Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are innate immune T cells that are located at the mucosal barriers. They play a role in mucosal defense, especially against bacterial pathogens. They are able to produce inflammatory cytokines with a mixed Th1/Th17-like response, including TNF-a and IL-17A. MAIT cells have been implicated in the pathophysiology of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Indeed, recent studies showed a higher frequency of MAIT cells in the peripheral blood of patients with axSpA, especially MAIT cells expressing IFN-g, TNF-a, IL-17A and IL-22. Thus, MAIT cells are considered to be a source of IL-17A and IL-22, two cytokines involved in the inflammatory process and bone formation of axSpA, respectively. Previous studies in axSpA evaluated circulating MAIT cells, but not their presence at the pathological sites of inflammation. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the expression of MAIT cells in synovial biopsies from patients with axSpA.
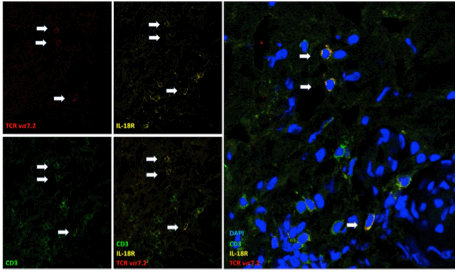
Methods: synovial tissue samples were obtained during surgical procedure for joint arthroplasty. Patients evaluated were axSpA (ASAS criteria) and compared to patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We also included a control group of patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and a positive control group with the previously reported MAIT expression at a tissue level, i.e. giant cell arteritis (GCA). MAIT cells were defined by CD3+ TCRVa7.2+ CD161+ phenotype. Using confocal microscopy, MAIT cells in synovial tissue (axSpA, RA, OA) and in temporal artery biopsies (GCA) were identified by the co-staining of CD3, TCRva7.2 and IL-18R using primary antibodies.
Results: 11 patients were evaluated: 3 patients with axSpA (2 nr-axSpA; 3 males; age [mean]: 62.6 years; disease duration [mean]: 16.3 years; two under TNFi, one under NSAIDs; BASDAI [mean]: 5.6; ASDAS [mean]: 3.05); 3 with RA (1 male; age: 69.3; disease duration: 14.3; 1 under MTX, 2 under ts/bDMARDs); 4 with OA (2 males; age: 65) and 1 with GCA. Synovial biopsies were obtained from hip (n=5), knee (n = 3), shoulder (n = 1) or hand (MCP) (n=1) joints. GCA positive control artery revealed a strong infiltrate of CD3+ T cells. Among these cells, few cells co-expressed CD3, IL-18R and TCRva7.2. In synovial tissue, CD3 staining revealed a weakest infiltrate of CD3+ T cells, especially in OA synovial samples. MAIT cells were present in a low proportion in one sample from axSpA patients (fig 1), while no MAIT cells were observed in RA and OA samples.
Conclusion: MAIT are observed in synovial tissue of an axSpA patient suggesting their potential contribution to local cytokine production and inflammatory response. They are represented in a low proportion and this may be related to disease duration and/or the treatments. Additional analysis on other relevant site of inflammation of axSpA, i.e. entheseal structures and in patients with shorter disease duration, are required.
Reference :
1- 1- Ghesquière T et al. J Autoimmun. 2021.
2- 2- Rosine N et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramon A, Saas P, Vauchy C, Samson M, TOUSSIROT E. Presence of MAIT Cells in Synovial Tissue of Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Comparative Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/presence-of-mait-cells-in-synovial-tissue-of-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-comparative-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/presence-of-mait-cells-in-synovial-tissue-of-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-comparative-study/