Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is the base of the pathophysiology of spondyloarthritis. Recently, our research group has shown that computer analysis of static images can be used in the evaluation of patients with enthesic inflammatory diseases with good intra-patient and intra-observer validity and sensitivity to change.
The purpose of this study is to determine the enthesic evolution in patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) treated with three different biological therapies through the computer analysis of ultrasound images.
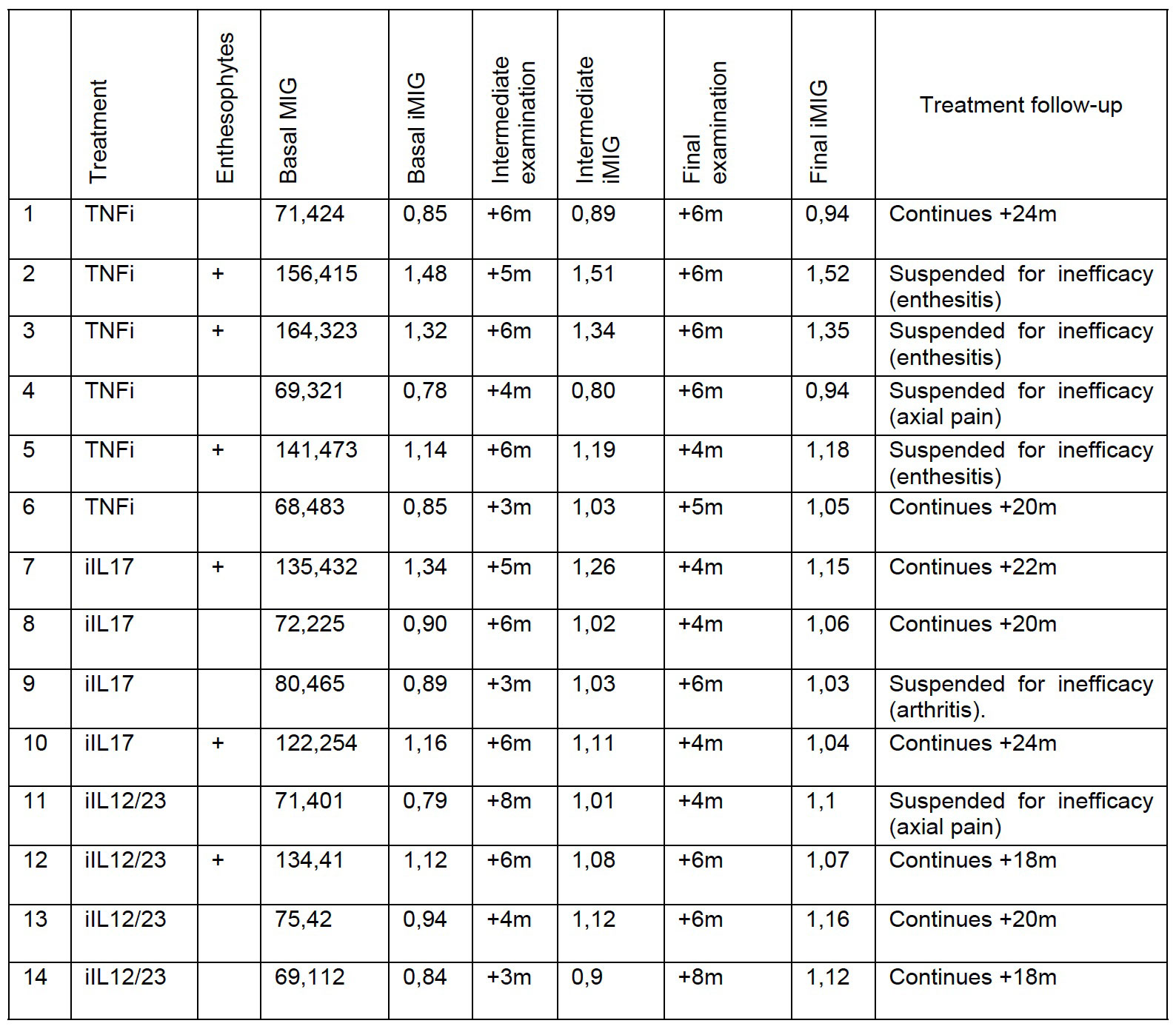
Methods: We selected patients diagnosed with SpA and enthesitis followed by imaging, who started biological therapy with a TNF inhibitor, an IL17 inhibitor or an IL12/23 inhibitor. For the records to be included, it was necessary to have clinical information from the period of perfoming the ultrasound. All images were obtained from the Achilles tendon, with the same ultrasound equipment, grayscale and settings for each patient.
To homogenize the results of the analysis, the gray intensity mean index (iMIG) was used. It is defined as mean gray intensity in the clinically affected enthesis/mean gray intensity in the same healthy enthesis. It has been shown to appropriately discriminate the inflammatory pathology from the mechanical or healthy controls as well as being sensitive to change.
Results: 14 patients were included: 6 treated with a TNF inhibitor, 4 with an IL17 inhibitor and 4 with an IL12/23 inhibitor. Patients 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 11, and 12 had enthesophytes.
In the global analysis, the iMIG did not show statistically significant differences between the treatment groups at the start of the treatment, at the intermediate and at the final evaluation (P=.588, .739 and .674, respectively).
Patients with enthesophytes presented significantly higher baseline, intermediate and final iMIG than patients without them: 1.26 SD 0.14 vs 0.85 SD 0.05 (t=7.407, P=.001), 1.24 SD 0.15 vs 0.97 SD 0.1 (t=3.659, P=.006); and 1.21 SD 0.12 vs 1.05 SD 0.07 (t=2.342, P=.037), respectively.
Analyzing only the patients without enthesophytosis, the final iMIG showed statistically significant differences between the 3 administered treatments (ANOVA, F=8.142, P=.027), being relevant between the use of IL12/23 and TNF inhibitor in favor of the former (Bonferroni, P=.03).
In the same subgroup of patients without enthesophytosis, iMIG analysis over time showed statistically significant differences between final and baseline iMIG (Friedman -1.938 P=.000).
Conclusion: Computer analysis of ultrasound images using the iMIG distinguishes therapeutic response in patients without enthesophytosis.
The interposition of enthesophytes impede the correct visualization of the enthesis and does not allow ultrasound changes to be detected in some areas of the image.
Although there are indications that the use of this analysis could also predict the behavior of certain therapies, it is convenient to propose prospective studies with homogeneous ultrasound controls.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tortosa Cabanas M, GUILLEN ASTETE C, Andreu Suarez A. Quantification of the Enthesic Response to Biological Therapies in Patients with Spondyloarthritis by Computer Analysis of Ultrasound Images [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantification-of-the-enthesic-response-to-biological-therapies-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-by-computer-analysis-of-ultrasound-images/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantification-of-the-enthesic-response-to-biological-therapies-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-by-computer-analysis-of-ultrasound-images/