Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Inter-individual variation to methotrexate (MTX) therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is attributed at least in part to the presence of genetic variation in methotrexate pathway genes. However, the majority of the candidate-gene association studies published to date have focused on the effect of common allelic variants on drug efficacy and toxicity. Prevalence of rare variants in methotrexate pathway genes remains largely unknown.
Methods:
Variants in 3 major MTX pathway genes (Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), solute carrier family 19 member 1 (SLC19A1), and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC)) were queried using data from NHLBI Exome sequencing project (ESP) which provides high-coverage (average>100x), high quality data for 6,503 individuals of white and black ethnicity (http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/) [accessed in June, 2013, data release ESP6500SI-V2]. Variants were categorized based on their function as well as minor allele frequency: common (>5%), low frequency (0.1-5%), and very rare (<0.1%). Polyphen2 scores were utilized to assess possible impact of aminoacid substitutions on protein structure and function.
Results:
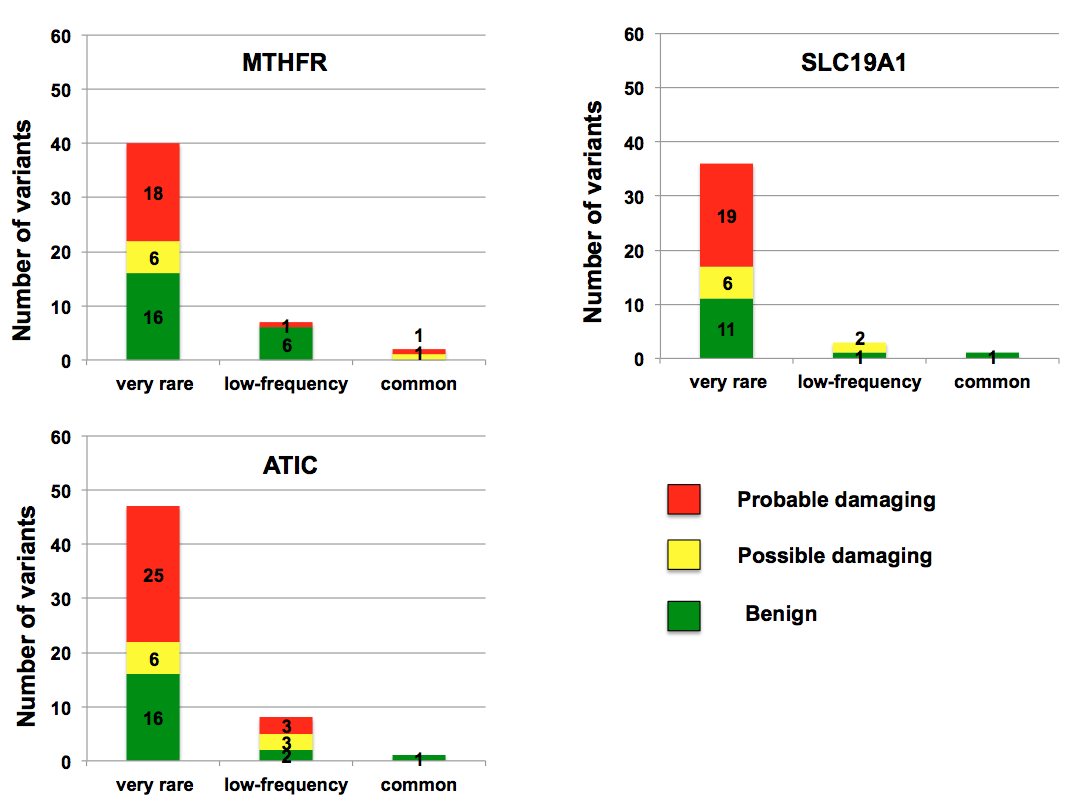
Overall, 272 exomic variants were present in MTHFR, SLC19A1, and ATIC genes. Majority of these variants were missense (n=145, 53.3%), followed by coding/synonymous (n=96, 35.3%), utr (n=17, 6.3%), and splice-nonsense-frameshift (n=14, 5.1%) mutations. Only 9 (3.3%) variants were common (MAF>5%), compared to 40 variants with low frequency, and 223 variants with very rare frequency (MAF <0.1%). Overall, 143 variants (52.5%) were private mutations, that is distinct to an individual. Analysis of missense variants accurately identified known common variants of MTHFR pathway including MTHFR 677C>T, MTHFR 1298A>C, SLC19A1 80G>A, and ATIC 347 C>G SNPs. Polyphen2 scoring suggested that 62.1% of missense mutations were potentially damaging to protein structure (Figure).
Conclusion:
Exome sequencing data suggests that nearly 1.6% of population carry a potentially pathologic variant in any of the 3 major MTX pathway genes. As the technology and cost of the sequencing platforms improve, exome and/or whole-genome sequencing could potentially improve outcomes in patients with RA on MTX therapy.
Disclosure:
F. Malik,
None;
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalance-of-rare-variants-in-methotrexate-pathway-genes-implications-from-the-national-heart-lung-blood-institute-nhlbi-exome-sequencing-project/