Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0380–0422) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Seropositive and ACPA positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is associated with significant cardiovascular and pulmonary comorbidity. However, screening for early detection of pulmonary involvement especially intestitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with seropositive and ACPA positive Rheumatoid Arthritis is not yet established.
Methods: We included a total of 50 consecutive patients with a confirmed diagnosis of seropositive and ACPA positive Rheumatoid Arthritis without symptoms for or known cardiopulmonary disease. For the purpose of this study, we used a noninvasive radiation-free approach to screen for pulmonary, pleural or vascular manifestation of the disease by means of pulmonary function tests (PFT), cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET), echocardiography and pleuro-pulmonary transthoracic ultrasound (LUS).
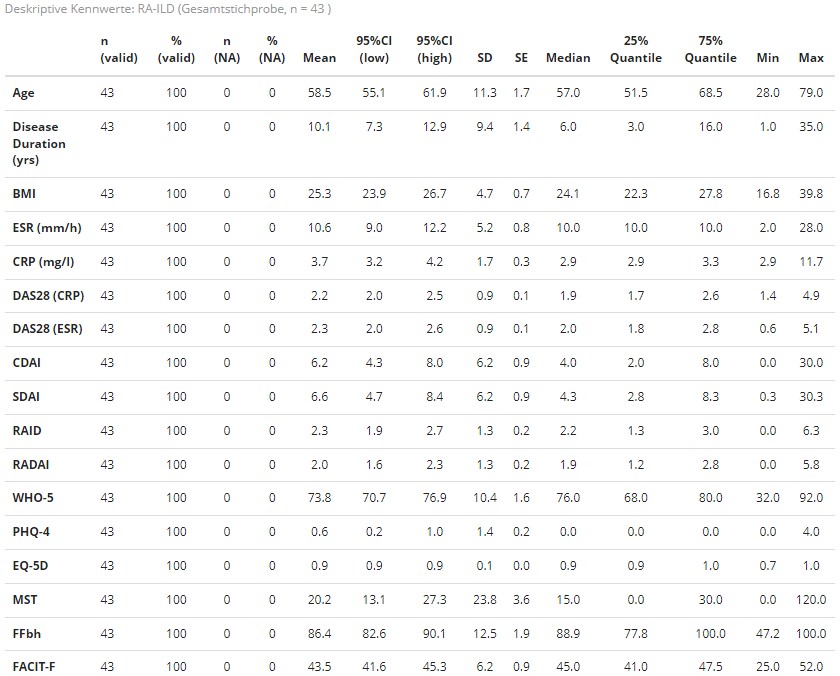
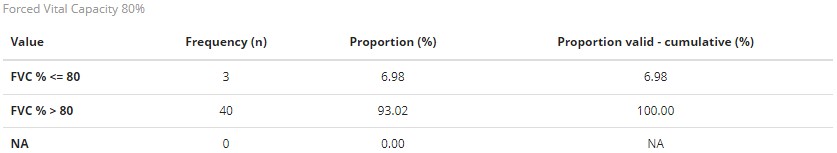
Results: The data of 43 patients (mean age 58.5 years, 81.4% female, 93.02% non-smokers) were available for this analysis, as data collection is still ongoing. With an average disease duration of 10.1 years and with a mean remission of DAS28 ESR 2.3, DAS28 CRP 2.2 or low disease activity (CDAI 6.2, SDAI 6.6), respectively, depending on the used disease activity score, 34.88 % showed an erosive course. A reduced forced vital capacity (FVC ≤80%) on PFT was shown in 3 patients (6.98%), a reduced CO-diffusion capacity (DLCOc-SB ≤80%) in 14 patients (32.56%). In 39% of patients, we found noticeable changes in LUS, 23% with a pattern consistent with ILD. ILD was suspected in 13% with changes on LUS and additional PFT.
Numerous other RA- and ILD-associated parameters were collected in the present study (table 1 and 2).
Other findings included pleural consolidation suspicious for malignancy and pleural effusion on LUS, severe aortic stenosis in bicuspid aortic valve on echocardiography, severe impaired diffusion capacity due to lung emphysema and obstructive lung disease on PFT.
None of the patients showed signs of pulmonary vascular involvement or cardiac ischaemia on echocardiography or CPET.
Conclusion: In conclusion screening of RA-patients for pulmonary involvement with a non invasive, radiation free screening approach may detect a significant number of asymptomatic patients with signs consistent with pulmonary manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis, along with a variety of other cardiopulmonary comorbidities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Popp F, Hoffmann M, von Kempis J, Welcker M, von Wulffen W, Reichenberger F. Pulmonary Involvement in Patients with Seropositive and ACPA Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA-ILD) – Novel Screening Protocol for Early Detection of Pulmonary Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pulmonary-involvement-in-patients-with-seropositive-and-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-ild-novel-screening-protocol-for-early-detection-of-pulmonary-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pulmonary-involvement-in-patients-with-seropositive-and-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-ild-novel-screening-protocol-for-early-detection-of-pulmonary-involvement/