Novel Methodology to Quantify Erosion Volume in Rheumatoid Arthritis using Computed Tomography
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causes two key structural changes that are visible on plain radiographs: narrowing of the joint space width (JSN) and erosion of the juxta-articular bone. Hand radiography is a low-cost and widely available tool to assess RA and is used extensively in clinical studies. However, plain radiography provides only a two-dimensional (2D) projection of structures that have a complex three-dimensional (3D) shape. Highly accurate quantification of erosion size will become increasingly important to use in longitudinal studies of RA treatment and may also be useful to monitor drug therapy in routine patient care. Computed tomography (CT) provides superb imaging of bone margins and, as a 3D modality, it is ideal to measure erosion volume.
Methods:
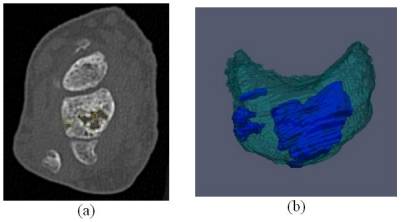
We have developed a semi-automated software method to segment (outline) the margins of erosions in 3D, from high-resolution CT scans of the hand and wrist, and to calculate erosion volume. A reader operates the software and guides the computer to segment the erosions on each CT slice. Figure 1 illustrates a CT slice with erosion (a) and its 3D rendering (b). The method was validated using CT scans of both hands and wrists from 5 subjects (10 hands) with moderate to severe RA. Each hand was scanned twice during a single session, after repositioning subjects between scans. The repositioning reproducibility for the 10 hands was quantified using intra-cluster correlation (ICC), the root-mean square standard deviation (RMSSD), and the coefficient of variation (CoV) (Table). For each scan, we measured the erosion volume of the total hand and wrist, as well as for two sub-regions: sub-region 1 included the radius, ulna, carpal bones and carpometacarpal (CMC) joints and sub-region 2 included the PIP, MCP, and DIP joints.
Results:
See table. The total erosion volume for the 10 hands ranged from 34.5 mm3 to 1,492.4 mm3. The ICC values demonstrate excellent correlation. The RMSSD and CoV suggest that this technique should be capable of detecting erosion volume change on the order of 20 to 30 mm3 or 4-7 percent.
Conclusion:
Our semi-automated high-resolution CT method reproducibly detects and quantifies the volume of juxta-articular erosions in RA and can be applied to studies of RA treatment to detect longitudinal changes in erosion volume.
|
|
Total
|
Subregion 1
|
Subregion 2
|
|
Intra-cluster correlation
|
1.00 |
0.99 |
0.97 |
|
Root Mean Square, Standard Deviation (mm3)
|
22.9 |
17.3 |
30.1 |
|
Coefficient of variation
|
5.3 % |
4.0 % |
7.0 % |
Disclosure:
J. W. Duryea,
Eli Lily Inc.,
2;
D. H. Solomon,
Lilly, Amgen, CORRONA,
2,
Lilly, Novartis, BMS, Pfizer,
6,
Lilly, BMS, Novartis,
9;
B. LU,
Lilly Inc.,
2;
R. Russell,
Eli Lilly Inc.,
2;
R. Han,
Eli Lilly Inc,
5;
E. M. Gravallese,
Eli Lilly Inc.,
2;
J. Kay,
Ardea Biosciences, Eli Lilly, Fidia Farmacutici, SpA, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis,
2,
Amgen, Baxter Healthcare Corporation, BMS, Celgene, fourteen22 Inc., Genentech, Hospira, Inc., Horizon Pharma, Inc., Janssen, Medac Pharma Inc., PanGenetics, B.V., Pfizer, Roche, Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., UCB, ,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-erosion-volume-measurement-from-computed-tomography/