Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Enthesitis is a prominent feature of spondyloarthropathy (SpA), including psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The evaluation of enthesitis has conventionally been conducted by clinical exam, a method with significant limitations mainly its low sensitivity. Ultrasound can image entheses in high fidelity and may assist in the diagnosis and management of SpA patients. As part of the GRAPPA US sub-committee "Enthesitis Project" we performed a systematic review of the literature in order to assess the evidence and knowledge gaps in scoring systems of enthesitis in PsA.
Methods:
A systematic search of Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane was done. The search strategy was constructed to find original publications in English containing terms related to US, enthesitis, SpA or PsA. Two reviewers screened all abstracts for eligibility. Studies that reported used global sonographic scoring systems for assessment of enthesitis in patients with spondyloarthritis or their modifications were included. Data was extracted independently by 2 reviewers. Data extraction focused on the properties of the enthesitis scoring system used in each study. Specifically, we assessed the following component of the OMERACT filter: reliability of acquisition, feasibility, and construct validity as related to clinical assessment of enthesitis, biomarkers and imaging of enthesitis by other modalities, discriminative validity and responsiveness to treatment.
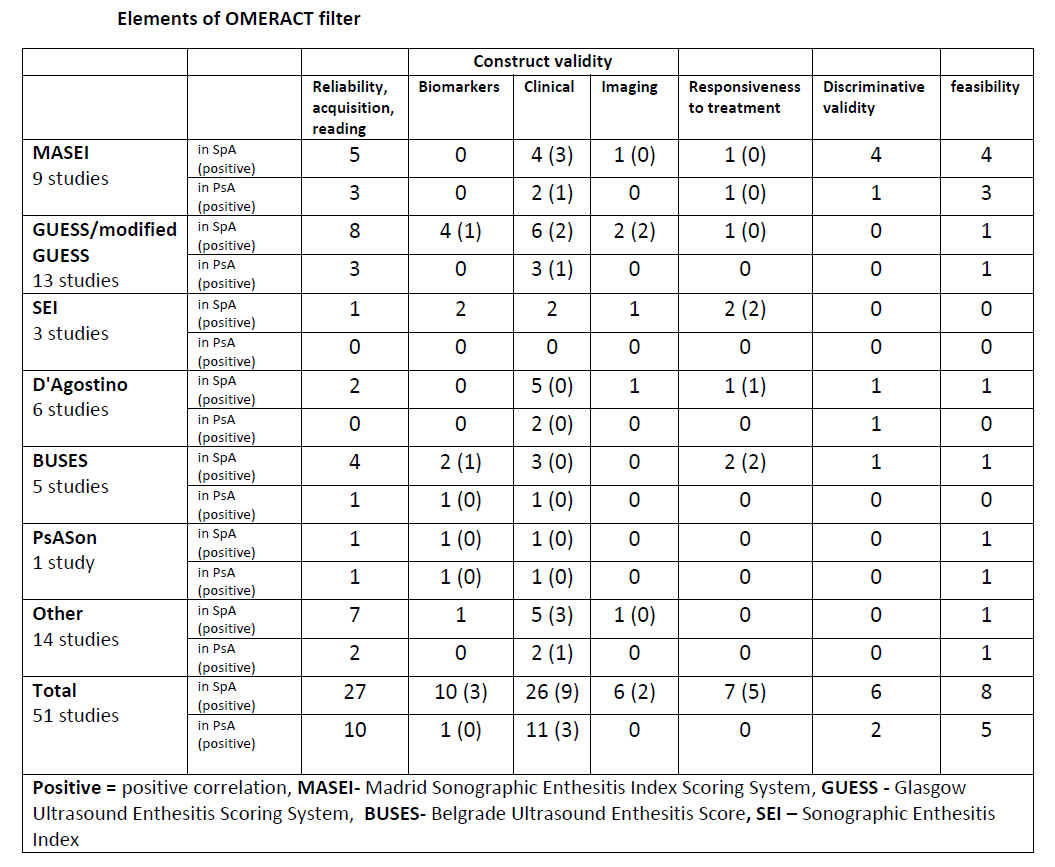
Results:
Fifty-one of 310 identified manuscripts were included. 13 studies used Glasgow Ultrasound Enthesitis Scoring System (GUESS) or its modifications, 9 used Madrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index Scoring System (MASEI), 6 used D’Agostino scoring system, 5 used Belgrade Ultrasound Enthesitis Score (BUSES), 3 used Sonographic Enthesitis Index (SEI), 1 used PsASon-Score, and 14 did not use a formal score. Only one of these scoring systems (PsASon) was developed and validated in patients with PsA. Only 18 (35%) of the studies involved patients with PsA, while the rest focused on SpA. Concerning the OMERACT filter, construct validity was assessed using biomarkers in 10 (19.6%) studies, only one study (2%) in PsA. Construct validity using clinical examination was assessed by 26 (51%), 11 (21.5%) were in PsA, only 6 (11.7%) compared US finding to imaging – none of them was performed on PsA. Responsiveness to treatment was assessed in 7 studies, none of them included PsA patients. Six (11.7%) studies evaluated discriminative validity two (4%) of them in PsA.
Conclusion:
Although sonographic indices have been developed for Spondyloarthropathy, only a few have been validated for PsA. None of them fulfilled all the OMERACT filter criteria in patients with PsA. Additional research is needed to assess the validity or modification of existing scoring systems in patients with PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elalouf O, Bakirci S, Touma Z, Anderson MA, Kaeley GS, Aydin SZ, Eder L. Psoriatic Arthritis Sonographic Enthesitis Scores – Systematic Review of the Literature [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-sonographic-enthesitis-scores-systematic-review-of-the-literature/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-sonographic-enthesitis-scores-systematic-review-of-the-literature/