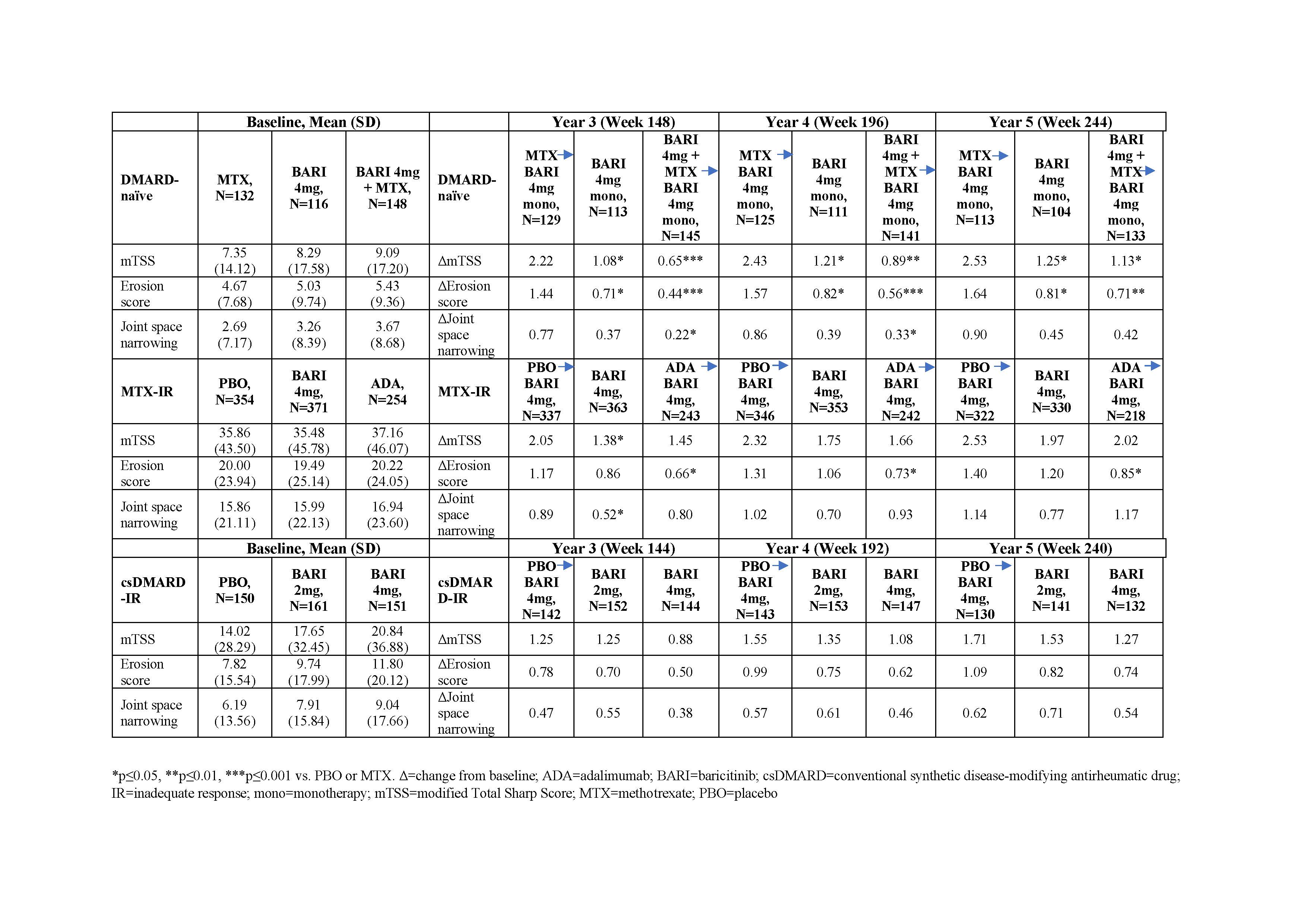 Table 1: Changes from baseline in mTSS and its components in different patient populations
Table 1: Changes from baseline in mTSS and its components in different patient populations
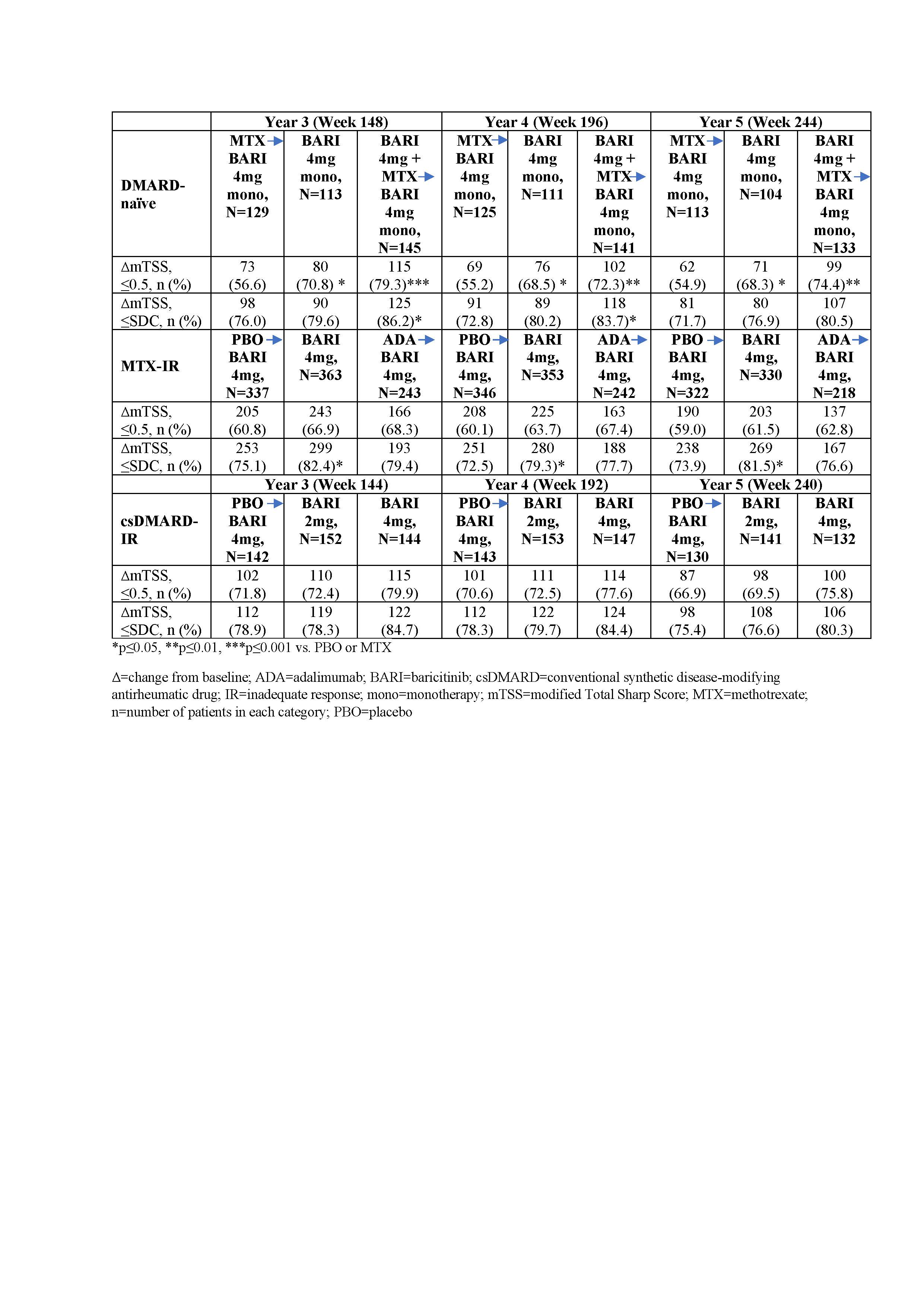 Table 2: Percentage of patients without structural damage progression in different patient populations
Table 2: Percentage of patients without structural damage progression in different patient populations
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Heijde D, Kartman C, Xie L, Beattie S, Schlichting D, Durez P, Tanaka Y, Fleischmann R. Radiographic Progression of Structural Joint Damage over 5 Years of Baricitinib Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from RA-BEYOND [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiographic-progression-of-structural-joint-damage-over-5-years-of-baricitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-ra-beyond/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/radiographic-progression-of-structural-joint-damage-over-5-years-of-baricitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-ra-beyond/
