Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Many clinical
trials have revealed that biologic agents inhibit destruction of small joints,
however, there have been a few reports demonstrating their inhibitory effects
on destruction of large joins. In this study, we investigated progressive
destruction of large joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated
with biologic agents and determined risk factor(s) associated with progressive
destruction.
Methods: We assessed a
total of 273 large joints in upper and lower extremities including the
shoulder, elbow, hip, knee and ankle of 67 patients. Prior to the treatment
with biologic agents, X-rays for tender and/or swollen large joints in
individuals were taken, and the follow-up X-rays were taken at least once
between 11 and 36 months (mean 18.6) after the initial examinations. At the
time of follow-up, progressive destruction was defined when at least one of the
following changes was detected: 1) progressive Larsen grade (LG), 2) increase
in bone erosion and/or appearance of new bone erosion, and 3) progressive joint
space narrowing.
Results: Progressive destruction
was seen in 14 patients (20.9%) and 17 joints (7.2%). To determine factors
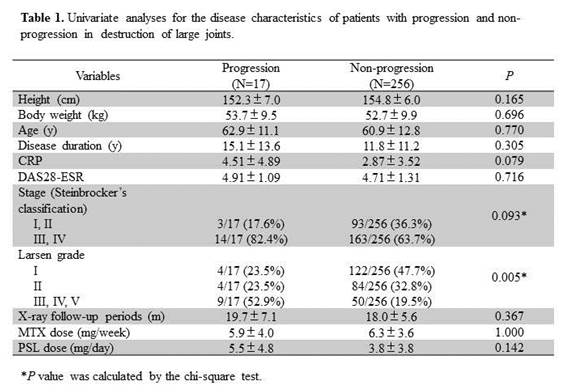
associated with the progressive destruction, we first performed a univariate
analysis regarding variables including height, body weight, age, disease
duration, CRP, DAS28, stage, LG, MTX dose, PSL dose, and X-ray intervals
between the initial and the follow-up time. As shown in Table 1, LG alone was
statistically significant (P<0.01). Next, the variables with a P
value of <0.1 in the univariate analysis, which included LG, stage and CRP,
were subject to a multivariate logistic regression analysis. As a result, LG
alone was extracted as a risk factor associated with progressive destruction
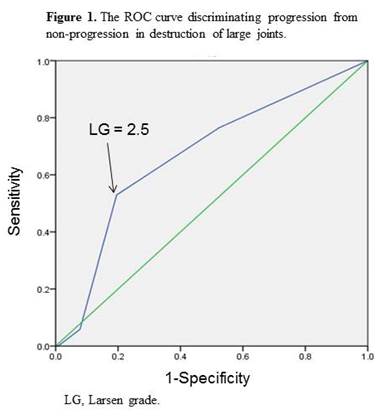
(odds ratio: 2.28, 95%CI: 1.19-4.36). The cutoff value of LG that discriminated
progression from non-progression by the ROC curve was determined to be 2.5
(sensitivity: 0.529, specificity: 0.805), suggesting that progressive
destruction of large joints is expected to be increased when LG is 3 or higher
(Figure 1).
Conclusion: These results
suggest that progressive destruction of large joints cannot be stopped
completely even under the tight control using biologic agents. Furthermore, results
of the ROC curve indicate that the bone damage of large joints should not be
advanced to LG-3. Since the risk factor(s) of progressive destruction are
associated with the extent of individual joint damage but not with patients’ disease
characteristics, regular X-ray examinations for large joints are indispensable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nakajima A, Sonobe M, Nakagawa K. Progressive Destruction of Large Joints in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Biologic Agents [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/progressive-destruction-of-large-joints-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-agents/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/progressive-destruction-of-large-joints-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-agents/