Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Presepsin (sCD14 subtype) has recently been identified as a novel biomarker for
predicting sepsis. Because presepsin is
produced as a consequence of cellular phagocytosis, it may reflect monocyte
activation. Recent evidence indicates that monocytes play an extremely
important role in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Little is known
regarding presepsin in patients with SLE. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis
that presepsin concentrations are elevated and associated with disease activity
in patients with SLE without infection.
Methods: Thirty-three patients with SLE (4 men, 29 women) with a mean age of
46.6 and 22 healthy controls (5 men, 17 women) with a mean age of 48.1 were
enrolled in this study. No patient had an apparent infection. Concentrations of plasma presepsin, serum C3, C4,
and total hemolytic complement (CH50) levels were measured. The plasma presepsin concentration was measured
using a chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay. The levels were compared
between the groups. The SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) was calculated in
the SLE group. Eight out of 33 SLE patients who underwent intensified
immunosuppressive therapy were tested twice at 2 weeks after treatment.
Results: Patients with SLE had higher concentrations of presepsin [238.5
(48–741) pg/mL] than the healthy controls [118.4 (74–270) pg/mL; P =
0.0003]. The mean SLEDAI of all SLE patients was 10.8 (0–30). In patients with
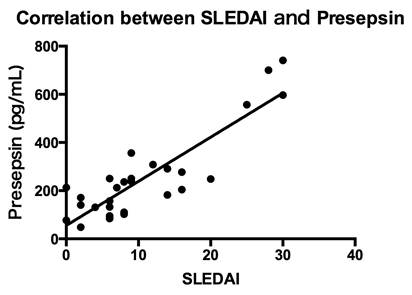
SLE, the concentration of presepsin was significantly correlated with disease
activity, as assessed by SLEDAI scores (R2 = 0.77; P <
0.0001; Fig. 1). There were significant correlations between presepsin and
compliment CH50 (R2 = 0.12; P =0.046) and C4 (R2 =
0.034; P =0.034) but not between presepsin and C3 (R2 =
0.073; P =0.12). The concentration of presepsin was significantly
decreased after treatment (before: 351.3 pg/mL; after: 134.0 pg/mL; P =
0.016; Fig. 2). The ROC curve analysis was conducted to compare the predictive
values of presepsin. Area under the curve of presepsin was 0.7803. According to
the ROC analysis, the optimal cut-off value of presepsin for the diagnosis of
SLE was 156.5 pg/mL. Using this cut-off value, the sensitivity and specificity
were 66.67% and 86.36%, respectively.
Conclusion: Measurements of plasma
presepsin can be useful in assessing the disease activity of SLE and may
be used to monitor treatment.
Figure
1
Figure
2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsujimoto K, Fujita M, Shinkawa Y, Shirasugi I, Taniguchi M, Hatachi S, Yagita M. Presepsin (sCD14 subtype) Concentration Is Elevated and Reflects Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematous Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/presepsin-scd14-subtype-concentration-is-elevated-and-reflects-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematous-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/presepsin-scd14-subtype-concentration-is-elevated-and-reflects-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematous-patients/