Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – ePoster I: Basic Science, Biomarkers, & Sclerodermic Fever
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologics have transformed the treatment of Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and escalation toTumour Necrosis Factor – α inhibitors (TNFi) after failure of methotrexate (MTX) was enshrined as NHS standard practice in National Institute of Clinical Excellence guidelines in 2002. The aim of our study was to explore the clinical response to first TNFi including duration on treatment before discontinuation due to loss of efficacy (secondary failure), clinical remission or side-effects. We looked at six sub-types of JIA. Group A consisted of subtypes of JIA with polyarticular course of disease encompassing Seropositive and Seronegative polyarticular JIA (SPPJIA, SNPJIA) and Extended oligoarticular JIA (EOJIA). The other groups were Persistent oligoarticular JIA (PO JIA), Psoriatic arthritis (Ps JIA) and Enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA). We excluded Systemic and undifferentiated JIA as we wanted to focus on the response to TNFi.
Methods: This was a retrospective, single centered, observational real-life study of the cohort of patients with JIA at UCLH (University College London Hospitals). We took a single data extract from our clinical database in January 2019. We included patients diagnosed with JIA (fulfilling International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria) starting on TNFi from October 2012 (database inception) to December 2018. All had at least six months of follow-up since the introduction of the TNFi to 2018. The patients remaining on TNFi 6 months after initiation were defined as responders in accordance with national guidelines (NHS England stipulate that TNFi must be stopped if there is a failure to respond after 6 months). IBM statistics 2017 SPSS and Prism 8 for macOS was used for data analysis.
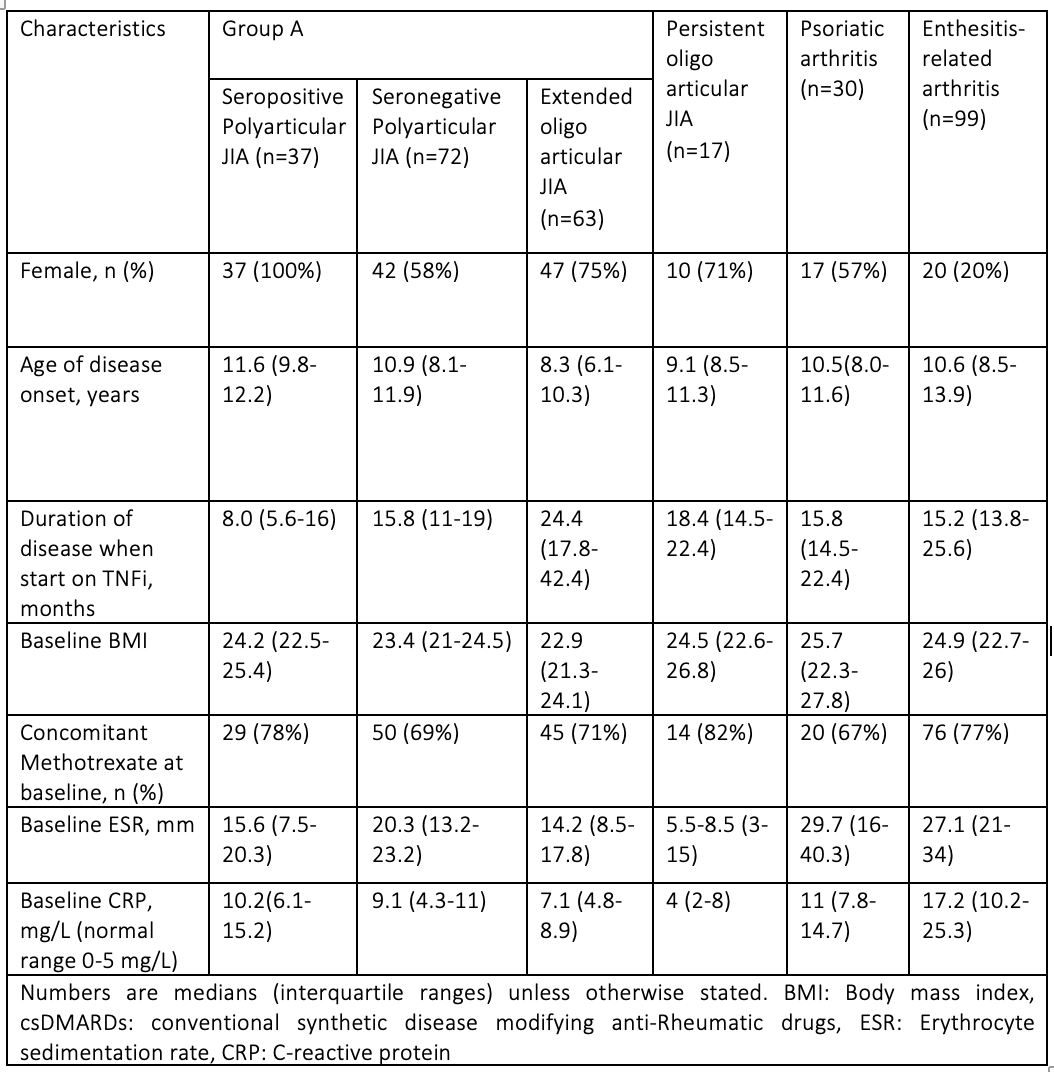
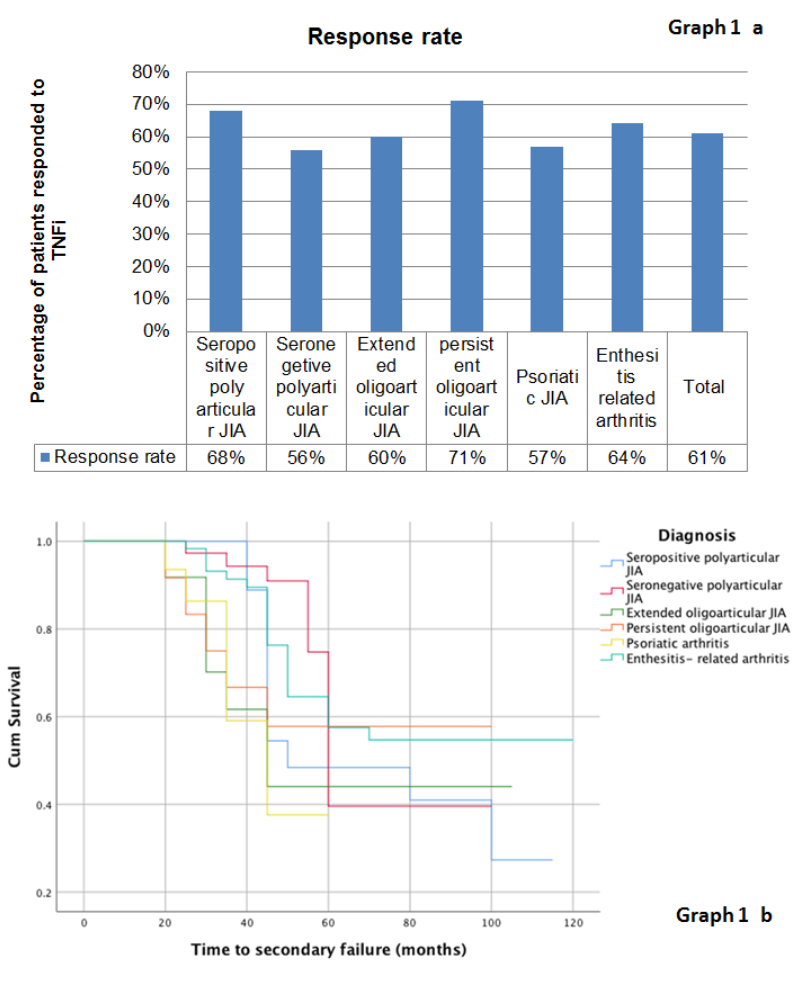
Results: We initially included a total of 328 JIA patients. Ten were excluded (5 missing data, 3 with treatment duration < 6 month, 2 malignancies). The baseline characteristics of the 318 patients are presented in table 1. Overall, the response rate was 61% (195/318) (Graph 1 a). Of the 195 responders, 77 (39.5%) eventually stopped their treatment (Graph 1 b).Of these 45 (60%) had secondary failure due to inefficacy, 21 (27%) were in remission and 10 (13%) due to an adverse reaction.
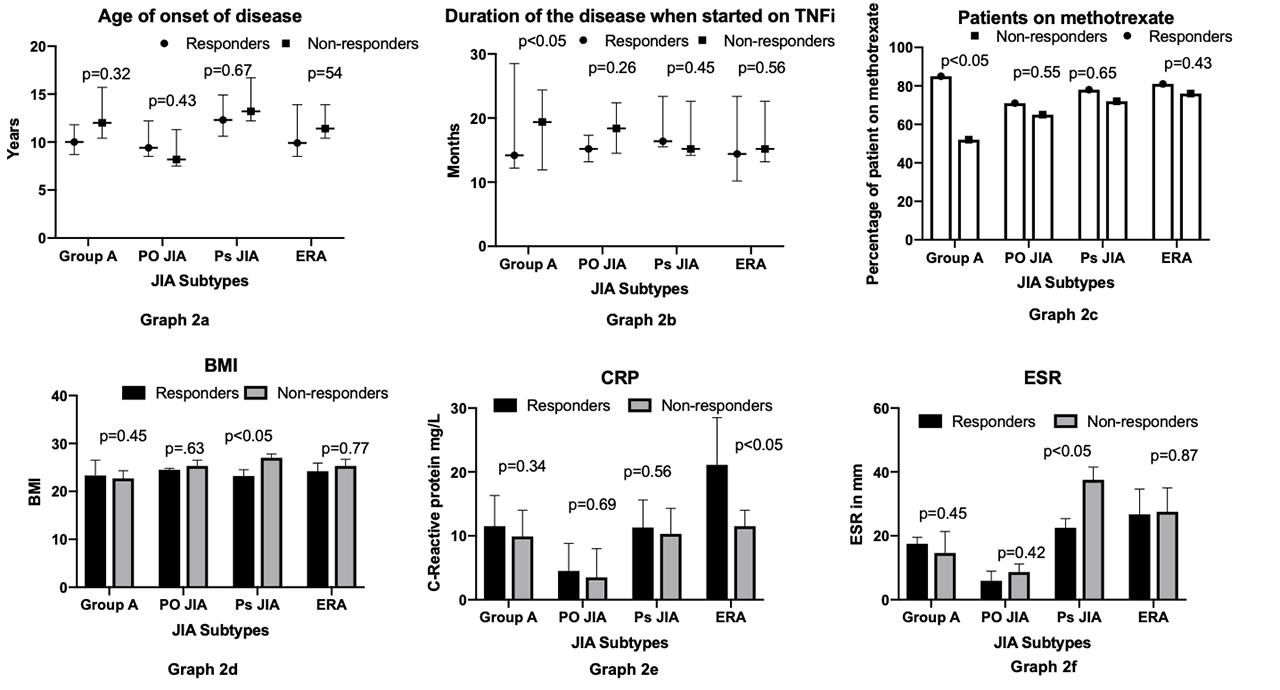
Unlike other studies, there was no significant correlation between age of disease onset and treatment response (graph 2 a). Group A showed significantly better response if treatment was started earlier (graph 2 b). However, this was not demonstrated in other subtypes. Group A only demonstrated a better response if on MTX (graph 2 c). There was no significant difference among the other subtypes. A higher basal metabolic index (BMI) was associated with poorer response to TNFi in Ps JIA group (graph 2 d). A higher baseline C-reactive protein (CRP) was associated with better response to TNFi for ERA (graph 2 e). In Ps JIA a good response to TNFi was associated with a significantly lower Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (graph 2 f) at initial presentation.
Conclusion: We found that a good response to TNFi treatment in patients with JIA was associated with:
- Polyarticular course disease (group A) – Early start of treatment, concomitant use of MTX.
- Ps JIA: Lower BMI, Lower ESR.
- ERA: Higher CRP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shipa M, Madenidou A, Choida v, Radziszewska A, fisher c, ciurtin c, Leandro m, Sen D. Predictors of Response to Tumour Necrosis Factor – α Inhibitors (TNFi) in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): A Single-center Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-response-to-tumour-necrosis-factor-%ce%b1-inhibitors-tnfi-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-jia-a-single-center-experience/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-response-to-tumour-necrosis-factor-%ce%b1-inhibitors-tnfi-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-jia-a-single-center-experience/