Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Protein carbamylation is induced by activated neutrophil: ex vivo analysis
Background/Purpose:
Anti-carbamylated protein (anti-CarP) antibodies were reported to be detected in 45% of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients [1]. We previously reported that carbamylated albumin (CarALB) was one of the target antigens of anti-CarP antibodies, and serum myeloperoxidase (MPO) level was elevated in rheumatoid arthritis patients with anti-CarALB antibody [2]. Protein carbamylation occurs by cyanate which MPO produces from thiocyanate (SCN–) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and MPO abundantly exists in neutrophil. Therefore, neutrophil is a strong candidate for the production of carbamylated antigen. The purpose of this study is to demonstrate that activated neutrophil induces protein carbamylation.
Methods:
Human neutrophils were isolated from whole blood by ficoll-dextran methods. They were pre-treated for 30 min at 37ºC in RPMI medium with or without 10ƒÊM diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), which inhibits NADPH-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Subsequently, they were incubated overnight at 37 ºC in RPMI medium containing 0.01mg/mL ALB with or without 10ƒÊM DPI, 20nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 100ƒÊM potassium thiocyanate (KSCN). Then proteins in the medium were collected by trichloroacetic acid/acetone precipitation. The carbamylation of ALB was confirmed by Western blotting using anti-carbamyl-lysine (CBL) polyclonal antibody. MPO in the medium was detected by Western blotting using anti-MPO polyclonal antibody.
Results:
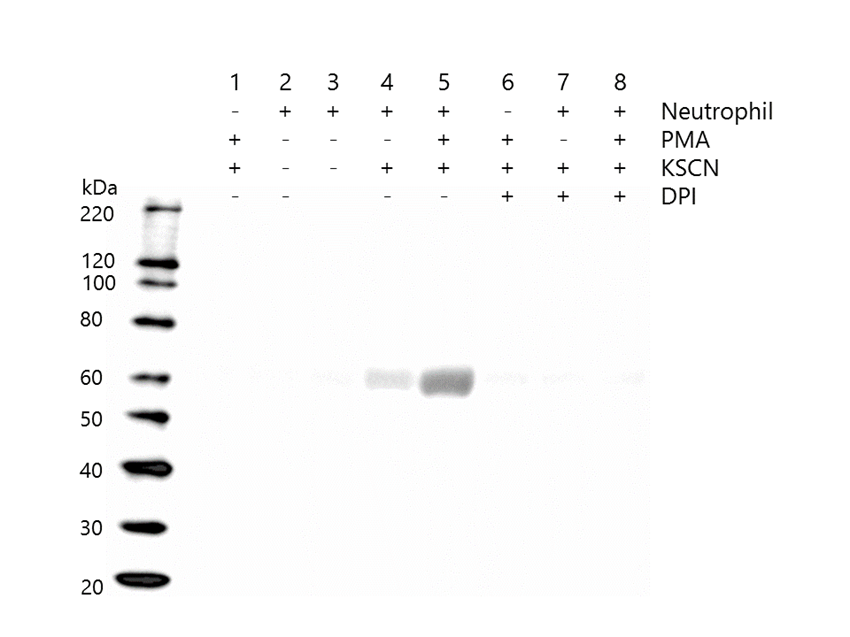
ALB was carbamylated only when both neutrophil and KSCN were present (Figure 1, lanes 4 and 5). Although the carbamylation occurred in the medium both with and without PMA, the level of the carbamylation was much higher in the medium with PMA (lane 5) than without PMA (lane 4). Carbamylation was inhibited by the presence of DPI, which diminishes ROS (lanes 7 and 8). MPO was released into the culture supernatant from the neutrophils (Figure 2, lane 2), and its release was accelerated by PMA (lanes 3 and 5), but attenuated by DPI (lanes 7 and 8).
Conclusion:
ALB in the culture medium was carbamylated by neutrophil. Given that PMA induces ROS production of neutrophil, and this reaction subsequently increases the MPO release, our data suggest that carbamylation is dependent on ROS and MPO from neutrophil. Addition of KSCN was necessary. This is the first report that showed direct relationship between neutrophil and protein carbamylation.
Reference:
[1] Shi J. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. [2] Nakabo S. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017.
Figure 1: Western blotting of carbamylated albumin
Figure 2: Western blotting of MPO
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nakabo S, Ohmura K, Akizuki S, Kuramoto N, Murakami K, Nakashima R, Hashimoto M, Yoshifuji H, Tanaka M, Mimori T. Protein Carbamylation Is Induced By Activated Neutrophil: Ex Vivo Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/protein-carbamylation-is-induced-by-activated-neutrophil-ex-vivo-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/protein-carbamylation-is-induced-by-activated-neutrophil-ex-vivo-analysis/