Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:45PM-2:00PM
Background/Purpose: Multimorbidity, the presence of multiple chronic conditions, is common in RA, and the progression of multimorbidity in RA is associated with poor long-term outcomes. However, the burden and progression of multimorbidity in high-risk RA populations, such as those with the extra-articular manifestation of RA-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD), is not well understood. Thus, we evaluated the prevalence and progression of multimorbidity in RA-ILD within the Veterans Health Administration (VA).
Methods: We performed a cohort study of RA-ILD patients using national VA data between 1999 and 2021. RA-ILD patients were identified with validated RA and ILD administrative algorithms ( >80% PPV), then followed from the date the RA-ILD algorithm was fulfilled (index date) until death or end of study period. Multimorbidity burden was quantified as the number of conditions present among 43 chronic conditions (based on prior published multimorbidity studies in RA), using diagnostic codes from inpatient and outpatient encounters prior to the index date and throughout follow-up. The prevalence of individual morbidities at baseline and newly developing annually through the end of follow-up was descriptively summarized. Group based trajectory modeling was utilized to derive unique longitudinal trajectories of multimorbidity burden, stratified by tertile of baseline multimorbidity burden (low, moderate, and high). Multimorbidity trajectory group membership was then used to predict respiratory-related hospitalizations (respiratory-related discharge diagnosis in primary position from VA administrative data) in Cox regression models that adjusted for age, sex, race, smoking status, baseline multimorbidity burden, and calendar year.
Results: We studied 6,232 RA-ILD patients (92.6% male, mean age 69 years) with a mean (SD) of 11.2 (5.3) morbidities at baseline that increased to 13.5 (5.5) over a median follow-up of 5 years. Cardiometabolic, respiratory, and musculoskeletal morbidities were the most frequent and present in most RA-ILD patients by the end of follow-up (Table 1). All morbidities increased in prevalence over follow-up, with cardiometabolic and cancer morbidities among those with the greatest increase in prevalence. Trajectory modeling identified 3 multimorbidity trajectories within each tertile of baseline multimorbidity burden representing slow, moderate, and rapid multimorbidity progression during follow-up (Figure 1). Within each baseline multimorbidity burden tertile, the rapid (group 3; aHR range 1.24 to 1.60) and moderate (group 2; aHR range 1.23 to 1.30) multimorbidity progression trajectory groups were associated with a higher risk of respiratory-related hospitalization compared to the slow progression group (group 1) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Multimorbidity was highly prevalent and progressive throughout the RA-ILD disease course in this national VA RA-ILD cohort. More rapidly progressive multimorbidity trajectories predicted higher risk of respiratory-related hospitalization independent of baseline multimorbidity burden. Together, these findings emphasize the need to monitor and manage multimorbidity in RA-ILD patients to optimize long-term outcomes.
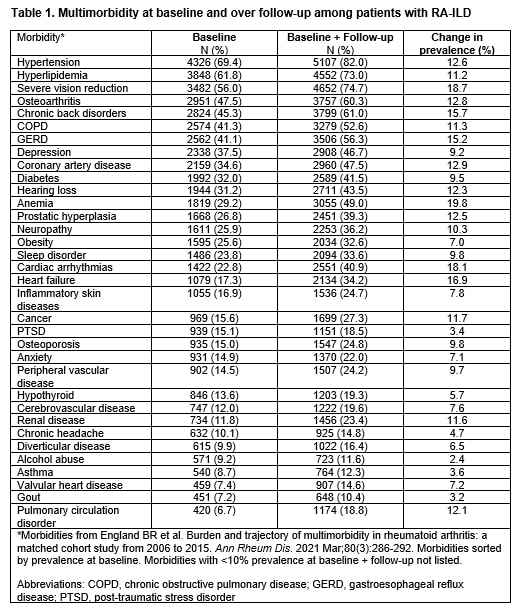 Multimorbidity at baseline and over follow-up among patients with RA-ILD
Multimorbidity at baseline and over follow-up among patients with RA-ILD
.jpg) Multimorbidity trajectory groups in RA-ILD stratified by baseline multimorbidity burden tertile.
Multimorbidity trajectory groups in RA-ILD stratified by baseline multimorbidity burden tertile.
.jpg) Adjusted hazard ratios for respiratory-related hospitalization among RA-ILD patients by multimorbidity trajectory groups.
Adjusted hazard ratios for respiratory-related hospitalization among RA-ILD patients by multimorbidity trajectory groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fagerland J, Yang Y, Roul P, Johnson T, Matson S, Cannon G, Sauer B, Curtis J, Baker J, Mikuls T, England B. Prevalence and Progression of Multimorbidity in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-and-progression-of-multimorbidity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-and-progression-of-multimorbidity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/
