Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Antibodies (Ab) toward Bicaudal D homolog 2 (BlCD2) can be found in 25% of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) sera, mostly in association with anti-centromere (ACA) or anti-topoisomerase I (ATA) abs, but also in isolation. Anti-BlCD2 single specificity has been associated with myositis and interstitial lung disease (ILD), however its prognostic significance is unclear. A retrospective-prospective study was conducted to evaluate disease evolution in anti-BICD2+ patients.
Methods:
Serum samples from 288 SSc (ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria) collected between 2012 and 2014 were stored at -80° C and sent for Ab determination to Inova Diagnostics (San Diego, CA). Samples were tested using a novel particle-based multi-analyte technology (PMAT) and with CTD Essential (which includes DFS70, dsDNA, RNP, Sm, Ro60, Ro52, SS-B, Jo-1, Scl-70, Centromere, Ribo-P) and CTD Comprehensive (RNA Pol lll, Th/To, Ku, BICD2, PM/Scl; both test research use only).
Clinical data regarding major organ complications were retrospectively collected; time of evolution from baseline to new clinical manifestations was recorded. For dcSSc subjects evolutions included death, new digital ulcers, worsening of lung function (forced vital capacity, FVC loss > 10% or diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide, DLCO loss > 15%), progression of ILD on high resolution computed tomography, HRCT, development of pulmonary hypertension (PAH); evolution for lcSSc included progression of skin thickening as well as dcSSc categories; evolution for definite SSc without skin fibrosis included the appraisal of skin fibrosis and the above categories. Survival analysis for interval-censored data with 1.000-fold permutations was used.
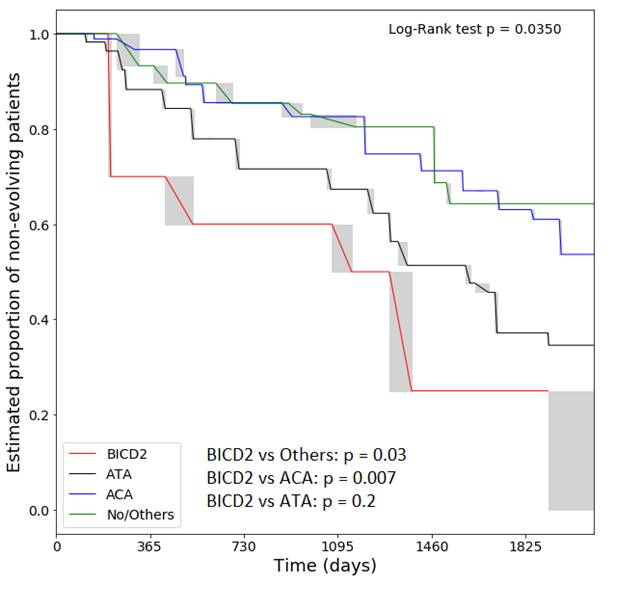
Our cohort included: 30 (10.4%) definite non-cutaneous SSc, 216 (75%) lcSSc and 42 (14.5%) dcSSc, mostly females (95.5%), aged 60 ± 12.7 years and with disease duration of 14 ± 13 years. Anti-BlCD2 Ab were found in 49 subjects (17%), in 10 (3.5%) as a single-specificity, in 8 (2.8%) in associations with ATA, in 31 with ACA (10.8%). Patients were followed for a median of 4.0 (interquartile: 2 – 5.1) yrs until the first sign of evolution. Single anti-BlCD2 Ab positivity was associated with myositis (3/10 vs. 11/278, p=0.0089) and weakly with dcSSc (4/10 vs. 38/278, p=0.045). Ab specificity was associated with different pattern of progression (Figure): Anti-BlCD2+ patients had shorter evolution times compared to anti-BlCD2- patients (p=0.03), ACA+ subjects (p=0.007) but were similar to ATA+ subjects (p=0.2). Crude mortality trended to be higher in anti-BlCD2+ than anti-BlCD2- patients (3/10 vs. 27/278, p=0.074).
Conclusion:
We confirm the association between anti-BlCD2 Ab and myositis in SSc and its overall prevalence. Anti-BlCD2+ patients have a worse prognosis and higher rates of disease progression compared to ACA+ subjects and behave similarly to ATA+ subjects.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Segatto G, Bellocchi C, Montanelli G, Casas S, Norvell K, Amino M, Roup F, Mahler M, Beretta L. Prognostic Significance of Bicaudal D2 Antibodies in Sistemic Sclerosis (SSc) Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-significance-of-bicaudal-d2-antibodies-in-sistemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-significance-of-bicaudal-d2-antibodies-in-sistemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients/