Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Studies have suggested that primary hyperparathyroidism could be a risk factor for hyperuricemia although the results were inconsistent across the studies. This systematic review and meta-analysis was performed in order to identify all available studies and summarize their results together.
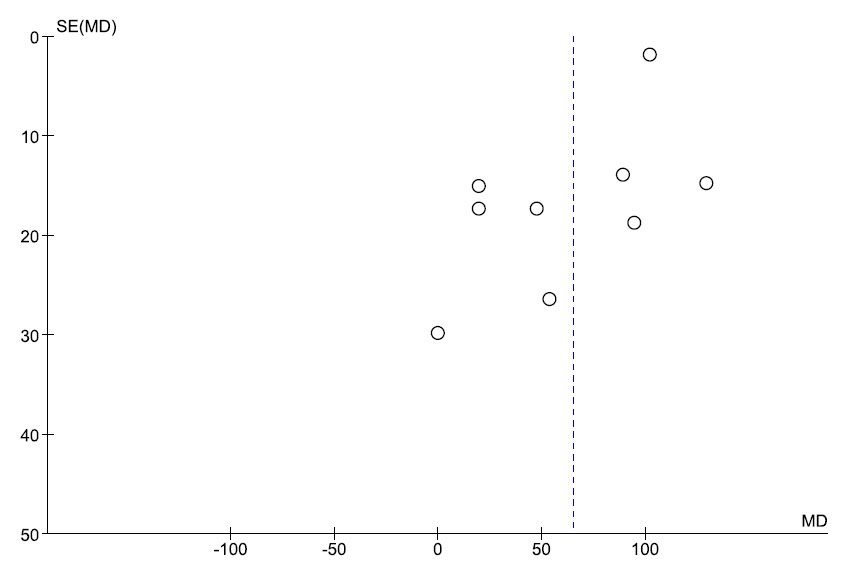
Methods: A systematic review was performed using EMBASE and MEDLINE from inception to August 2018 to identify all cohort studies that consisted of two cohorts, cohort of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and cohort of individuals without hyperparathyroidism. Eligible studies must provide data on mean serum uric acid level and standard deviation of both cohorts, which would be extracted to calculate mean difference (MD). Pooled MD was then calculated by combining MDs of each study using random-effects model. Funnel plot was used for evaluation for publication bias.
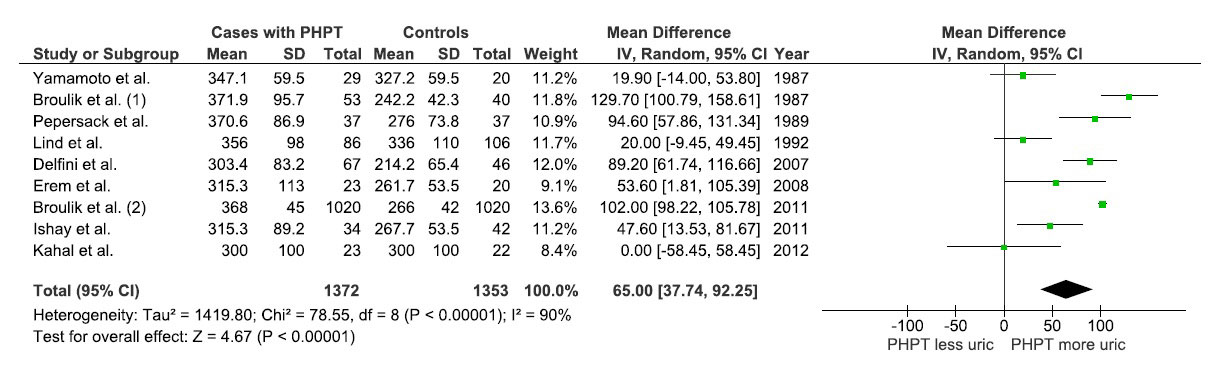
Results: A total of nine cohort studies met the inclusion criteria and were included into the meta-analysis. The pooled analysis found that patients with primary hyperparathyroidism had a significantly higher level of serum uric acid than individuals without hyperparathyroidism with the pooled MD of 65.00 µmol/L (95% CI, 37.74 – 92.25). The statistical heterogeneity was high with I2 of 90 %. The forest plot of this meta-analysis is shown as figure 1. The funnel plot was relatively symmetric and did not provide evidence for publication bias (figure 2). Reduced renal tubular secretion of urate due to the direct effect of PTH on renal tubules is one of the possible explanations for this observation.
Conclusion: Patients with primary hyperparathyroidism had a significantly higher level of serum uric acid compared to individuals without hyperparathyroidism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ponvilawan B, Charoenngam N, Ungprasert P. Primary Hyperparathyroidism Is Associated with a Higher Level of Serum Uric Acid: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/primary-hyperparathyroidism-is-associated-with-a-higher-level-of-serum-uric-acid-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/primary-hyperparathyroidism-is-associated-with-a-higher-level-of-serum-uric-acid-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/