Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Manifestations (0855–0896)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus quality of life (Lupus QoL) questionnaire is a disease specific patient reported outcome that is available in multiple languages1. Indian SLE inception cohort for research (INSPIRE) is a multi-institutional cohort having patients from different parts of India who speak different languages2. The study aimed to assess the QOL in this cohort and study its association with measures of disease activity.
Methods: Patients satisfying the SLICC classification criteria for lupus enrolled in the INSPIRE cohort1 were asked to fill the Lupus QoL questionnaire in their native language. Any help needed in understanding a question was provided by the study nurse or the physician. Internal consistency of the questions in the various domains of the Lupus QoL was assessed using Cronbach’s Alpha. Associations between Lupus QoL domains with age, SLEDAI, and BILAG were analyzed using Spearman correlation.
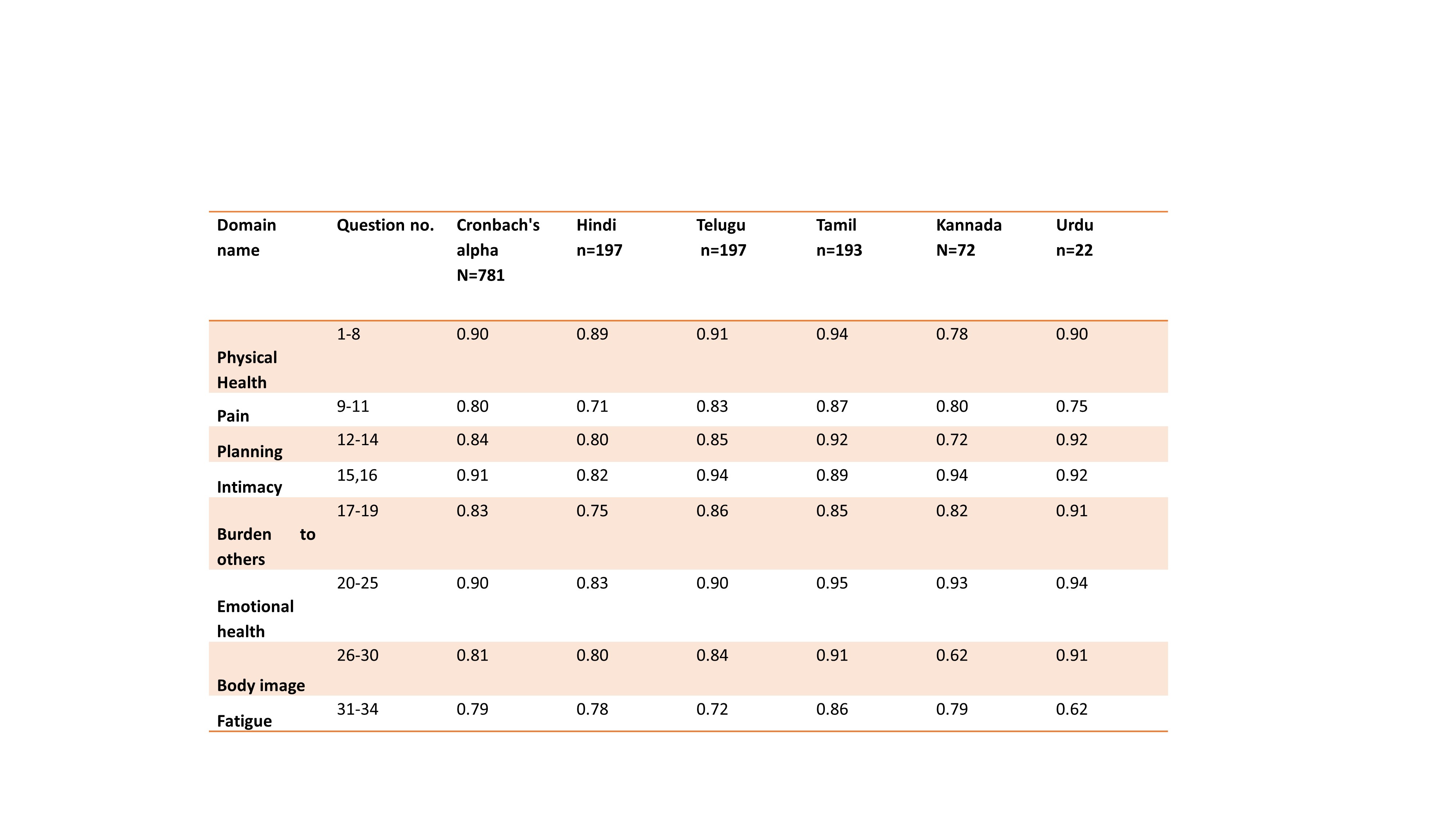
Results: Seven hundred and eighty-one lupus patients answered the Lupus QoL in either Hindi, Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, Urdu, Punjabi, Bengali and English. The mean age of the patients was 28+ 10 years. Disease duration was less than three years. The median (IQR) HAQ score was 0.5(0.25-1.0). The mean SLEDAI was 10.9+ 8.1. The internal consistency of the questions in various domains of the translated LupusQOL was high with Cronbach’s Alpha varying from 0.79-0.91 (Table1)
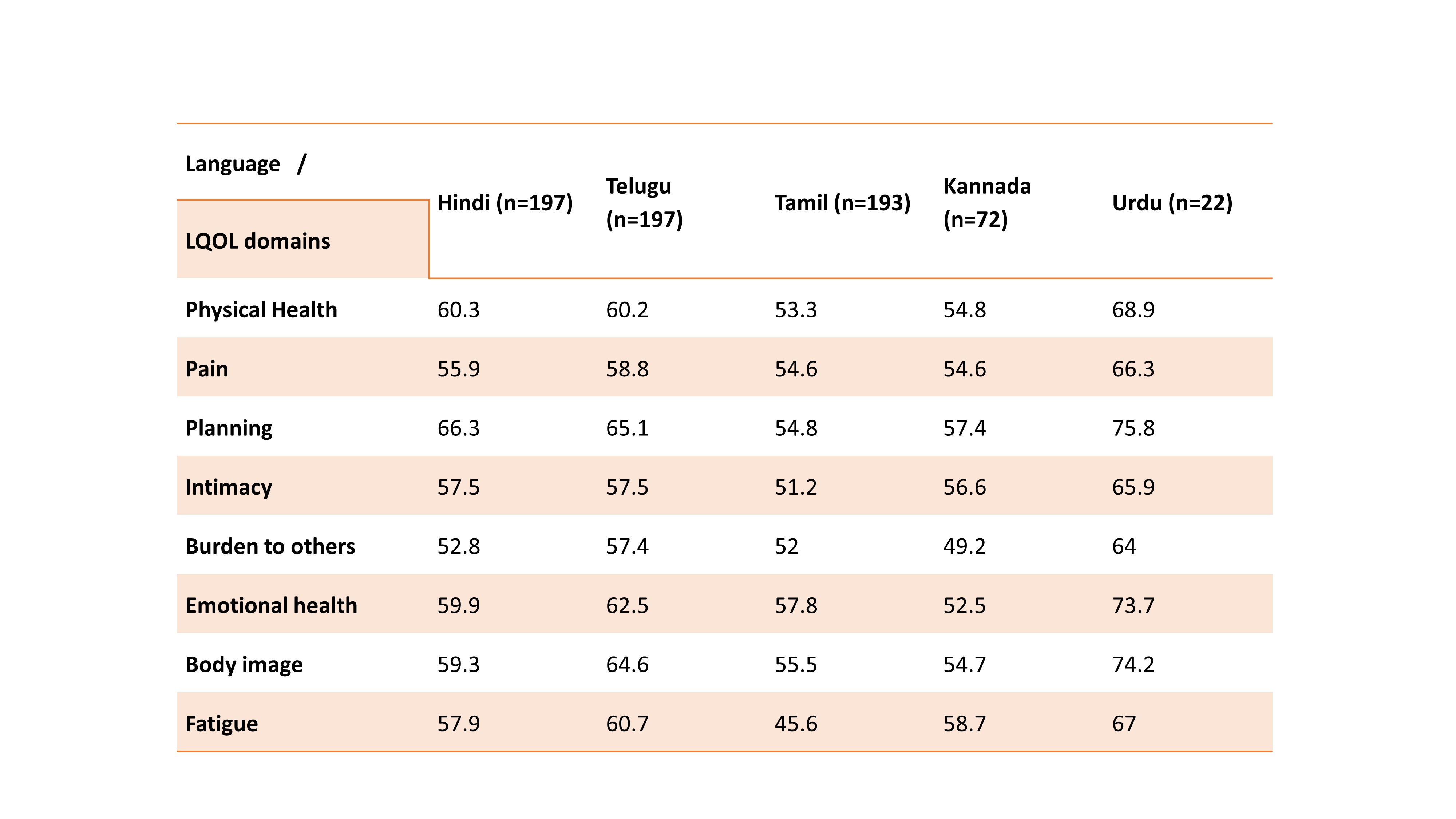
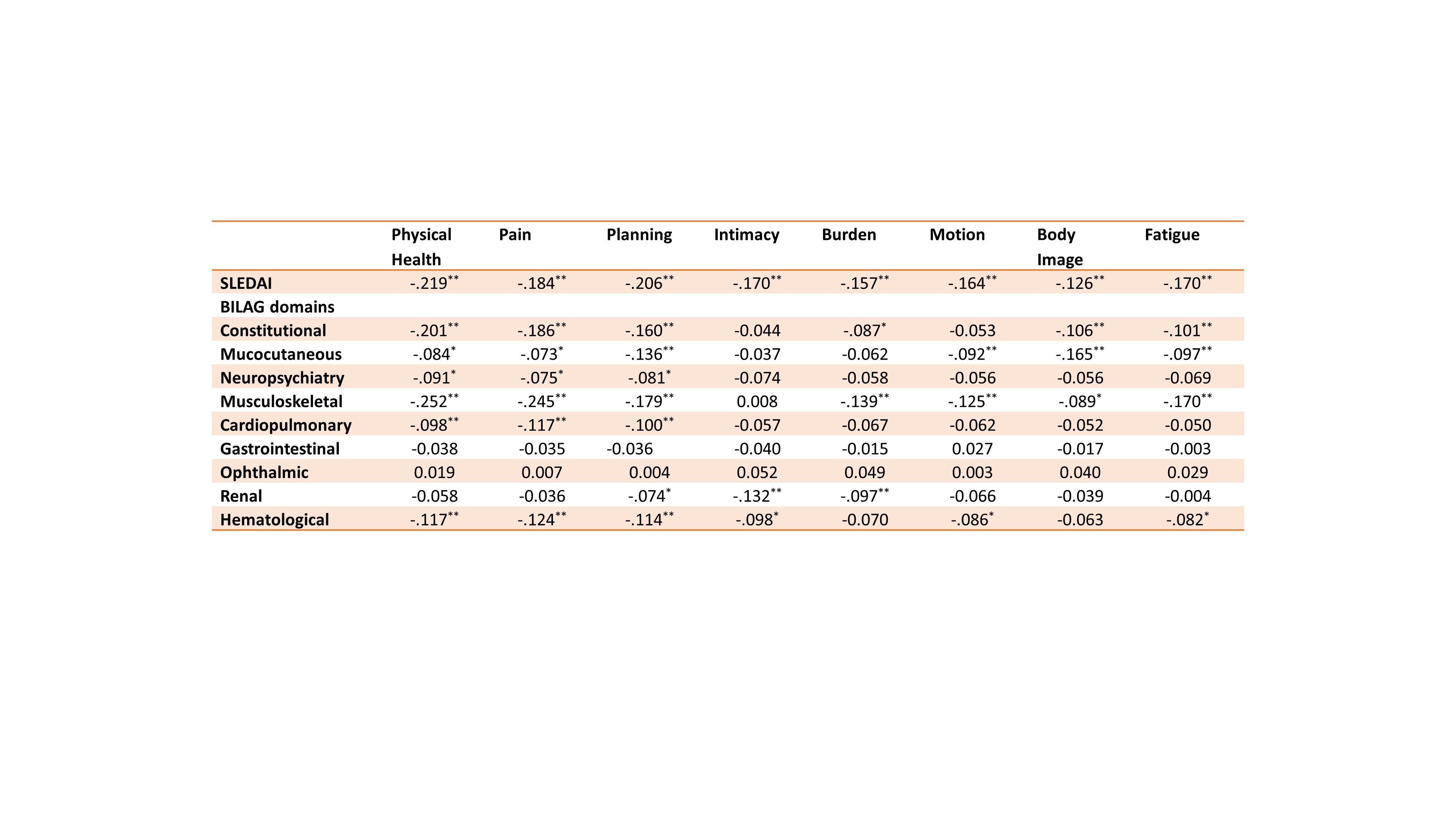
The mean scores in each domain of Lupus QoL among the patients were as follows: physical health 58.1, pain 55.9, planning 63, intimacy 54.8, burden to others 55, emotional health 59.7, body image 59.3 and fatigue 57.5 (Table 2). Higher SLEDAI scores correlated with poor LupusQoL across all domains, though the correlation was at mild. Looking at impact of different organ involvement on LUPUS QoL Physical health was affected by constitutional and musculoskeletal(MSK) domain and pain scores correlated with MSK domain, (Table 3).
Conclusion: Hindi, Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Urdu translations of Lupus QoL have good internal consistency. Indian lupus patients have significantly impaired quality of life. only some part of which could be accounted for by disease activity. Thus other factors contributing to poor QoL need to be addressed while managing patients.
1. Mcelhone K, Castelino M, Abbott J, Bruce I, Ahmad Y, Shelmerdine J, et al. The LupusQoL and Associations with Demographics and Clinical Measurements in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Rheumatology. 2010;37:2273–9.
2.Shobha V, Aggarwal A, Rajasekhar L, Jain A, Gupta R, Das B, Mathew AJ, Rathi M, Ghosh P, Negi VS, Tripathi A, Misra R. Indian SLE Inception cohort for Research (INSPIRE): the design of a multi-institutional cohort. Rheumatol Int. 2021 May;41(5):887-894. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04766-3. Epub 2021 Jan 12. PMID: 33433731.
*p<0.05, ** p<0.01
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rajasekhar L, Bhavani D, Tota S, Vijayalekshmi V, Gupta R, Kavadichanda C, Shobha V, Negi V, Aggarwal A. Quality of Life Assessment in an Indian Inception Cohort (INSPIRE) of SLE Using Lupus QoL Questionnaire [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-assessment-in-an-indian-inception-cohort-inspire-of-sle-using-lupus-qol-questionnaire/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-assessment-in-an-indian-inception-cohort-inspire-of-sle-using-lupus-qol-questionnaire/