Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Early diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is critical for timely intervention to prevent poor clinical outcomes. Despite well-known clinical predictors of PsA, the mechanisms responsible for the Psoriasis (PsO) to PsA transition are poorly understood. Dendritic cells are known contributors to both PsO and PsA, and their migratory ability may be altered in PsO patients at risk for PsA. Here, we investigated whether pro-migratory dendritic cells contribute to immune changes that may promote the transition to PsA.
Methods: To investigate differences in immune subsets in psoriatic disease, scRNAseq was performed on PBMCs from treatment-naïve patients with PsO or PsA. Patients were high-risk for PsA (HR-PsO) if they had ≥ 2 literature-based risk factors: nail pitting, scalp PsO, inverse PsO, BSA > 10%, BMI ≥ 35. Patients without risk factors were low-risk for PsA (LR-PsO). We used 10x Genomics Chromium 3’ platform with sequencing on the Illumina Novaseq 6000. Reads were aligned with Cell Ranger v7.1.0, followed by Seurat-based integration, clustering, and differential gene expression (DEG) analysis (1). For differential abundance analysis, we utilized the R package DCATS (2), which uses beta-binomial regression to identify compositional differences in scRNAseq data. We utilized flow cytometry of PBMC to quantify surface markers. We also performed transwell migration assays on dendritic cells isolated via magnetic bead negative selection. Surface marker expression and migration were compared using student’s t-test.
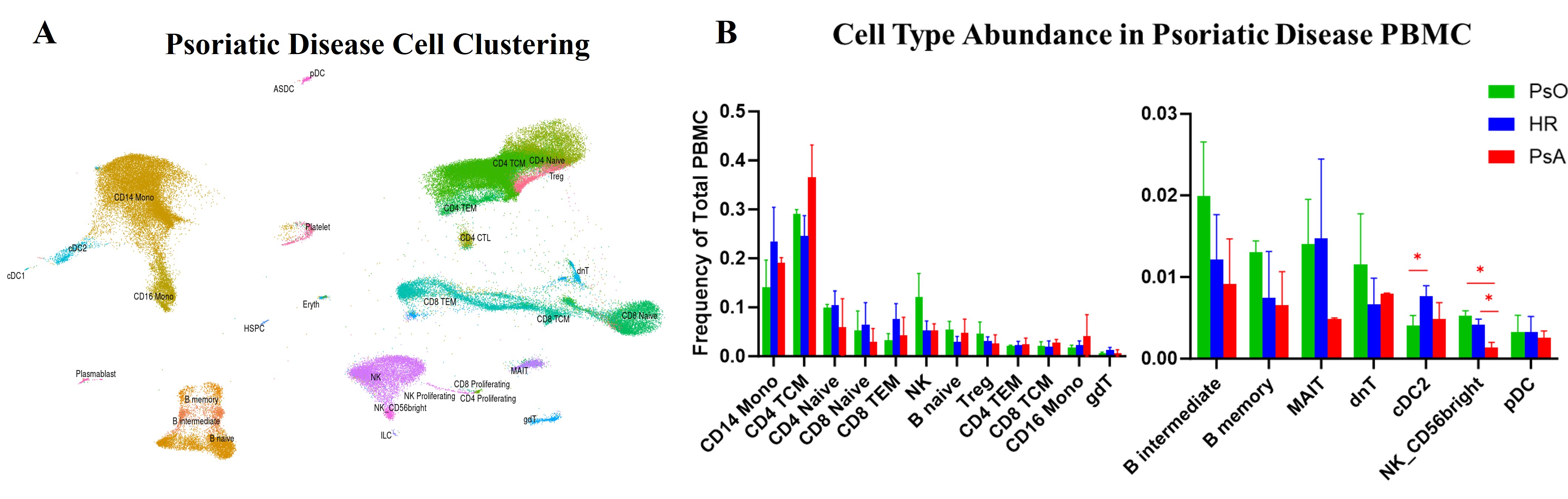
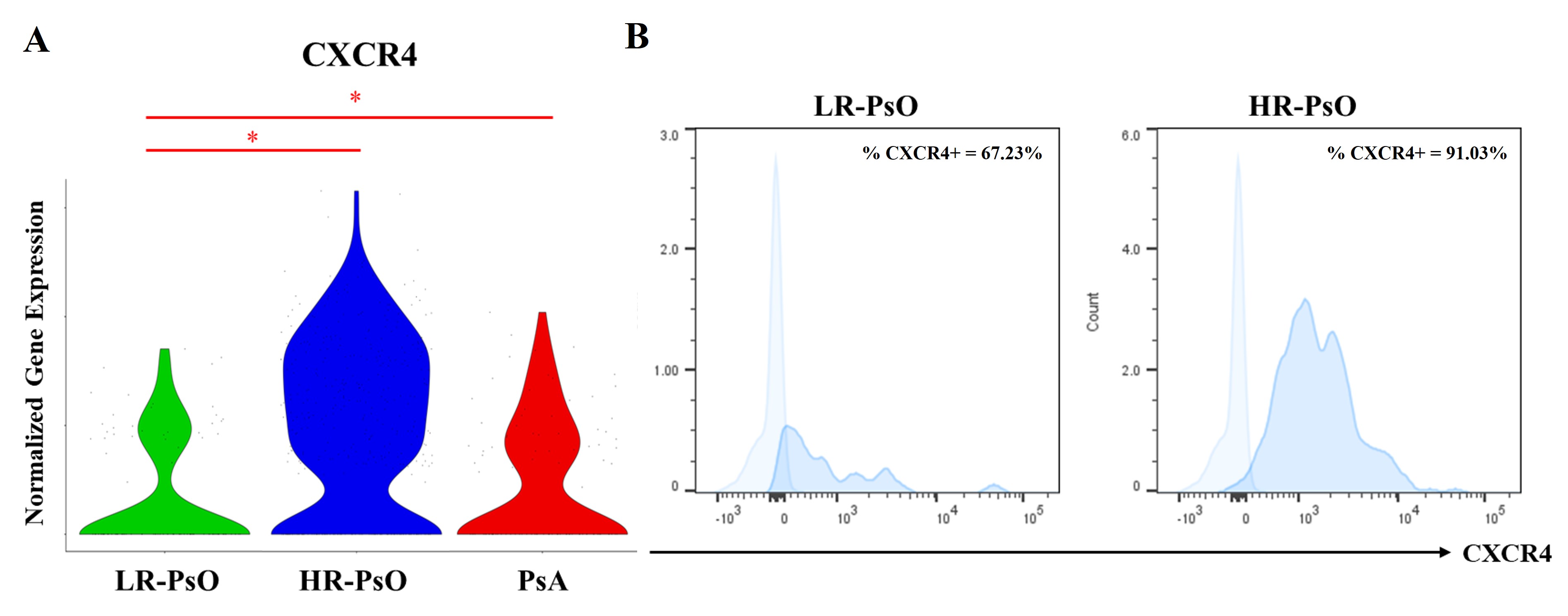
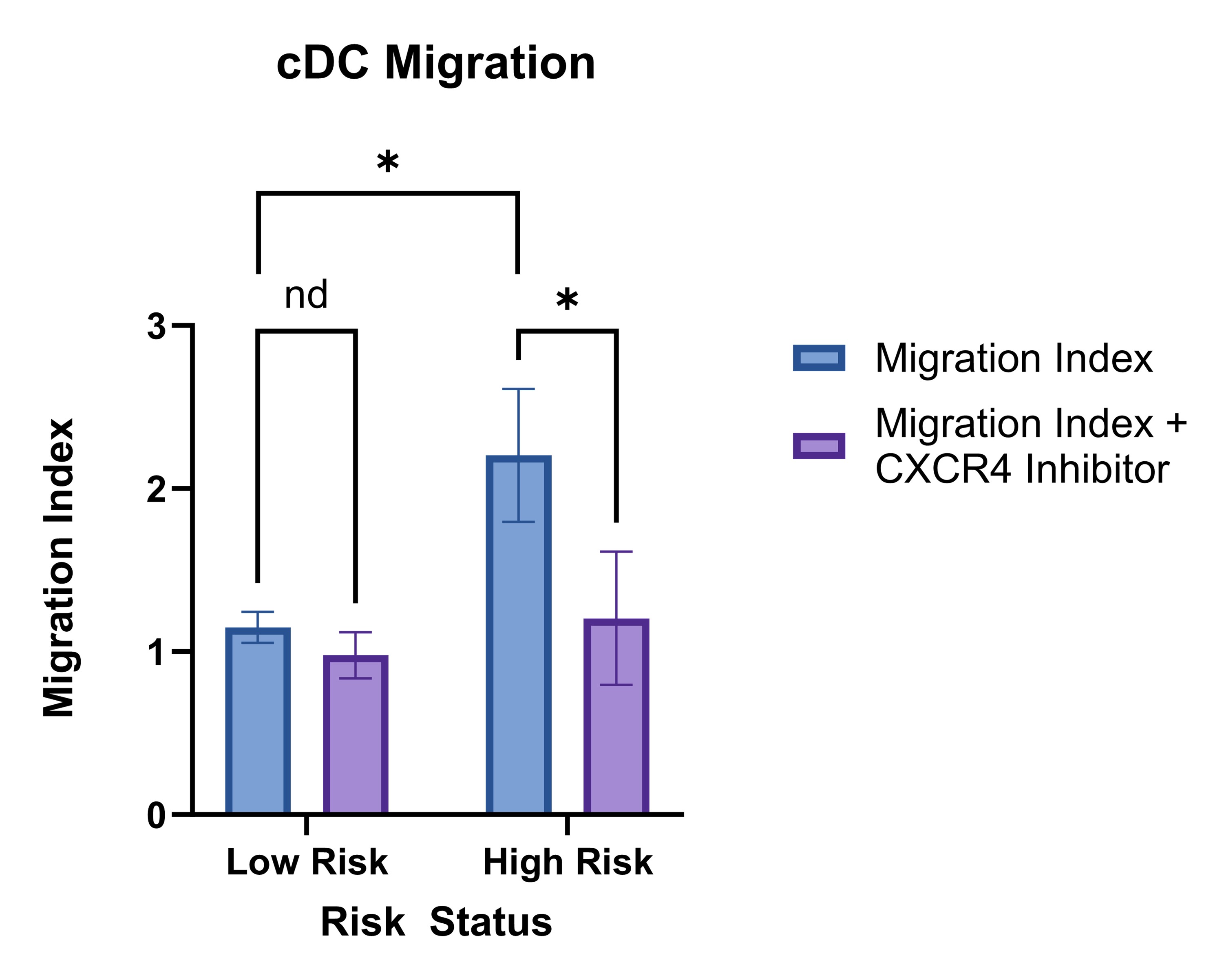
Results: Our integrative mapping of scRNAseq data from 2 LR-PsO, 4 HR-PsO, and 2 PsA patients (Figure 1A) revealed an increase in type II conventional dendritic cells (cDC2) in HR-PsO compared to LR-PsO (Figure 1B). cDC2 are antigen presenting cells whose polarization of naïve CD4 T cells to Th17 cells is crucial for psoriatic disease. DEG analysis showed increased expression of CXCR4 in HR-PsO and PsA cDC2 compared to LR-PsO cDC2 (Figure 2A), confirmed with flow cytometry (Figure 2B). CXCR4 is a chemokine receptor whose interaction with ligand CXCL12 induces cell migration, so we evaluated migration of DC using transwell migration assays with DC from LR-PsO and HR-PsO. We utilized CXCL12 as the chemoattractant, and assays were performed ± AMD3465, a selective CXCR4 inhibitor, to confirm the specificity of the migratory effect. HR-PsO DC migrated significantly more than LR-PsO DC, and the increased migration was abrogated by the addition of a CXCR4 inhibitor (Figure 3).
Conclusion: These results suggest a potential pathogenic role of CXCR4+ cDC2 in the transition from PsO to PsA. By combining scRNAseq and in vitro assays, we identified an increase in pro-migratory CXCR4+ cDC2 in PsO patients at high-risk to develop PsA. These findings may lead to future mechanistic studies investigating the role of CXCR4+ cDC2 in the transition from PsO to PsA and exploring these cells as targets for preventive therapies.
References
1. Hao Y et al. Dictionary learning for integrative, multimodal and scalable single-cell analysis. Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;42(2):293-304.
2. Lin X et al. DCATS: differential composition analysis for flexible single-cell experimental designs. Genome Biol. 2023 Jun 26;24(1):151.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheemalavagu S, Chandrasekharan U, Wessely O, Tran U, Husni M. Psoriasis Patients at Risk for Psoriatic Arthritis Have Increased Levels of Circulating Pro-migratory Dendritic Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriasis-patients-at-risk-for-psoriatic-arthritis-have-increased-levels-of-circulating-pro-migratory-dendritic-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriasis-patients-at-risk-for-psoriatic-arthritis-have-increased-levels-of-circulating-pro-migratory-dendritic-cells/