Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) scan has become a very useful diagnostic tool in patients with GCA with large vessel involvement. However, there are few studies on the prognostic utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT scan in these patients.
Our aim was to assess whether the assessment of baseline 18F-FDG uptake is able to predict the outcome of patients with GCA with large vessel involvement.
Methods: Study of patients diagnosed with GCA with large vessel involvement in a referral hospital who have a baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT scan and a control 18F-FDG PET/CT scan in the following 2 years. Patients were divided into two groups: a) favourable evolution (clinical improvement, normalisation of CRP and ESR and improvement on control 18F-FDG PET/CT scan); and b) unfavourable evolution (no clinical improvement or no normalisation of CRP and ESR or no improvement on control 18F-FDG PET/CT scan). The assessment of 18F-FDG uptake was performed using the Meller visual scale.
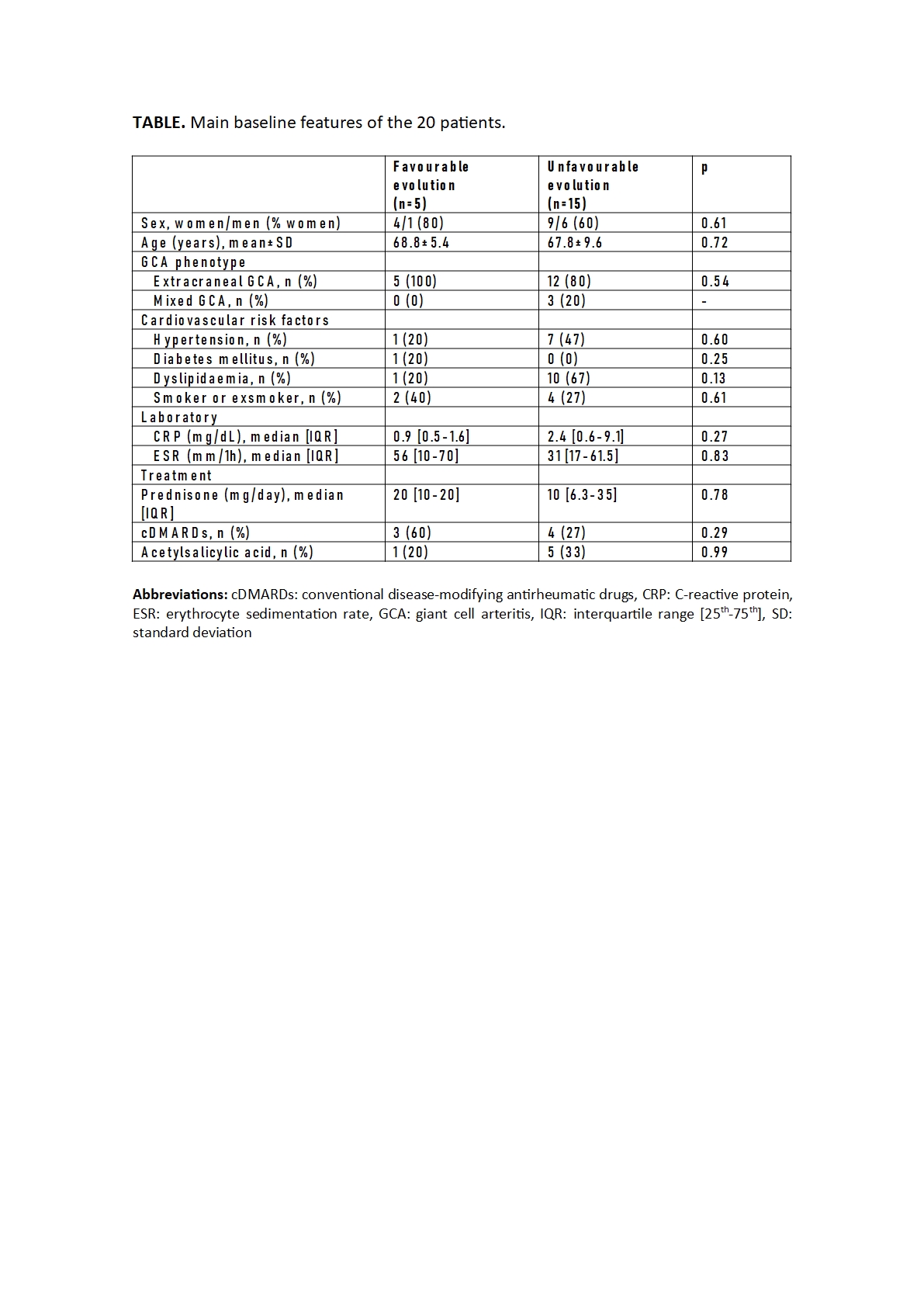
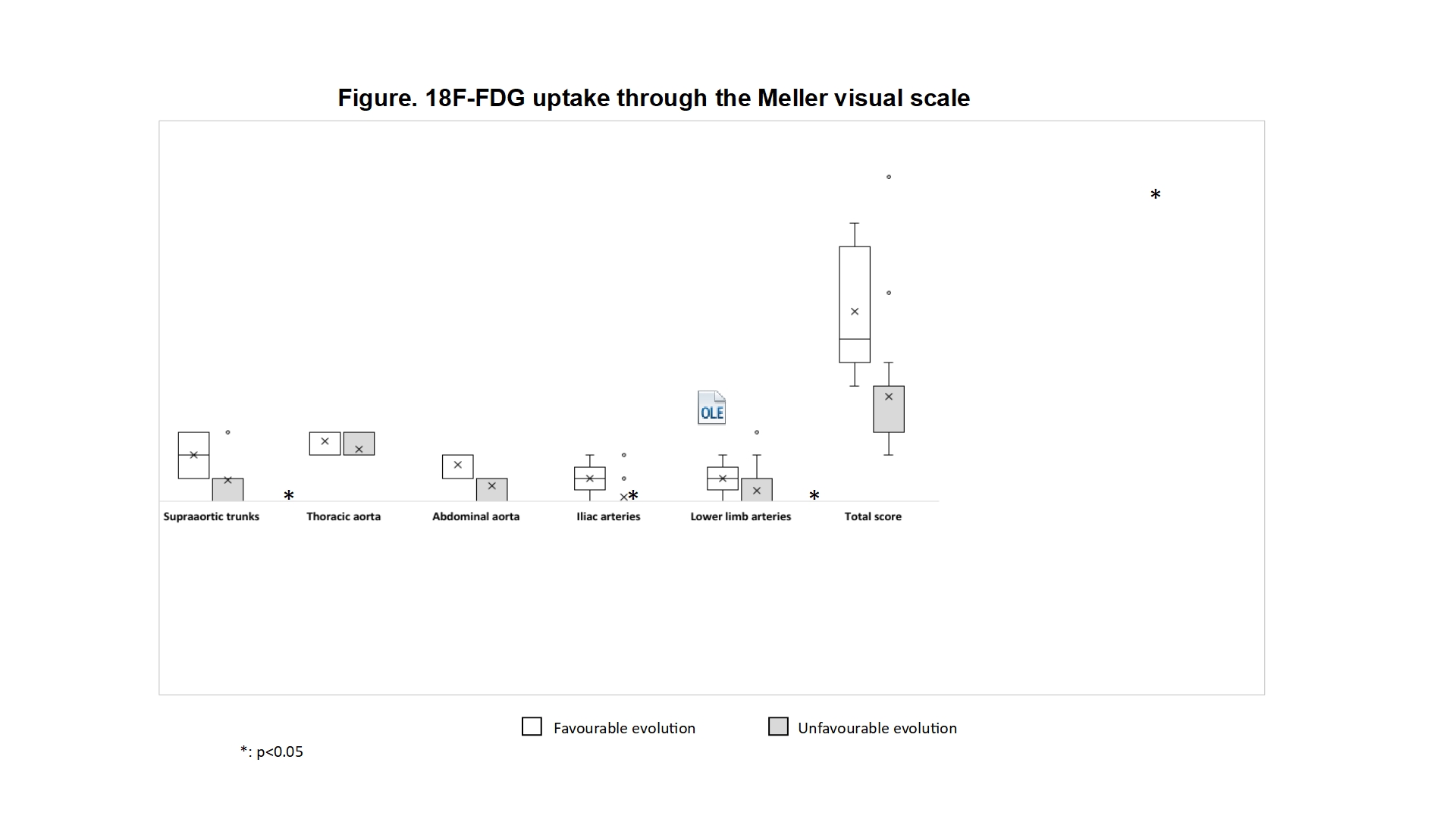
Results: We present 20 patients (13 females and 7 males) with a mean age of 68.0±8.6 years with GCA with large vessel involvement who had a baseline and a follow-up 18F-FDG PET/CT scan in the following 2 years (mean time between both 18F-FDG PET/CT scans: 13.6±3.9 months) . Five patients (25%) experienced a favourable outcome, while 15 (75%) patients experienced an unfavourable outcome. No significant differences were observed in the baseline characteristics of the two groups, although there was a greater tendency to present hypertension and dyslipidaemia, as well as to use lower doses of prednisone in the group of patients with unfavourable evolution (TABLE). Patients with favourable outcome had higher baseline 18F-FDG uptake in supra-aortic trunks (2 [1-3] vs 1 [0-1]; p=0. 042), abdominal aorta (2 [1-2] vs 0 [0-1]; p=0.029), iliac arteries (1 [1-1] vs 0 [0-0]; p=0.009), and in the total vascular score (7 [7-10] vs 3 [3-4.5]; p=0.013) (FIGURE).
Conclusion: In our series we observed that patients with GCA with large vessel involvement who have a higher 18F-FDG uptake on the Meller visual scale have a more favourable evolution in the two years following diagnosis, possibly helped by the tendency to use a higher dose of prednisone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sánchez-Martín J, Loricera J, Martinez-Rodriguez I, Ferraz-Amaro i, Martinez-Amador N, Quirce-Pisano R, Lopez-Gutierrez F, Blanco-Alonso R. Prognostic Value of Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan in Giant Cell Arteritis with Large Vessel Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-value-of-baseline-18f-fdg-pet-ct-scan-in-giant-cell-arteritis-with-large-vessel-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-value-of-baseline-18f-fdg-pet-ct-scan-in-giant-cell-arteritis-with-large-vessel-involvement/