Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster (1135–1149)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Few studies in Latin America and the Caribbean have evaluated osteoporosis and fracture epidemiology among populations at increased risk for secondary osteoporosis, such as women with HIV. We aimed to explore the prevalence of vertebral fracture (VF) and low bone mineral density (BMD) among women aging with HIV in Peru, in order to identify risk factors for osteoporosis and fracture in this population.
Methods: We enrolled HIV-infected and uninfected women aged ≥40 years from a large HIV clinic in Lima, Peru between October 2019 and March 2020. All participants completed a survey regarding sociodemographic, clinical and fracture-associated risk factors, and obtained a dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan to assess BMD at the lumbar spine, femoral neck and total hip. A subset of patients also obtained lateral thoracolumbar X-rays. Presence of VF was determined using the Genant semiquantitative method. Linear and logistic regression analyses were used to model associations between key risk factors and BMD at each site.
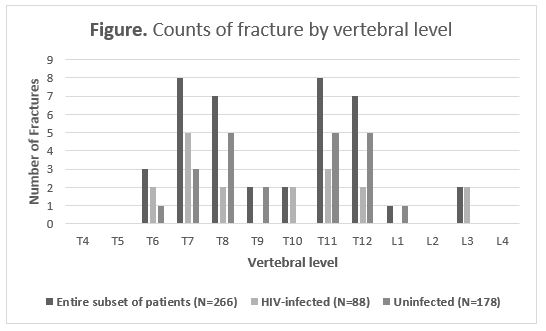
Results: A total of 104 HIV-infected and 212 uninfected women were enrolled with a mean age of 52.4±8.2 and 56.4±8.8 years (p< 0.001) and BMI of 26.4±5.1 and 27.6±4.1 kg/m2 (p=0.03), respectively. Among postmenopausal women (257/316, 81.3%), 26.3% of HIV-infected and 25.9% of uninfected had osteoporosis. Among the subset of 88 HIV-infected and 178 HIV-uninfected who obtained thoracolumbar x-rays, 12.5% and 6.2% respectively had at least one VF. Both of these comparisons were not statistically significant. The mean 10-year FRAX risk of major osteoporotic fracture and hip fracture was 2.65% and 0.59% among women with HIV. Based on DXA and the FRAX score, 22/104 HIV-infected women met criteria for osteoporosis treatment according to national guidelines, however, none were on treatment. Unadjusted logistic regression analysis among the pre and postmenopausal HIV-infected showed that age (p< 0.001), postmenopausal status (p=0.04) and years of antiretroviral therapy (p=0.05) were predictors for lower BMD. Adjusted linear regression analysis showed that BMD was negatively correlated with older age and positively correlated to higher BMI.
Conclusion: In this study, HIV-infected women had increased VF prevalence compared to the slightly older uninfected group. Age and BMI were independent predictors for BMD at the lumbar spine, hip and femoral neck among women with HIV, and there was a treatment gap among osteoporosis diagnosed women. Larger prospective studies are needed in this region to identify individuals at risk for fracture and to inform prevention guidelines.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cabrera D, Cornejo M, Slotkin R, Pinedo Y, Yu W, Guan W, Garcia P, Hsieh E. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Vertebral Fractures and Low Bone Mass Density Among Women Aging with HIV in Peru [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-and-risk-factors-for-vertebral-fractures-and-low-bone-mass-density-among-women-aging-with-hiv-in-peru/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-and-risk-factors-for-vertebral-fractures-and-low-bone-mass-density-among-women-aging-with-hiv-in-peru/