Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:50AM
Background/Purpose: Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE) is an autoimmune skin disease that may occur with or without systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Active CLE lesions present with erythema and scale on photoexposed areas that can lead to dyspigmentation and scarring. This study aims to compare the QoL of patients with CLE on the face versus patients without facial lesions, and to determine the impact of facial lesion activity (erythema, scale) and damage (pigmentation, scarring) on patient QoL.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of a prospectively collected database of CLE patients seen at the Autoimmune Skin Diseases Unit of the University of Pennsylvania from 2007 to 2019. Patients were included if a Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index (CLASI) assessment and Skindex-29+3 questionnaire were completed on the initial visit. The CLASI is a validated instrument that quantifies CLE disease activity and damage in several exposed and covered areas of the body. Skindex-29+3 is a skin-specific QoL questionnaire that includes several domains such as symptoms, emotions, functioning and three additional lupus-specific questions on alopecia, photosensitivity and limitation of outdoor activities. A higher Skindex-29+3 domain score translates to poorer patient QoL. Based on clinical findings, patients were categorized into one of four groups, defined as those with: 1) active facial disease, 2) facial damage, 3) both facial activity and damage, or 4) no facial lesions. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni correction were used to compare QoL across the four groups. In addition, a multivariable regression analysis was used to determine the relationship of facial disease and other pre-determined clinical variables to the QoL of CLE patients.
Results: A total of 366 CLE patients were included in the study. Among them, 255 (68%) had facial CLE. Specifically, 99 (27%) patients had both activity and damage, 124 (33%) had activity only, and 32 (8%) had damage only (Table 1). The mean Skindex-29 Symptoms (S), Emotions (E) and Functioning (F) scores of facial CLE patients who had both activity and damage (S=47.34, E=55.06, F=43.45) or activity alone (S=43.55, E=53.72, F=43.91) were significantly higher compared to those who had no facial lesions (S=35.05, E=42.50, F=31.78) (p < 0.05) (Figure 1). Further, having both activity and damage on the face and having active facial CLE alone were significantly associated with poorer QoL across all three Skindex-29+3 indices, even after controlling for female gender and current smoking status, which are known to be associated with poor QoL scores in CLE patients (Table 2).
Conclusion: Patients with facial CLE have worse QoL compared with patients having no facial lesions. Facial CLE activity has a more significant effect on QoL than facial damage. A possible explanation for this finding is that patients with facial activity are concerned about potential systemic flares, while the damage is typically persistent but less worrisome to the patient. Clinicians should be aware that patients with facial activity are more affected in terms of quality of life and their fears of systemic disease should be addressed.
 Table 1. Characteristics of CLE patients
Table 1. Characteristics of CLE patients
 Table 2. SKINDEX-29+3 scores in patients with facial cutaneous lupus erythematosus – multivariable regression
Table 2. SKINDEX-29+3 scores in patients with facial cutaneous lupus erythematosus – multivariable regression
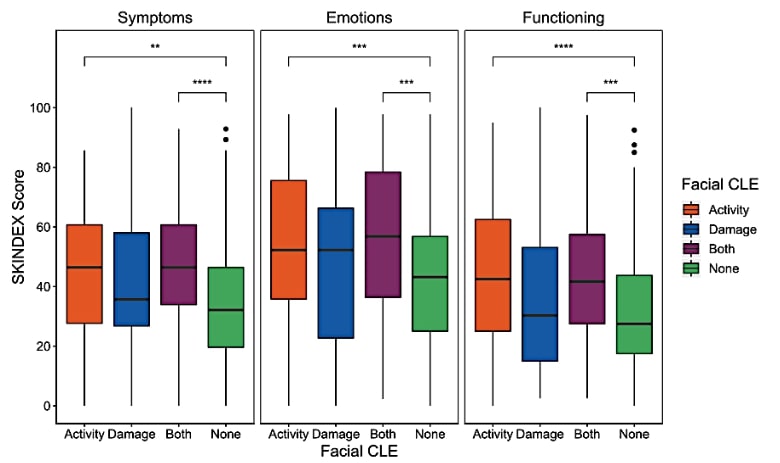 Mean Skindex symptoms, emotions, and functioning scores of patients with facial disease who had both activity and damage, or activity alone, were higher and significantly different from those who had no facial lesions. Scores of patients who only have lesions of damage on the face did not significantly differ from those who have no facial lesions. (** = p ≤ 0.01, *** = p ≤ 0.001, **** = p ≤ 0.0001)
Mean Skindex symptoms, emotions, and functioning scores of patients with facial disease who had both activity and damage, or activity alone, were higher and significantly different from those who had no facial lesions. Scores of patients who only have lesions of damage on the face did not significantly differ from those who have no facial lesions. (** = p ≤ 0.01, *** = p ≤ 0.001, **** = p ≤ 0.0001)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concha J, Yan D, Bax C, Ravishankar A, Borucki R, Feng R, Werth V. Quality of Life of Patients with Facial Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-of-patients-with-facial-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-of-patients-with-facial-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/
