Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) has a synovial ultrasound (US) pattern, while soft tissue involvement is more frequently found in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA). No previous studies have analyzed if US findings differ between seropositive and seronegative RA patients. The objective is to analyze differences in the ultrasound pattern among patients with seropositive and seronegative RA. To assess if proliferative globular synovitis is associated to seropositive RA.
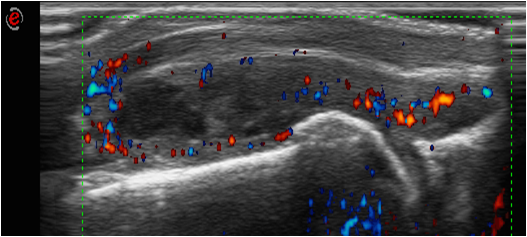
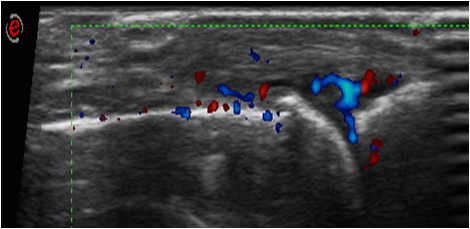
Methods: Retrospective Analysis. We collected clinical, epidemiological and ultrasound images of patients with RA who met ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria with bilateral carpal and hand ultrasonography carried out during the last five years. Synovial hypertrophy (SH) and Power Doppler signal (PD) in wrist and 1-5 metacarpophalangeal (MCP) were evaluated. We calculated the SH score (sum of the SH degrees of each joint), PD (sum of the PD degrees of each joint) and the total score (sum of the score of SH and PD) for each patient. We also evaluated the presence of proliferative globular synovitis, defined as big synovial hypertrophy with exophytic growth and a convex upper limit
Results: 145 RA patients were collected. 80% were women. Mean age was 59.06 (14.8) years and the mean time of disease evolution was 114.6 (112.8) months. 68.3% were RF positive and 74.5% ACPA positive. Overall, 115 of the 145 (79.3%) patients were seropositive for RF/ACPA. 53.1% had radiographic erosions, 73.1% used conventional synthetic Disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs), 29.7% biological therapy, and 57.2% low doses of corticosteroids (< 5 mg prednisone). The mean DAS28 was 2.81 (1.14), the number of swollen joints was 3 (3.4), and CRP was 0.99 mg/dl (1.6). No significant differences between seropositive and seronegative patients in terms of disease activity (swollen joints count [SJC], tender joint count [TJC], CRP, DAS28), treatment (use of corticosteroids, DMARDs, biological), time of evolution or US scores (SH, PD and total scores) were found. Globular synovitis was present in 71 patients 61.7% and 10.3% (62% and 13.7%) of seropositive and seronegative RA patients, respectively (p< 0.0001). Globally, 75 (51.7%) out of 145 patients had “globular” synovitis by US (Figure 1). 71 out of 75 patients were FR /ACPA positive (95.9%). Only three patients with seronegative RA had this US pattern (p < 0.001). Furthermore, patients with “globular” synovitis had more erosions (72% vs 32.9%, p 0.000), higher SJC (3.3and higher SH and PD scores (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: The presence of proliferative globular synovitis was significantly associated with the presence of RF/ ACPA in patients with RA. This US pattern identified a subgroup of RA patients with poor prognosis: more erosions and greater inflammatory activity both at clinical and ultrasound level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Azuaga-Piñango A, Frade-Sosa B, Gumucio R, Cajiao-Sanchez K, Mandelikova S, Ruiz-Esquide V, Castellanos-Moreira R, Sanmarti R, Cañete J, Ramirez J. Proliferative Globular Synovitis, an Ultrasound Pattern Associated with Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proliferative-globular-synovitis-an-ultrasound-pattern-associated-with-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proliferative-globular-synovitis-an-ultrasound-pattern-associated-with-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis/